

Biocytogen offers comprehensive in vitro functional evaluation services for a broad range of therapeutics, including antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), CAR-T cells, small molecules, oncolytic viruses, and beyond. Our assessments leverage advanced techniques such as flow cytometry, ELISA, HTRF, and Incucyte live-cell imaging.
on this page
Biocytogen delivers robust in vitro cell function evaluation services. Utilizing primary cells and established cell lines, we assess the in vitro pharmacology of candidate antibodies, examining their binding capacity and Fc- and Fab-related properties. Our approach incorporates advanced techniques such as flow cytometry, ELISA, HTRF, and Incucyte cell imaging, among others. These evaluations offer valuable insights into the efficacy and toxicity mechanisms of candidate antibodies, supporting clinical translational studies.
In vitro pharmacology services include the following assays:
1. General Assays
2. Fab-related Function Assays
Non-immune cell
Cytokine
3. Immunocyte based Assays
Flow Cytometry:
IncuCyte:
Cytokine Analysis:






Fc–related Function Assays
Fab–related Function Assays

PBMCs were used as effector cells. Target cells are Jurkat-h4-1BB cells labeled with a high concentration of CFSE, while control cells are Jurkat WT cells labeled with a low concentration of CFSE. These cells are incubated for 18 hours in the presence of varying concentrations of anti-human 4-1BB antibody.
The cytotoxicity percentage is calculated as follows: [1 - (control well ratio / experimental well ratio)] × 100. The ratio is determined by dividing the number of CFSElow cells by the number of CFSEhigh cells.
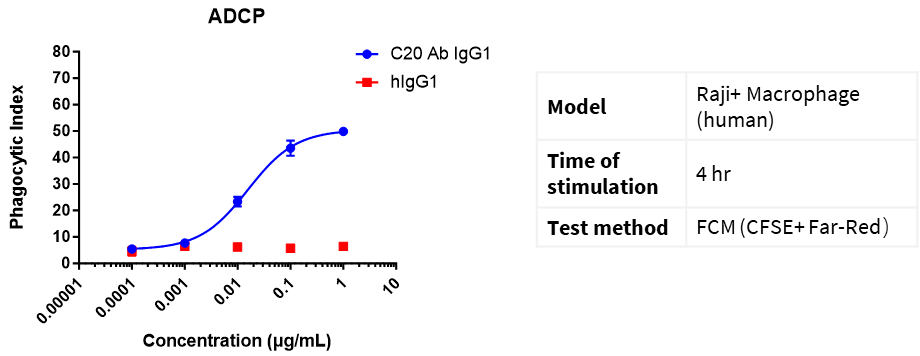
Far Red dyes were used to label macrophages (E), and CFSE dyes were used to label Raji cells (T). E:T = 1:5. Different concentrations of CD20 IgG1 antibodies were added and incubated for 4 h, and the phagocytosis of macrophages was detected by flow cytometry.
Phagocytic Index (PI) = (number of ingested macrophages)/(total number of macrophages) × 100%
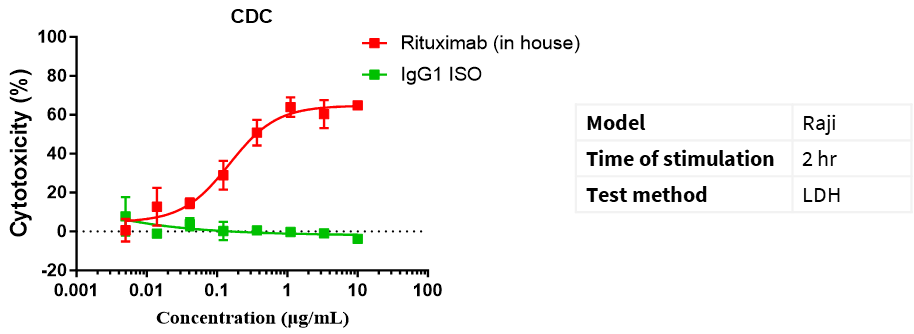
CD20 IgG1 antibody-mediated CDC assay. Raji cells were mixed with different concentrations of CD20 IgG1 antibodies in the presence of complement and then incubated for 2 h. The cytotoxic effect of antibodies was detected by the LDH method.
Cytotoxicity % = (LDH value of test wells − LDH value of spontaneous release wells)/(maximum LDH release from target cells − LDH value of spontaneous release wells) × 100%
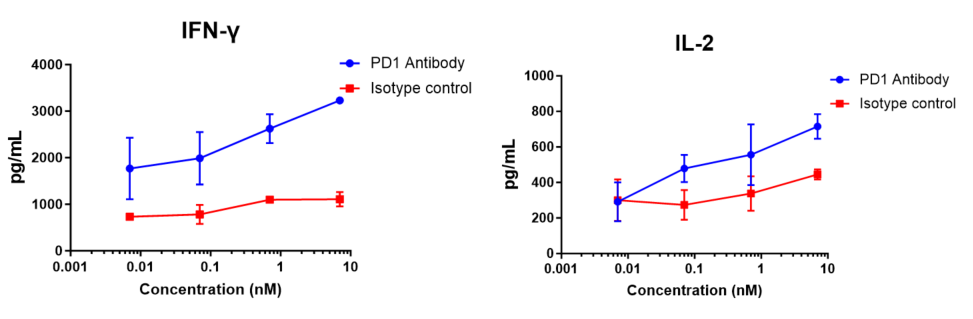
Human CD4+ T cells and allogeneic dendritic cells were mixed in a 96-well round-bottom plate at a ratio of 10:1, different concentrations of nivolumab (in house) were added, and the content of released IFN-γ was measured by ELISA after 120 h of incubation. The results showed that nivolumab (in house) dose-dependently enhanced IFN-γ and IL-2 production in the mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR).
