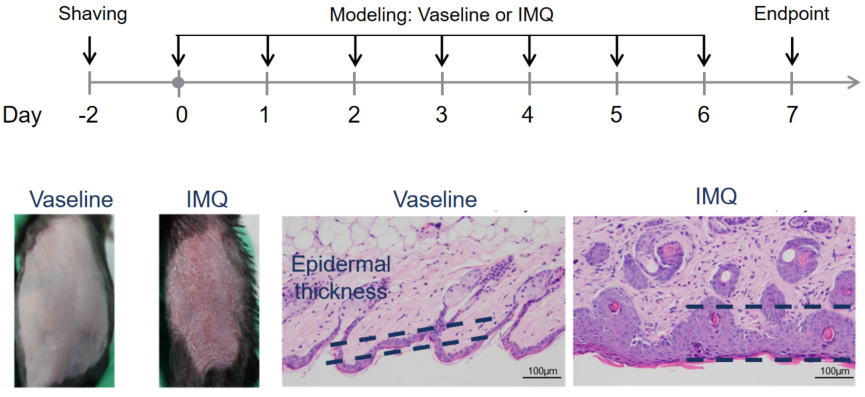
Psoriasis Mouse Model
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by epidermal hyperproliferation, parakeratosis, and immune cell infiltration. It involves complex interactions between the innate and adaptive immune systems, influenced by genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. A widely used psoriasis mouse model is the imiquimod (IMQ)-induced model, which phenotypically mimics human psoriasis, displaying skin inflammation, erythema, scaling, and epidermal thickening.
In this IMQ-induced psoriasis model, disease severity in mice can be evaluated using standardized clinical scoring. Histological features include cutaneous thickening, parakeratosis, and leukocyte infiltration, primarily in the dermis. Importantly, the IL-23/IL-17 axis plays a central role in psoriasis pathogenesis, with elevated IL-17 cytokine levels observed in the model.
To support psoriasis drug discovery, Biocytogen offers target-humanized imiquimod-induced psoriasis model. We have developed B-hIL17A mice, in which the mouse IL-17A gene is replaced with the human IL-17A gene. This genetically humanized psoriasis mouse model provides a powerful in vivo platform for evaluating therapeutics targeting human IL-17A and studying IL-17A–mediated immune responses in psoriasis.
