

Biocytogen has developed humanized mice targeting lipid metabolism for testing novel therapeutics, such as antibody and nucleic acid drugs, as well as knockout models for studying disease mechanisms.
on this page
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial wall characterized by vascular endothelial dysfunction, infiltration of inflammatory cells, and gradual formation of atherosclerotic plaques. In the process of atherogenesis, disorders of lipid metabolism (increased levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and decreased levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)) can lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Biocytogen has developed humanized mice targeting lipid metabolism for testing novel therapeutics, such as antibody and nucleic acid drugs, as well as knockout models for studying disease mechanisms.
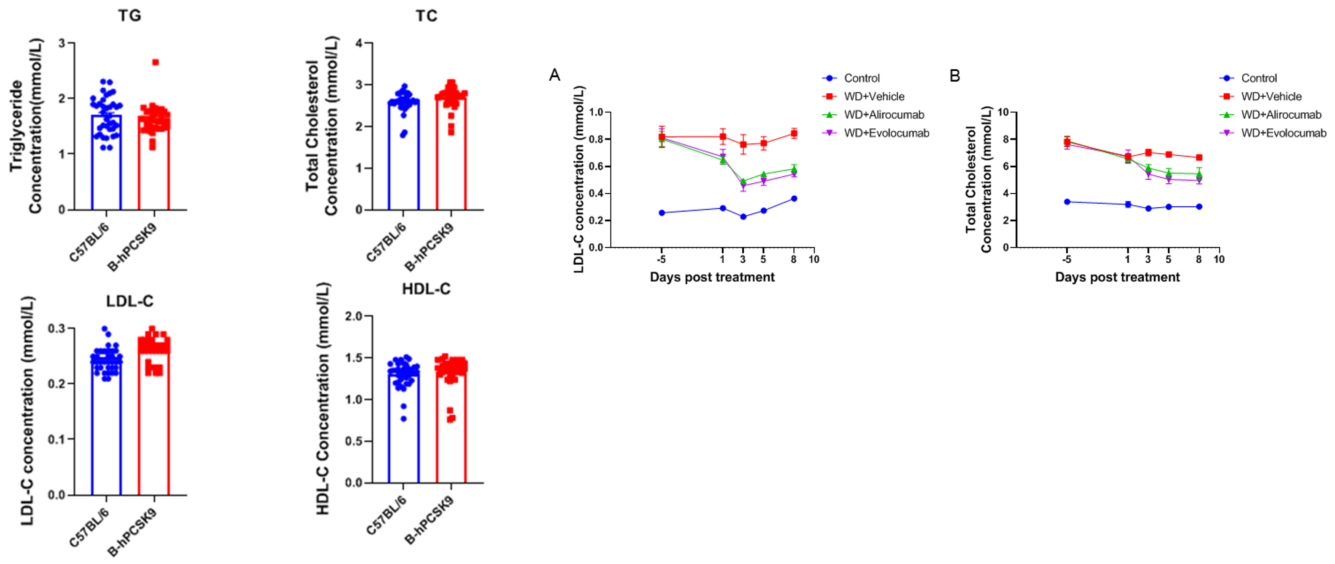
Anti-human PCSK9 antibody improved lipid metabolism in male B-hPCSK9 mice. Wild-type C57BL/6 and B-hPCSK9 mice were treated with Alirocumab (in house) / Evolocumab (in house) or isotype control antibody (single dose, s.c.) (n = 8) after 6 weeks of western diet induction. Blood were collected on Day -5, 1, 3, 5 and 8 for analysis. Serum levels of LDL-C (A) and TC (B) were reduced in the anti-human PCSK9 antibody treated male mice group compared to the isotype control. Results indicated that anti-human PCSK9 antibody were efficacious in controlling blood lipid in male B-hPCSK9 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. TC, total cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol.