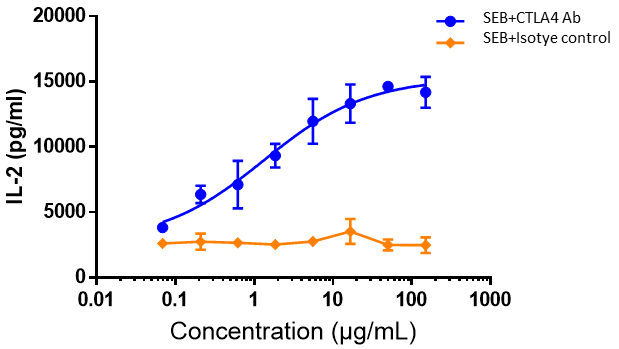
Human PBMCs were co-incubated with SEB (10 ng/mL), followed by the addition of different concentrations of ipilimumab or isotype control antibodies and then further incubation for 48 h. The release of IL-2 was measured by ELISA. The results showed that ipilimumab dose-dependently enhanced IL-2 production by SEB-stimulated PBMC.
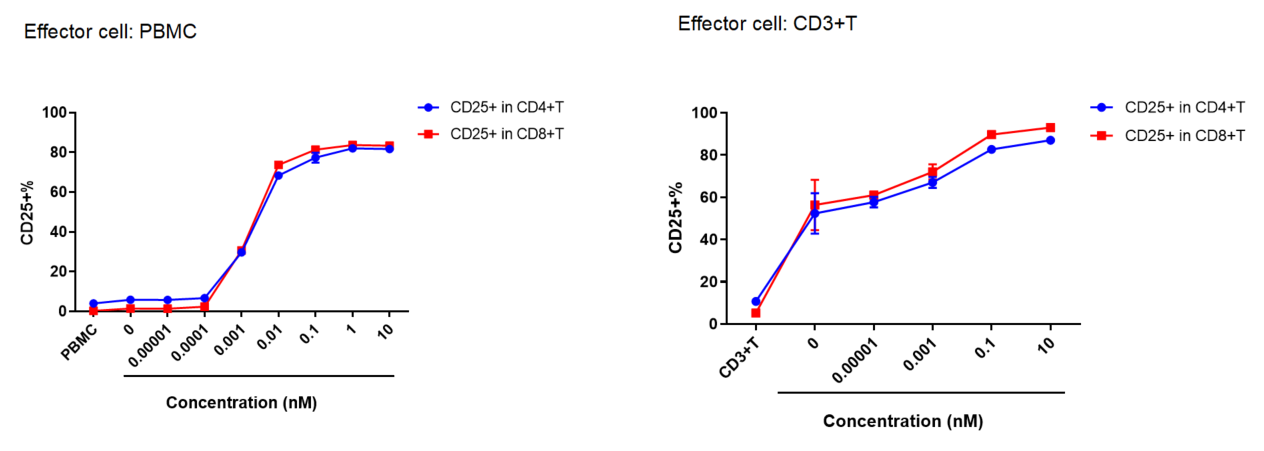
PBMC or CD3+ T cells were co-cultured with Daudi cells, and various concentrations of CD3, CD19 bispecific antibodies (BiTE) were added.
After 48 hours, the activation of CD4 and CD8 T cells is detected. As the antibody concentration increases, there is a significant increase in activated T cells (CD25+).


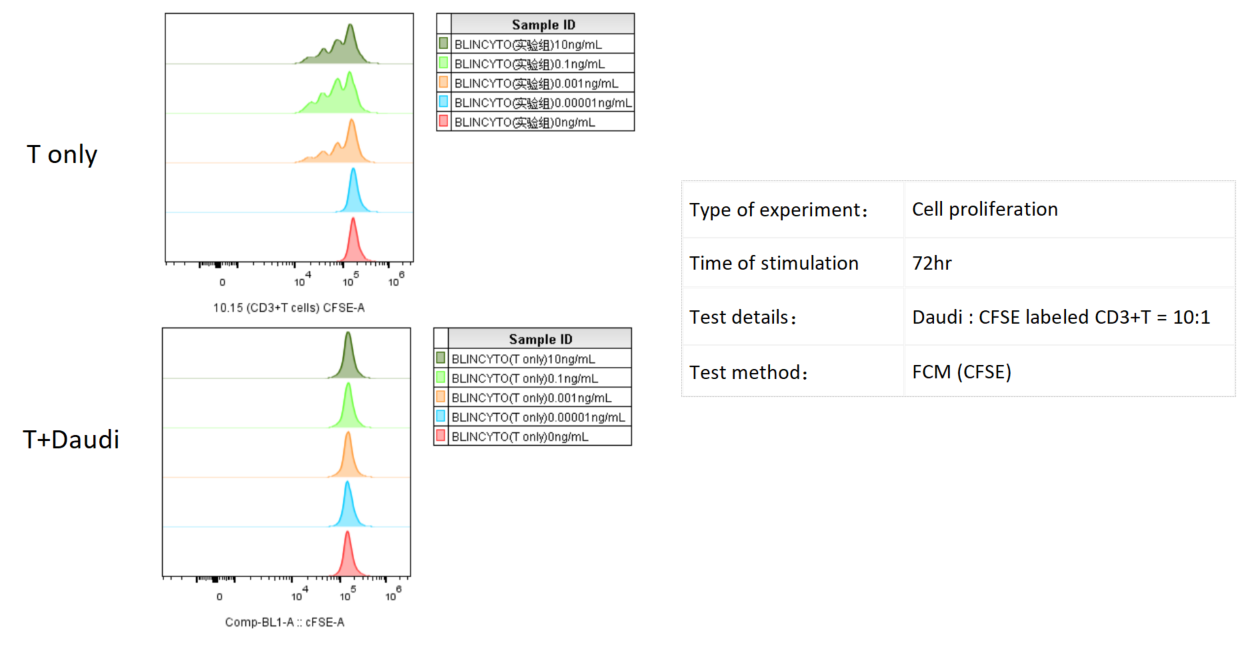
Daudi cells were incubated with CFSE-labeled CD3+ T cells and treated with various concentrations of Blinatumomab, which engages CD3 and CD20. T cell proliferation was assessed by flow cytometry after 3 days, which revealed more proliferation with higher doses of Blinatumomab, but only in the presence of Daudi cells.