Establishment of Psoriasis Mouse Model
- Experimental Animals: C57BL/6 or Balb/c, B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice, 7-8 weeks old, female
- Modeling reagent: Imiquimod (IMQ) cream
- Modeling method: Topically applicated on dorsal for consecutive 5-8 days, depends on the mouse strain.
| Readouts |
| Clinical scores |
Erythema |
| Scaling |
| Histopathology |
Dorsal skin epidermal thickness |
Histology scores
(epidermal hyperplasia, parakeratosis and hyperkeratosis, erosion, inflammatory infiltration) |
| Molecular levels |
Skin IL17, IL23 levels |
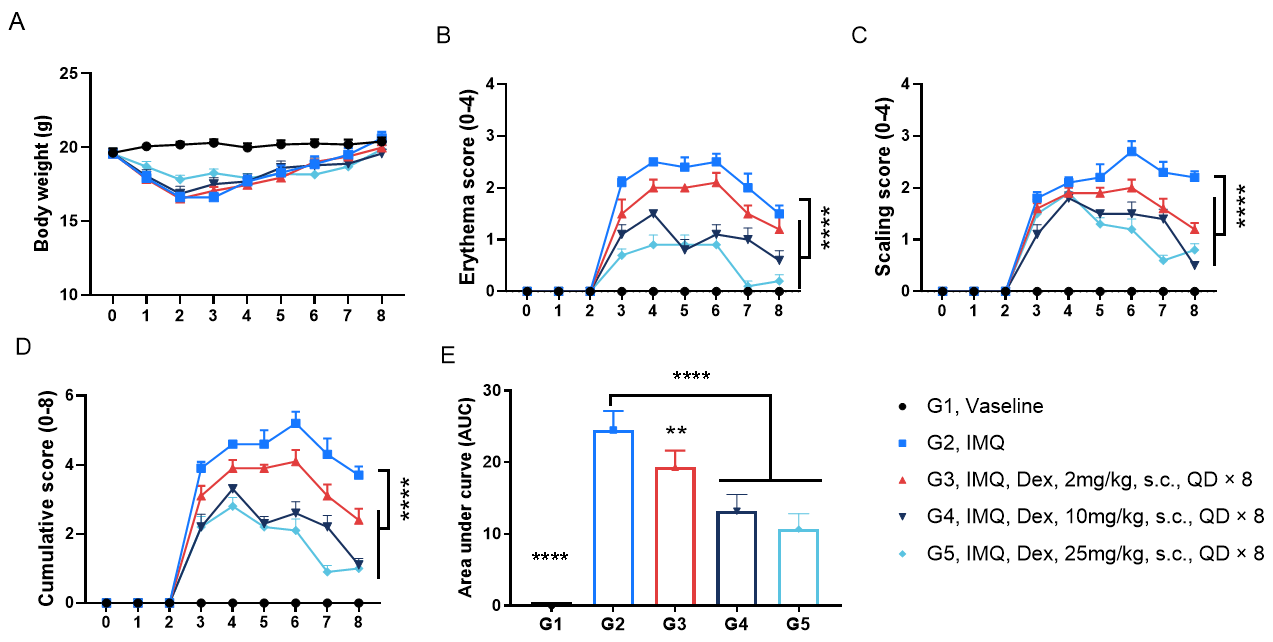
In Vivo Efficacy of Dexamethasone in a Psoriasis Model of C57BL/6 Mice
Dexamethasone (Dex) improved clinical scores in IMQ-induced psoriasis of C57BL/6 mice. A. Body weight change during treatment. B. Daily erythema scores. C. Daily scaling scores. D. cumulative score of each group. E. Area under the cumulative score curve in each group. (B-C. Two-way ANOVA; E. One-way ANOVA; ** p< 0.01, **** p< 0.0001.)
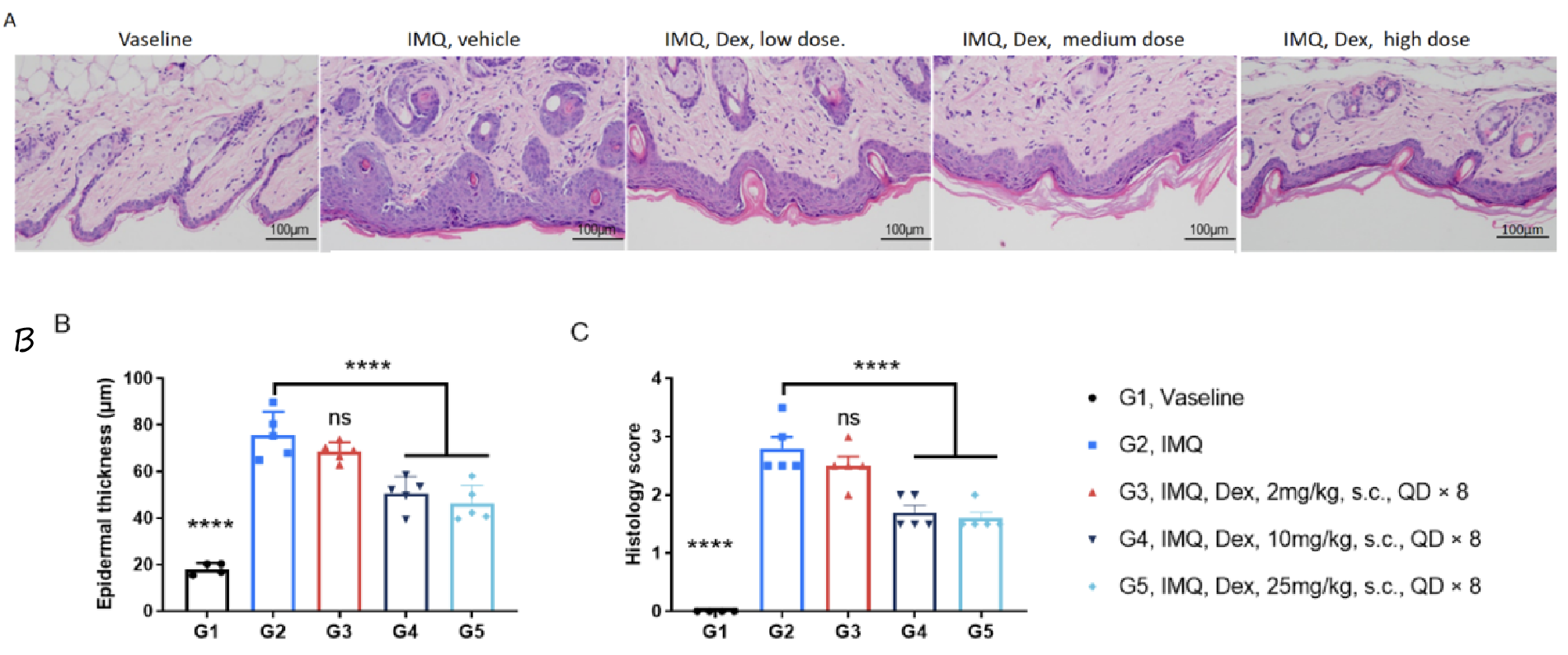
Dexamethasone inhibited keratinocyte proliferation and inflammatory cell infiltration in psoriasis model of C57BL/6 mice. A. H&E staining of dorsal skin. B. Mouse epidermal thickness. C. Histopathology score. (One-way ANOVA; **** p< 0.0001.)