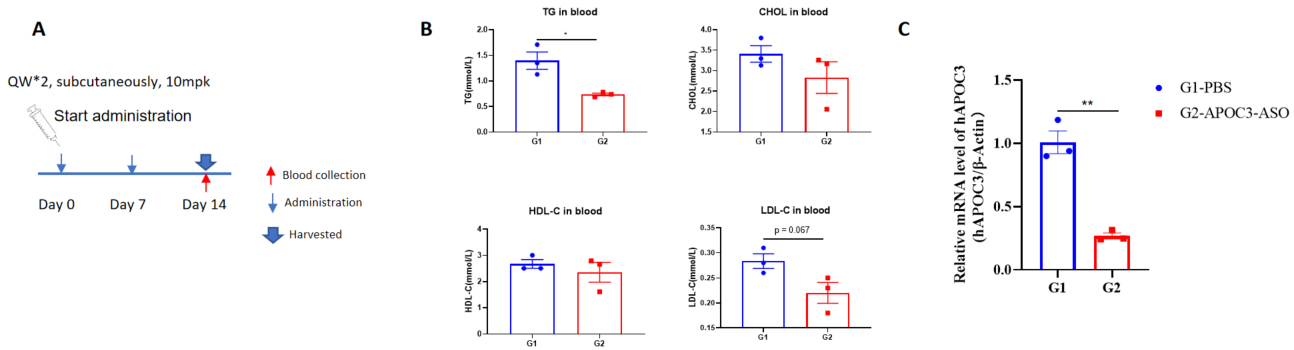
The inhibitory efficiency of the nucleic acid drugs against human APOC3 in B-hAPOC3 mice. B-hAPOC3 mice were randomly divided into two groups (n = 3 / group, 6 weeks old). The human APOC3 targeted nucleic acid drugs (synthesized according to patents) and PBS were administered to the mice individually. The nucleic acid drugs was administered in the form of PBS aqueous solution. The drug dosages for all animals were calculated according to the body weight. The mice were sacrificed on day 14, and the liver tissue was collected to detect the expression level of human APOC3 mRNA by qPCR. A, The schematic diagram of experimental processing. B, The blood lipids level of B-hAPOC3 mice after treatment. Compared with the control group (G1), the treatment group (G2) showed a significant decrease in TG. C, The expression of human APOC3 mRNA in liver. The human APOC3 in the treatment group (G2) was significantly reduced compared to the control group (G1) and the inhibition rate in the treatment group was 73.4%, demonstrating that B-hAPOC3 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of human APOC3 targeted nucleic acid drugs. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Establishment of special diet-induced atherosclerosis model in ApoE-/- mice
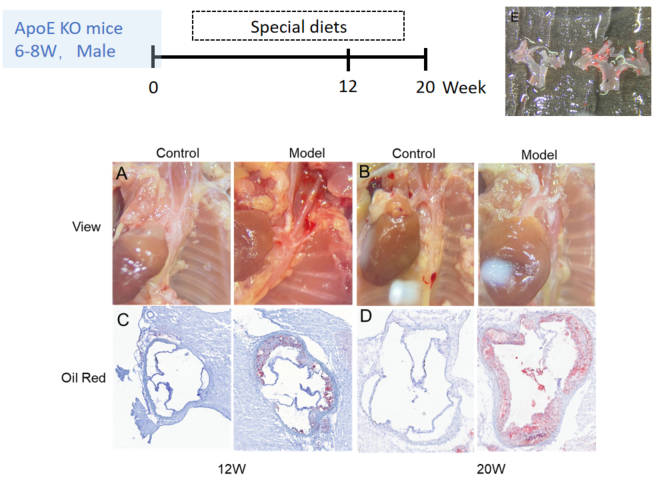
Establishment of special diet-induced atherosclerosis model. A-B, Atherosclerotic plaques of mice at 12 and 20 weeks. C-D, Oil Red results of aortic sinus at 12 and 20 weeks. E, Gross staining of aortic arch at 12 weeks. N = 8 mice per group.
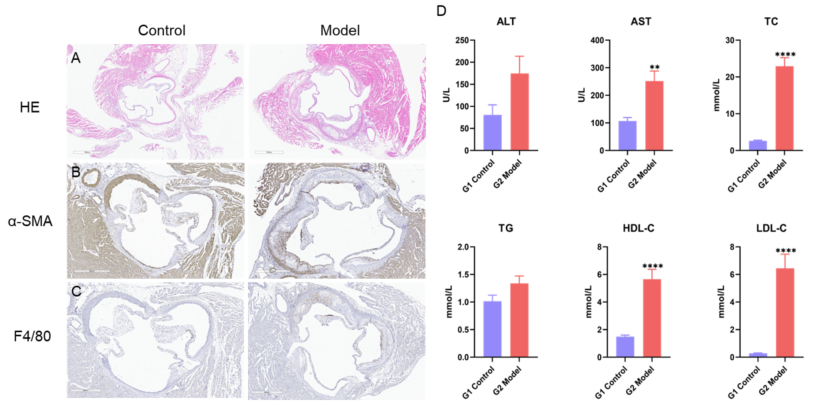
Tissue staining and blood biochemical results in the mouse model of atherosclerosis at 12 weeks A, H&E results of aortic sinus. B-C, Immunohistochemistry shows expression of α-SMA and F4/80. D, ALT, AST, TC, TG, HDL-C and LDL-C levels in serum. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM . N = 8 mice per group. **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.