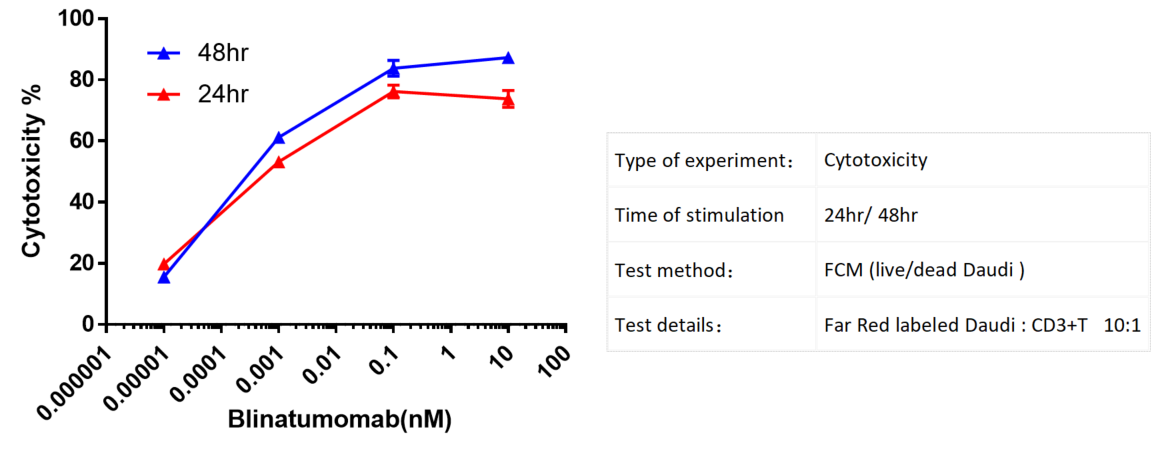
Far Red labeled Daudi cells were incubated with CD3+ T cells and treated with various concentrations of Blinatumomab. Cytotoxicity was assessed by flow cytometry after 24hr/ 48hr. There is a notable enhancement in the cytotoxicity as the concentration of the antibody increases.
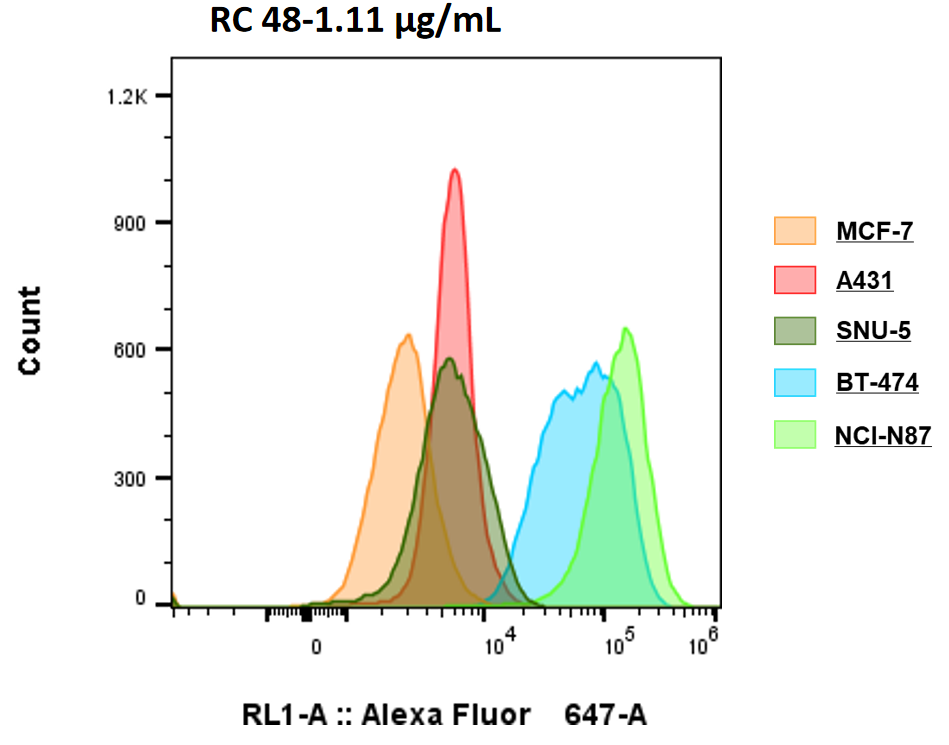
Her2 expression of 5 cell lines detected by Flow cytometry
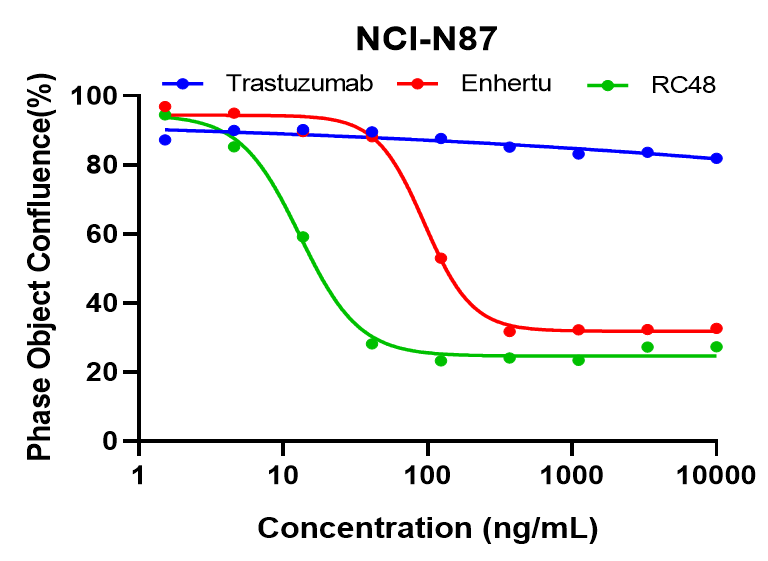
NCI-N87 cells were treated with varied concentration of trastuzumab, Enthertu or Disitamab Vedotin (RC48). Cell confluence were monitored continuously with Incucyte, the figures show the cell confluence after treated for 6 days. Enthertu or RC48 significantly inhibited NCI-N87 proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner, while trastuzumab was not.