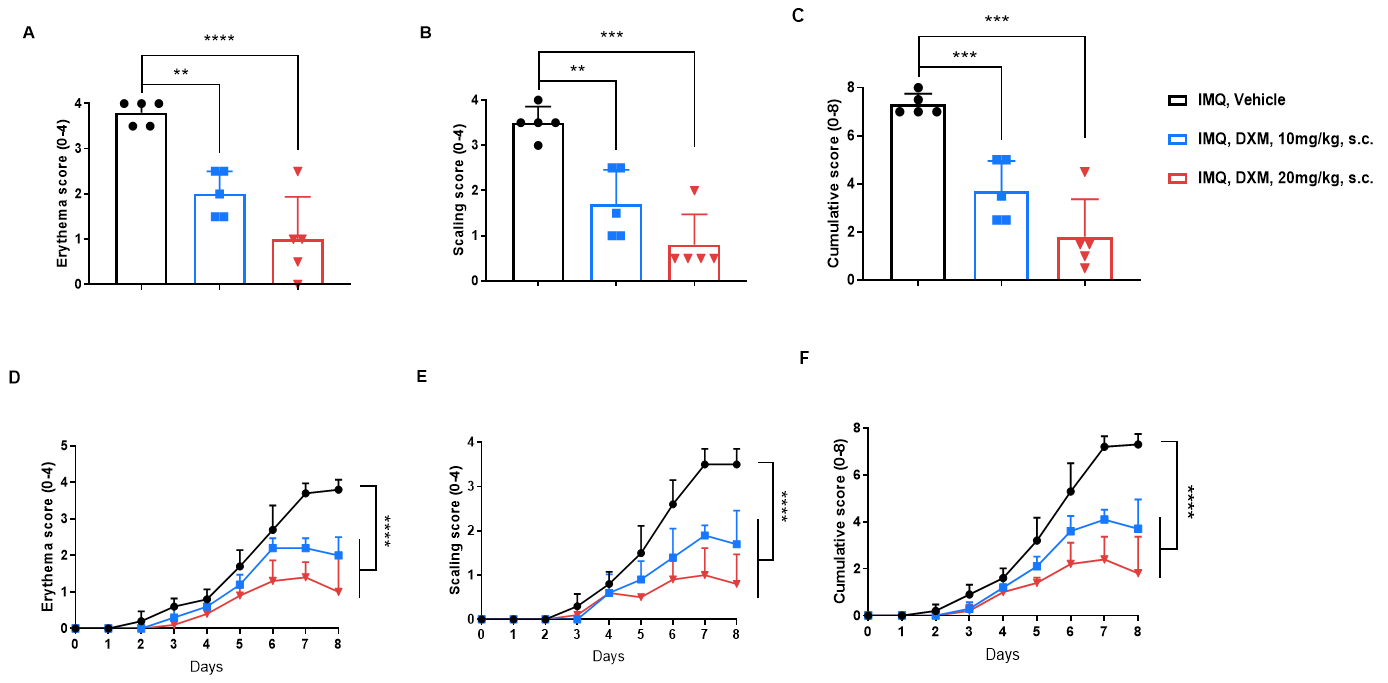
In Vivo Efficacy of Dexamethasone in a Psoriasis Model of BALB/c Mice
Dexamethasone (Dex) improved clinical scores in IMQ-induced psoriasis of BALB/c mice. A. erythema scores on day 8. B. scaling scores on day 8. C. cumulative score on day 8. D. Daily erythema scores. E. Daily scaling scores. F. cumulative score of each group. (B-C. Two-way ANOVA; E. One-way ANOVA; ** p< 0.01, **** p< 0.0001).
