

on this page
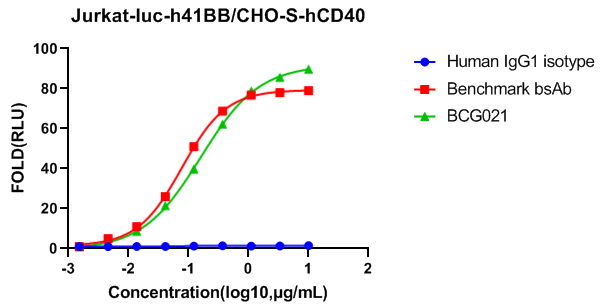
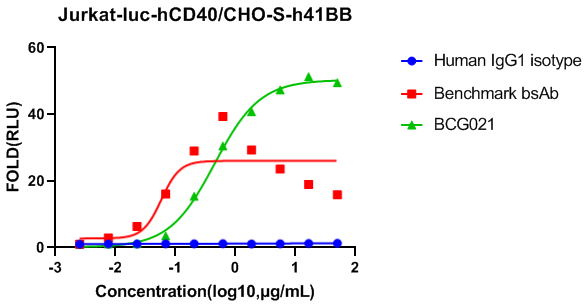
4-1BB is a costimulatory receptor expressed on activated T cells that enhances their proliferation, survival, and effector functions. It plays a key role in amplifying anti-tumor immune responses, making it a promising target for immunotherapy. However, therapeutic strategies targeting 4-1BB must balance efficacy with potential systemic toxicity.
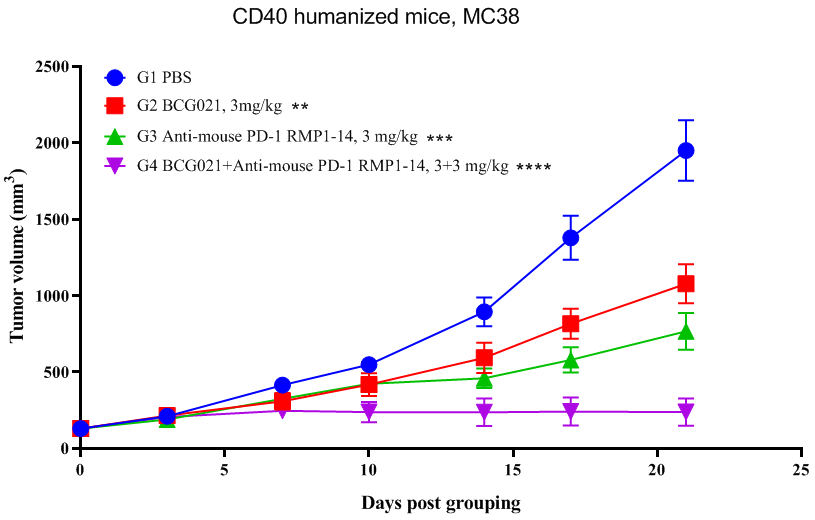
CD40 is a co-stimulatory protein found on antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, B cells, and macrophages. It is crucial for activating the adaptive immune response, including T cell priming and antibody production. Modulating CD40 signaling can boost anti-tumor immunity, but it requires careful control to minimize adverse inflammatory effects.