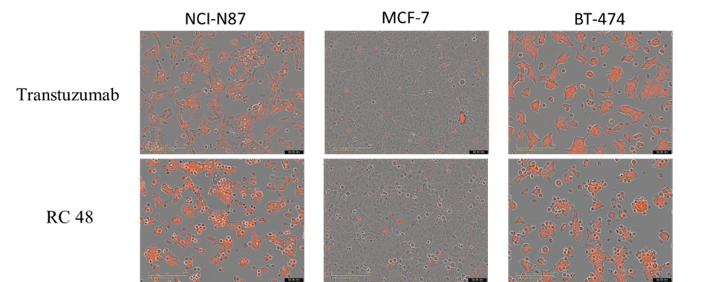
NCI-N87, MCF-7 and BT-474 cells were incubated with FabFluor-labeled Disitamab Vedotin(RC48) or transtuzumab for 24hr and were observed continuously with Incucyte. The orange signals in the photos indicate the internalized antibodies. Both Disitamab Vedotin(RC48) and transtuzumab were internalized into NCI-N87(high HER2 expression) and BT-474 (high HER2 expression) cells in a time-dependent manner, whereas not in MCF-7(no HER2 expression) cells.
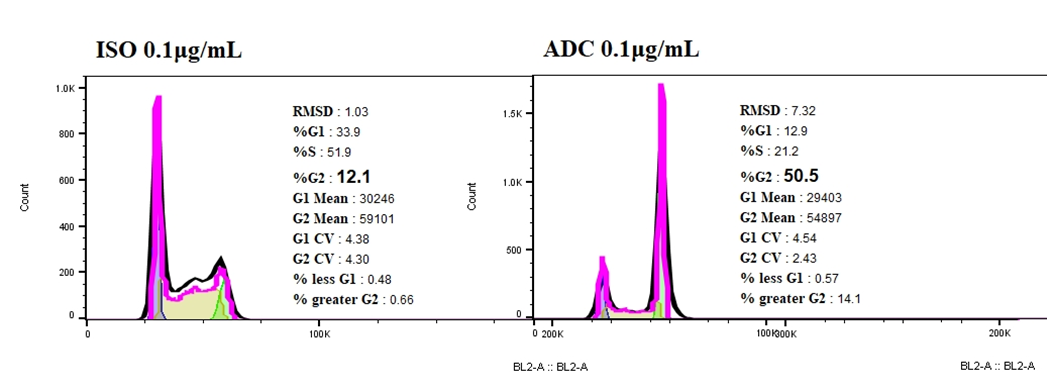
Compared with ISO-ADC, Her2-ADC could elicit cell-cycle arrest on NCI-N87, accompanied with a sharp increase proportion of cells in G2 phase.
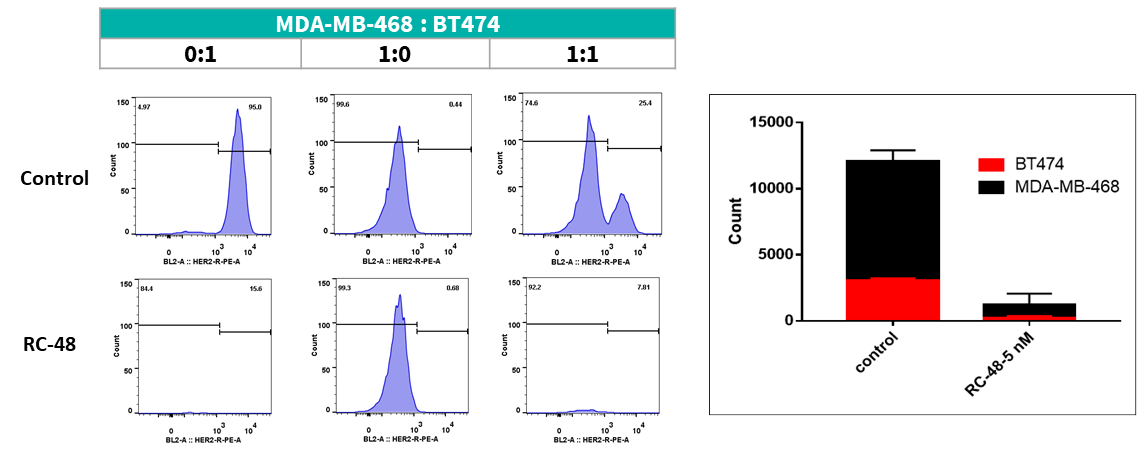
MDA-MB-468 cells ( Her2-) and BT474 (Her2+) were co-cultured overnight in different proportion (respectively 0:1, 1:0, 1:1). After treated with RC48 or vehicle for 5 days, cell number and ratio of HER2-positive and HER2-negative cells were determined by flow cytometer. RC48 showed great tumoricidal effects for BT474 cells, while almost no cytotoxicity for MDA-MB-468 cells. Importantly, RC48 could also kill MDA-MB-468 cells when cocultured with BT474 cells.