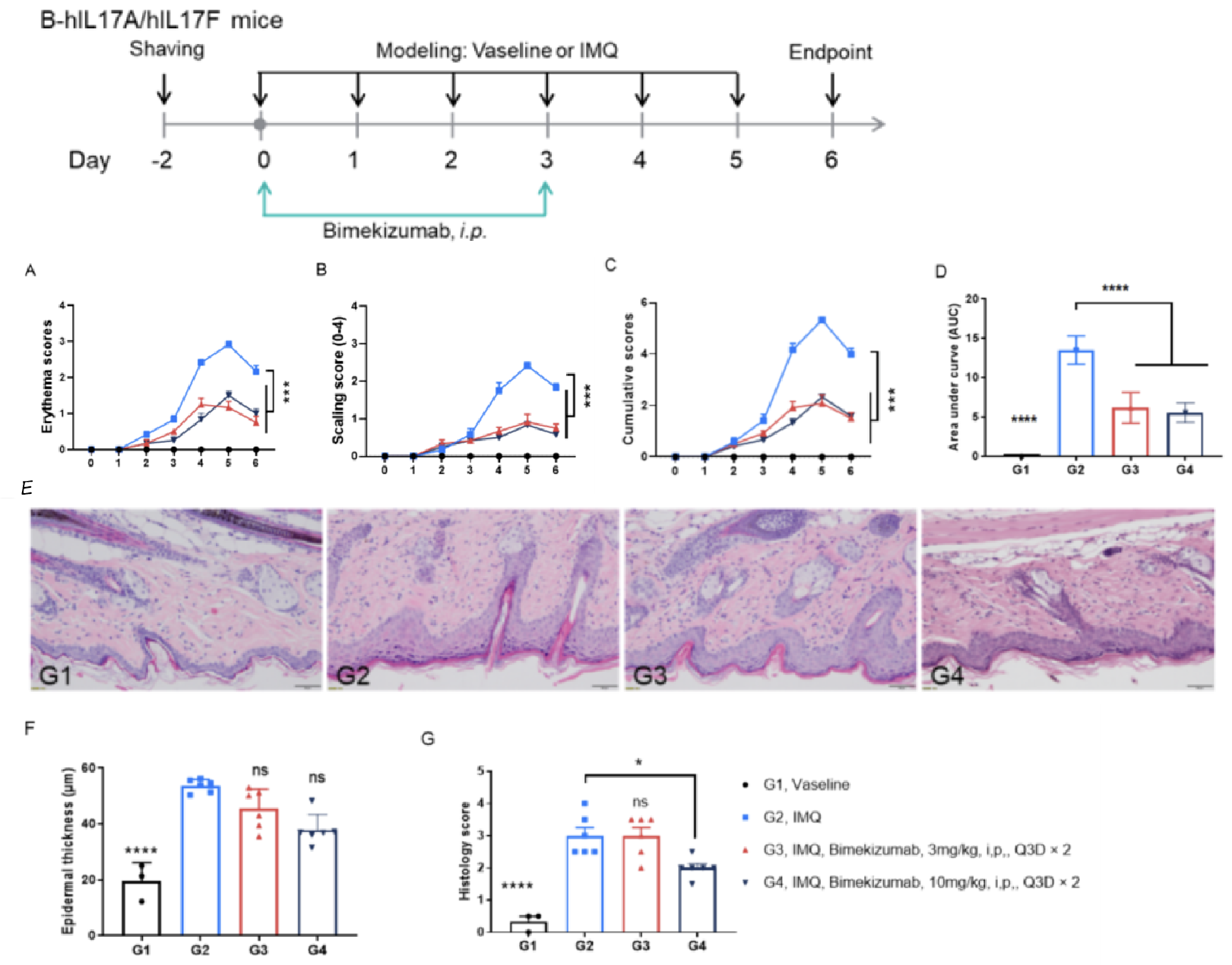
Bimekizumab improved IMQ-induced psoriasis in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice. A. Daily erythema scores. B. Daily scaling scores. C. cumulative score of each group. D. Area under the cumulative score curve in each group. E. H&E staining of dorsal skin. F. epidermal thickness. G. Histopathology score. (Two-way ANOVA or One-way ANOVA; * p< 0.05 , *** p< 0.001, **** p< 0.0001).