

on this page
Small nucleic acid drugs, also known as oligonucleotide drugs, can be primarily categorized into antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), small activating RNAs (saRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), aptamer RNAs, and CpG oligonucleotides. These drugs regulate gene expression by interacting with nucleic acids (RNA or DNA), thus functioning at the genetic or molecular level. They offer notable advantages such as high specificity, ease of design, shorter development cycles, broad target range, and prolonged efficacy.
Biocytogen has developed a series of humanized mice tailored for the preclinical research of small nucleic acid drugs. These models aim to facilitate the development of safer and more effective nucleic acid therapies.
| Efficacy | MOA | Safety |
|
|
|
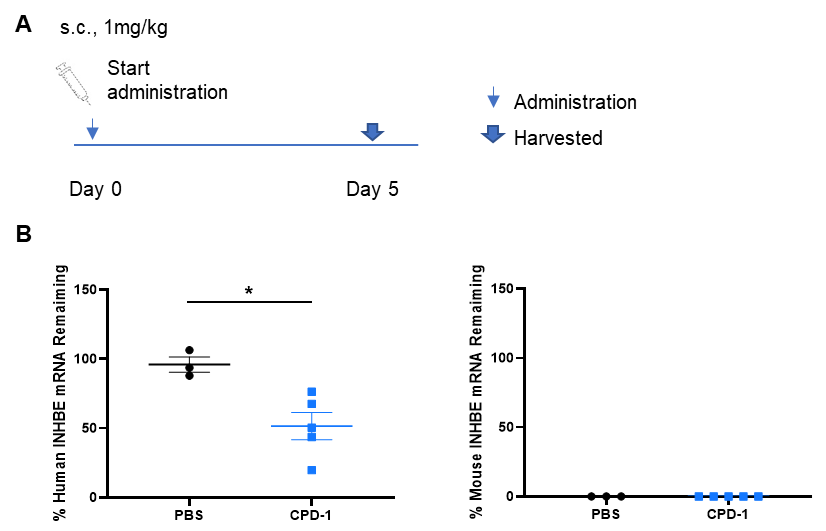
The inhibitory efficiency of the nucleic acid drugs against human INHBE in B-hINHBE mice. B-hINHBE mice were randomly divided into two groups (male, 9-10 weeks old). The human INHBE targeted nucleic acid drugs (provided by a client) and PBS were administered to the mice individually. The nucleic acid drugs was administered