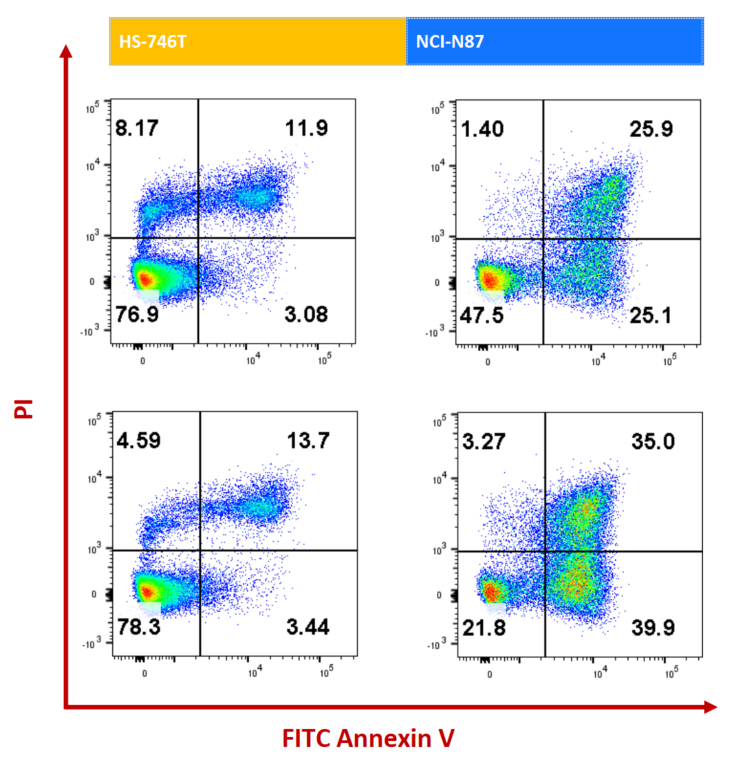
NCI-N87 (Her2+) and HS-746T (Her2-) cells were treated with ISO-MMAE and Enhertu for 72h. Apoptosis was detected with Annexin V/PI kit by flow cytometry. For Her2 high-expressed NCI-N87, Enhertu could induce significantly apoptosis.
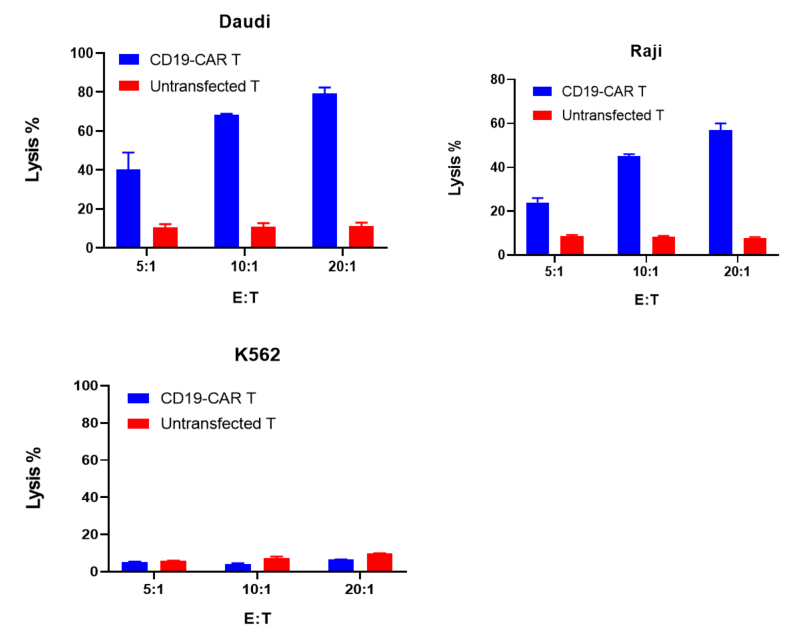
CD19-CAR T cells or untransfected T cells were co-cultured with target cells (Daudi, Raji, K562) at different ratios of 5:1, 10:1, and 20:1 for 24 hours. Tumor cytotoxicity was evaluated with Fixable Viability Dye by flow cytometry.
The results showed that compared to untransfected T cells, CD19-CAR T cells exhibited significant cytotoxicity against Daudi and Raji cells, which expressed CD19. However, CD19-CAR T did not show specific cytotoxicity towards K562 cells, which was CD19 negative.
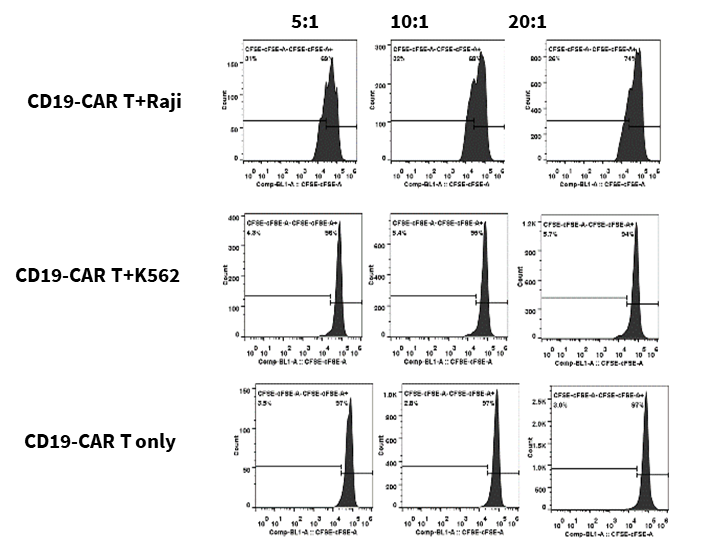
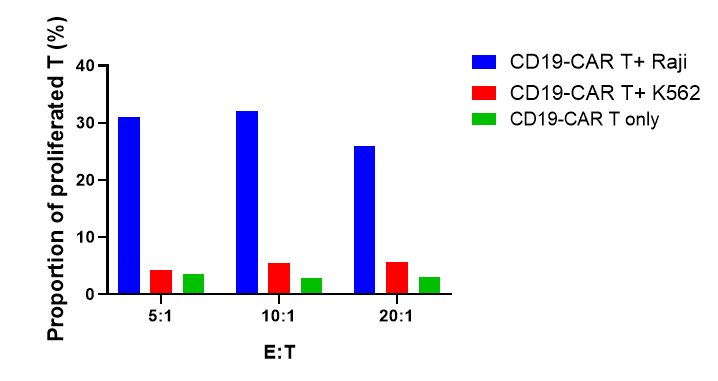
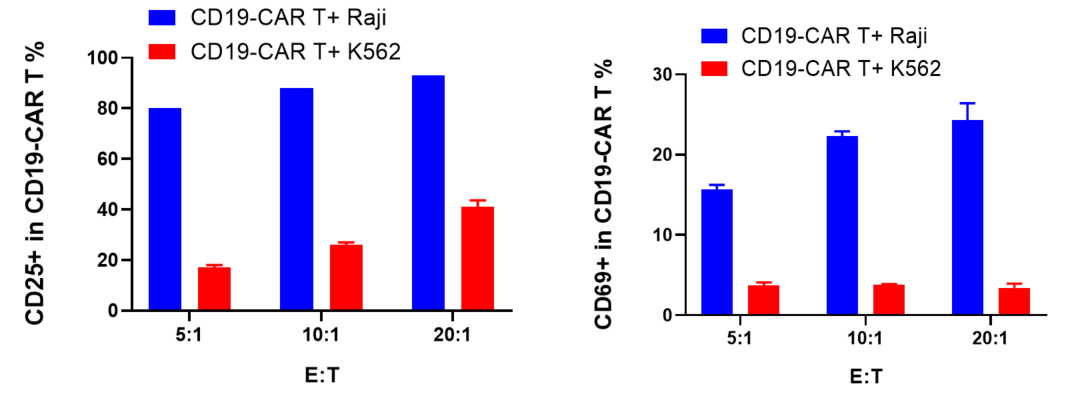
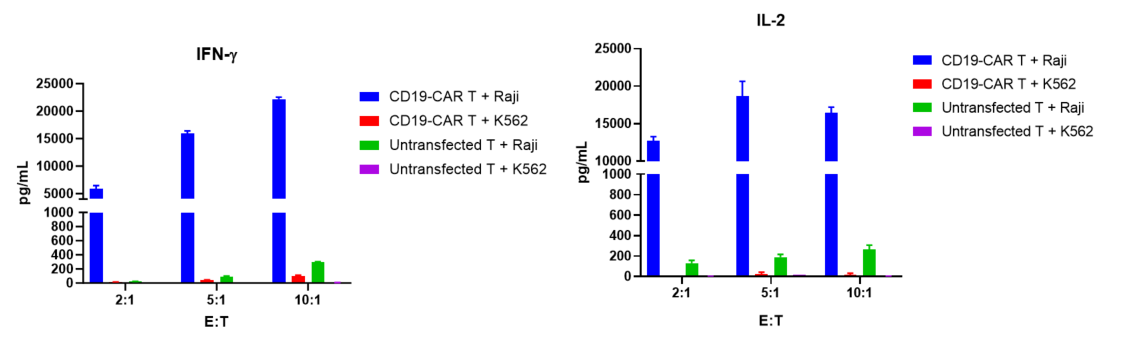
CD19-CAR T labeled with CFSE and were co-cultured with target cells (Raji, K562) at different ratios of 5:1, 10:1, and 20:1 for 72 hours. CD19-CAR T proliferation, activation and cytokine release were evaluated.
The results showed that CD19-CAR T cells exhibited significant proliferation, activation and cytokine release when co-culture with Raji cells, which expressed CD19, compared with K562 cells, which was CD19 negative.
FACS
Cytokine
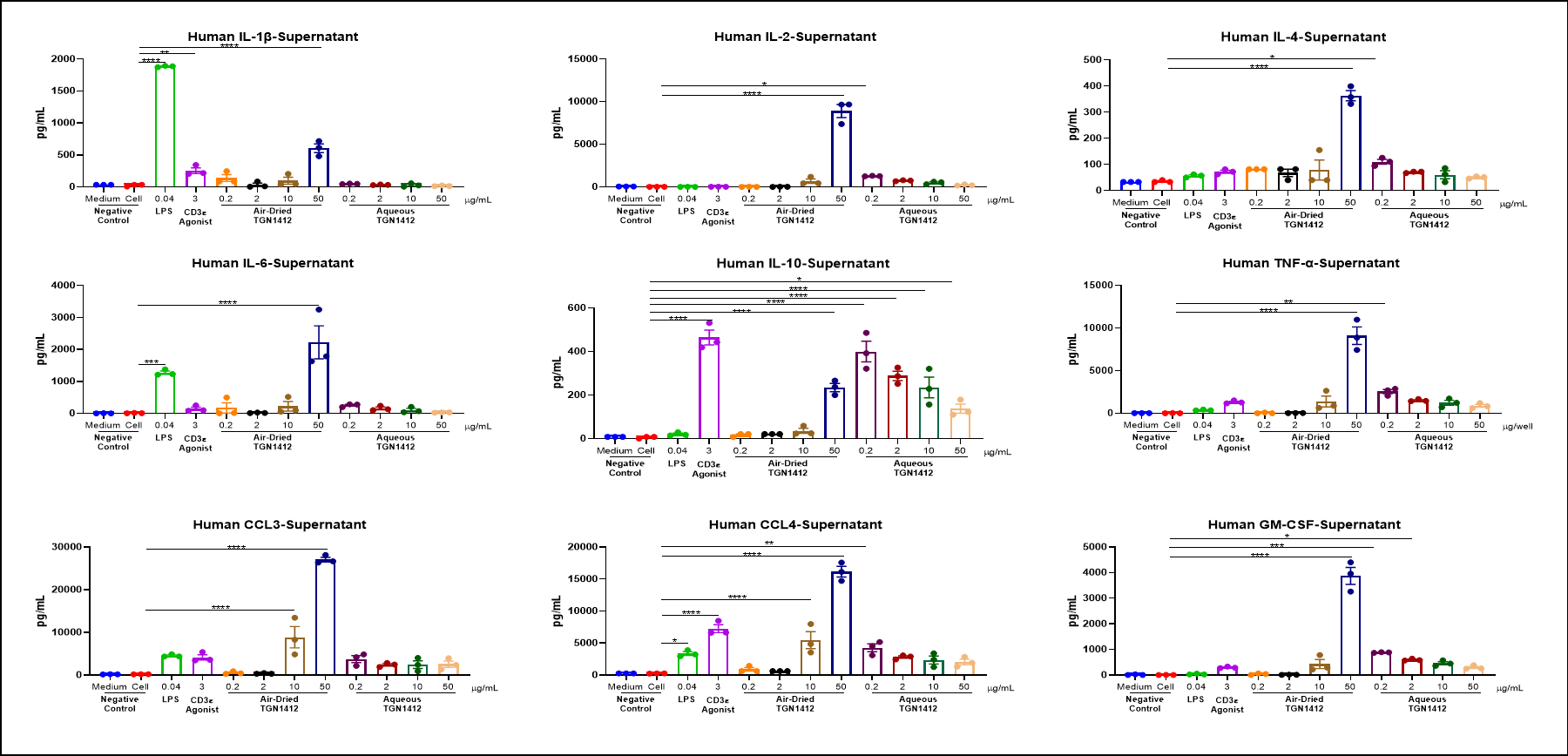
Air-dried TGN 1412 could induce inflammatory factor storm of PBMC in vitro.
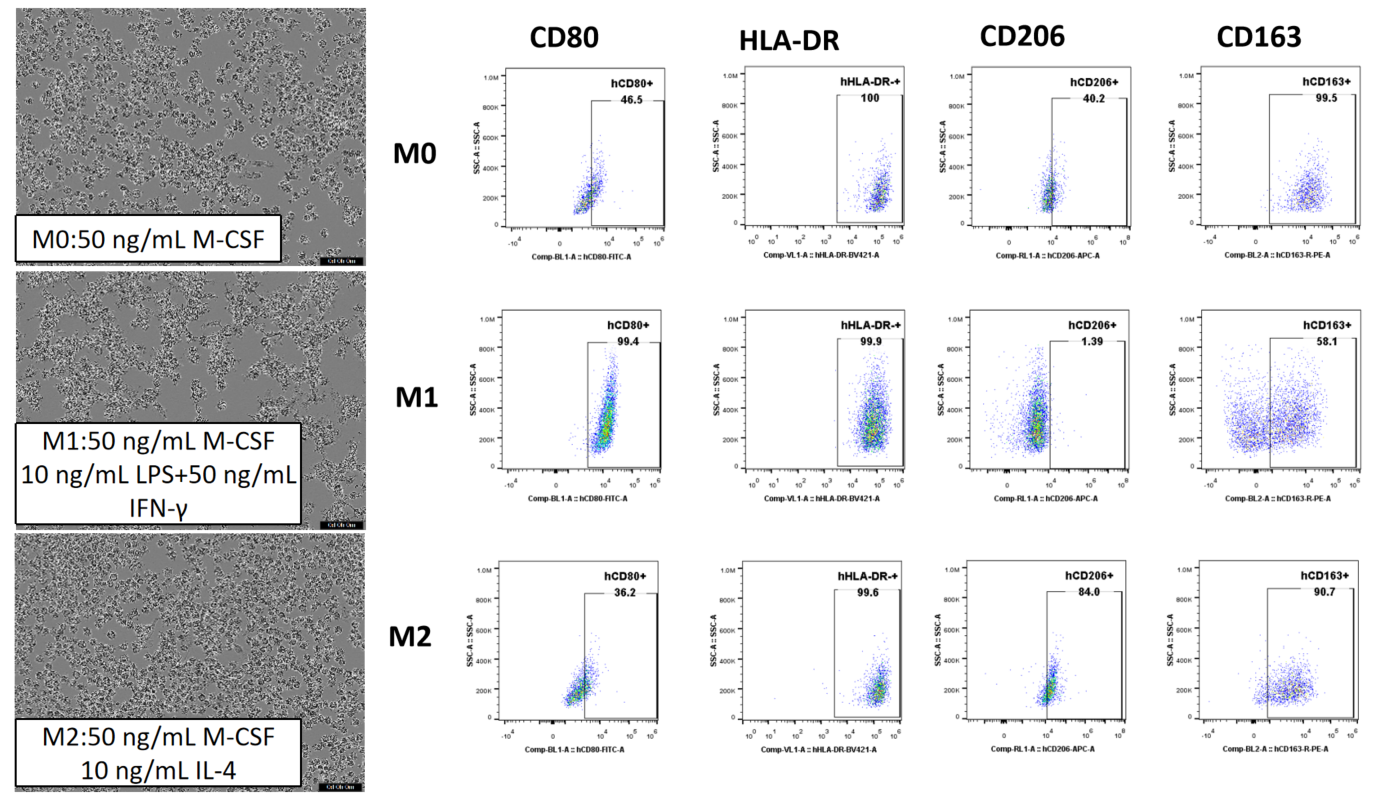
CD14+ monocytes were separated from human PBMCs with magnetic beads and then cultured with various cytokines for 6 days. This results in macrophages with distinct morphologies and surface markers, depending on the induction conditions.
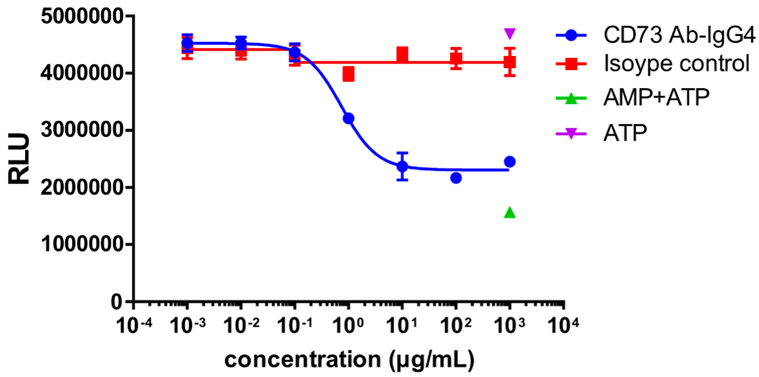
MDA-MB-231 cells were used as target cells and incubated with different concentrations of CD73 antibodies at 37 °C for 30 min; AMP was added and incubated for 3 h; ATP and luciferase + substrate were then added to detect the fluorescence value.
CD73 enzyme activity was inhibited, and the fluorescence value decreased with the increasing concentration of CD73 antibody.
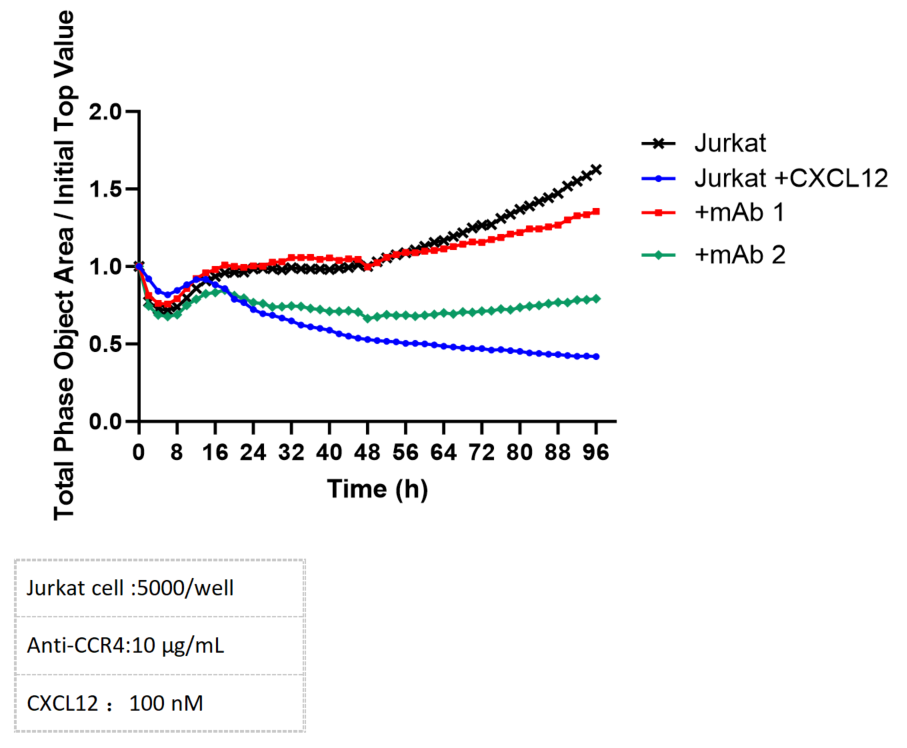
Chemotactic migration can be accurately monitored using the Incucyte system. The migratory response of CXCR4-expressing Jurkat cells to CXCL12 can be effectively inhibited by the administration of CXCR4-specific antibodies.