in the form of PBS aqueous solution. The mice were sacrificed on day 5, and the liver tissue was collected to detect the expression level of human INHBE mRNA by qPCR. (A) The schematic diagram of experimental processing. (B) The expression of human INHBE mRNA in the liver. The human INHBE in the CPD-1 group was significantly reduced compared to the control group. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
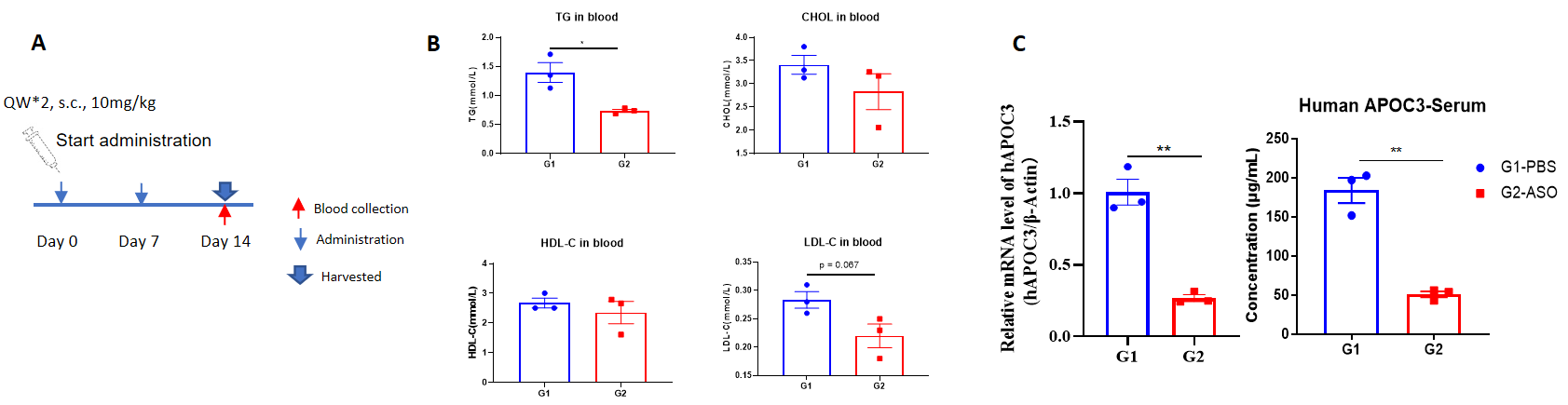
The inhibitory efficiency of the nucleic acid drugs against human APOC3 in B-hAPOC3 mice. B-hAPOC3 mice were randomly divided into two groups (n=3/group, 6 weeks old). The human APOC3 targeted nucleic acid drugs (synthesized according to patents) and PBS were administered to the mice individually. The nucleic acid drugs was administered in the form of PBS aqueous solution. The drug dosages for all animals were calculated according to the body weight. The mice were sacrificed on day 14, and the liver tissue was collected to detect the expression level of human APOC3 mRNA by qPCR. (A) The schematic diagram of experimental processing. (B) The blood lipids level of B-hAPOC3 mice after treatment. Compared with the control group (G1), the treatment group (G2) showed a significant decrease in TG. (C) The expression of human APOC3 mRNA in liver and human APOC3 protein in serum. The human APOC3 mRNA in the treatment group (G2) was significantly reduced compared to the control group (G1) and the inhibition rate in the treatment group was 73.4%, demonstrating that B-hAPOC3 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of human APOC3 targeted nucleic acid drugs. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
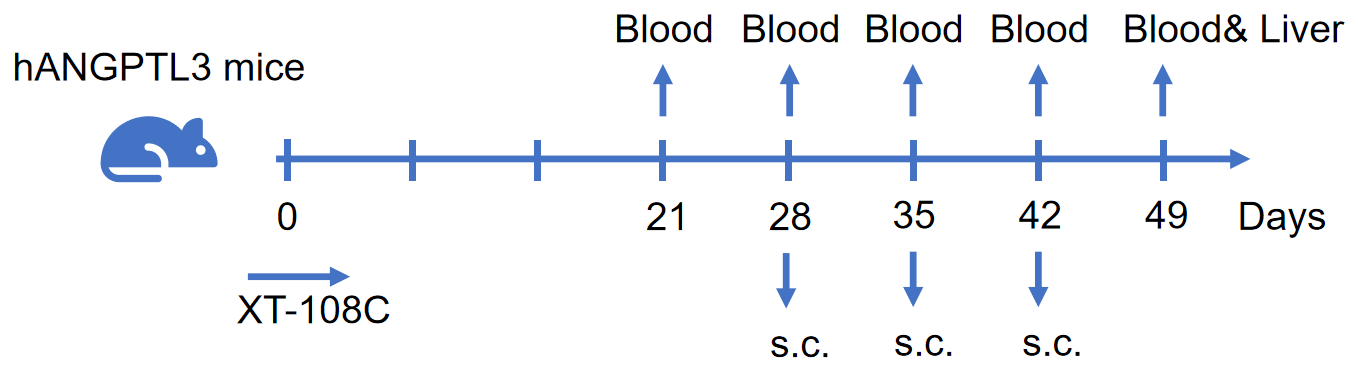
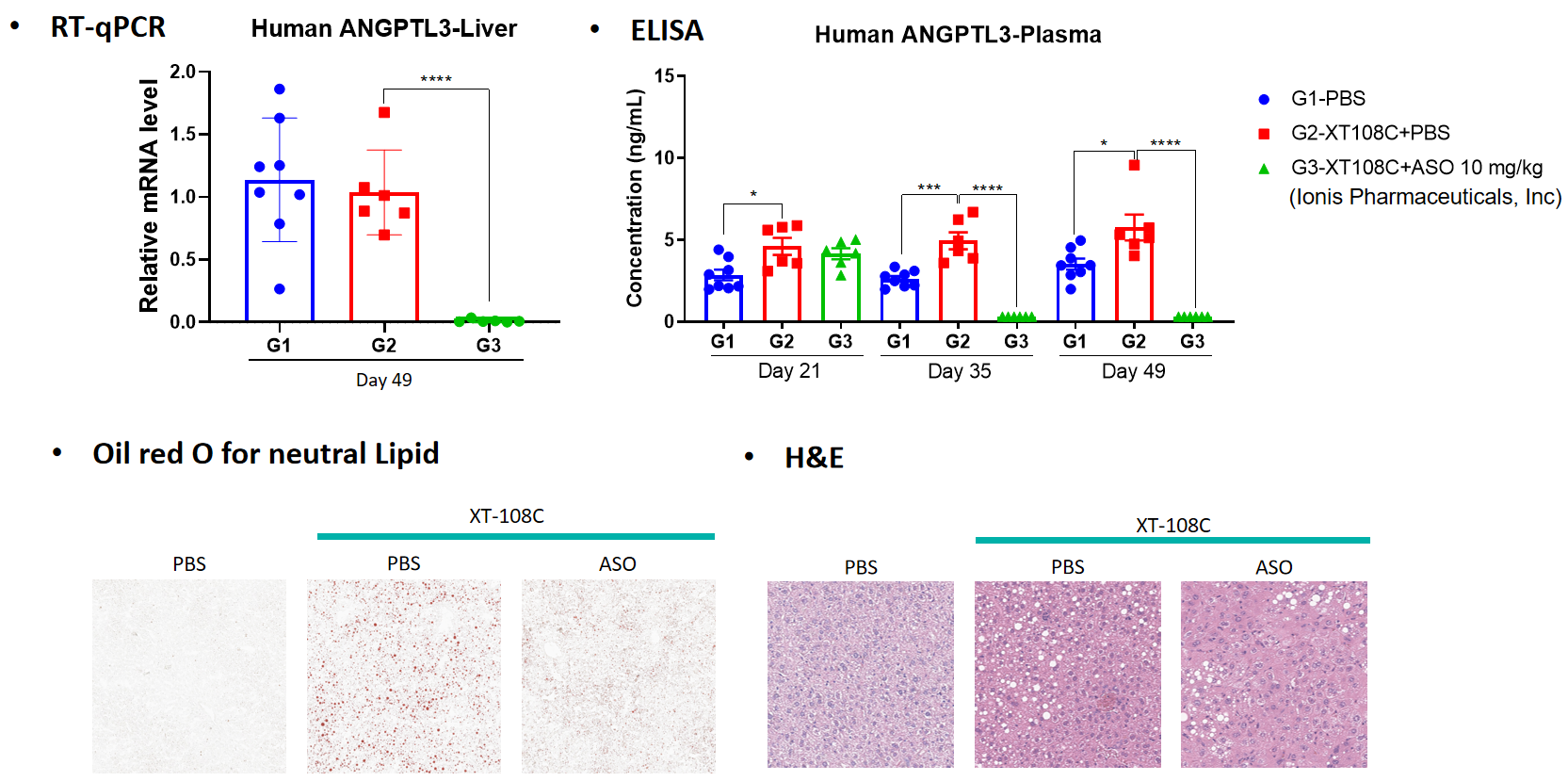
Pharmacodynamics:
Pathological analysis:
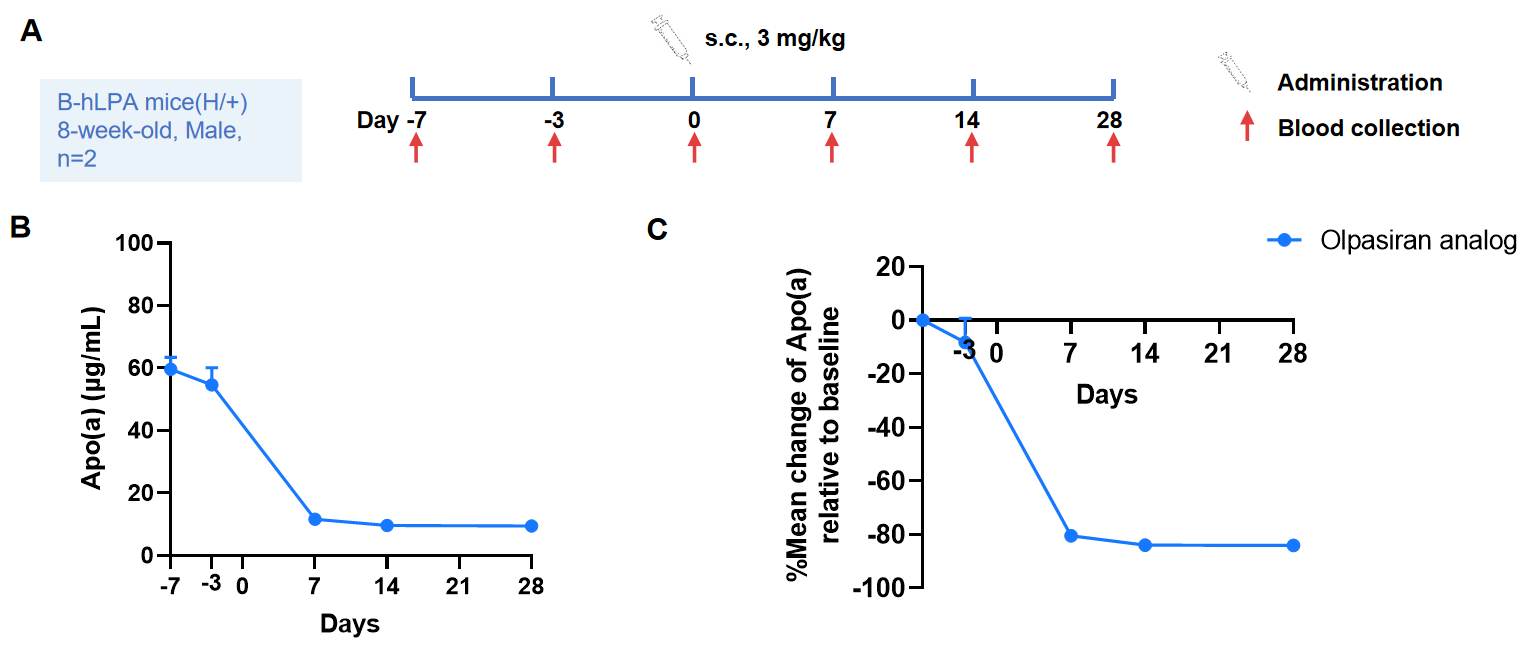
Changes of plasma apo(a) levels in heterozygous B-hLPA mice in response to olpasiran analog. Olpasiran analog (provided by the client) is a double-strand small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting lipoprotein(a) and potently reduce plasma Lp(a) concentration. As shown in the panel, Olpasiran analog reduced Apo(a) concentrations in heterozygous B-hLPA mice(A), achieving up to over 80% reduction from baseline(B) after administration of a single dose. The mice can be used for preclinical studies of efficacy.
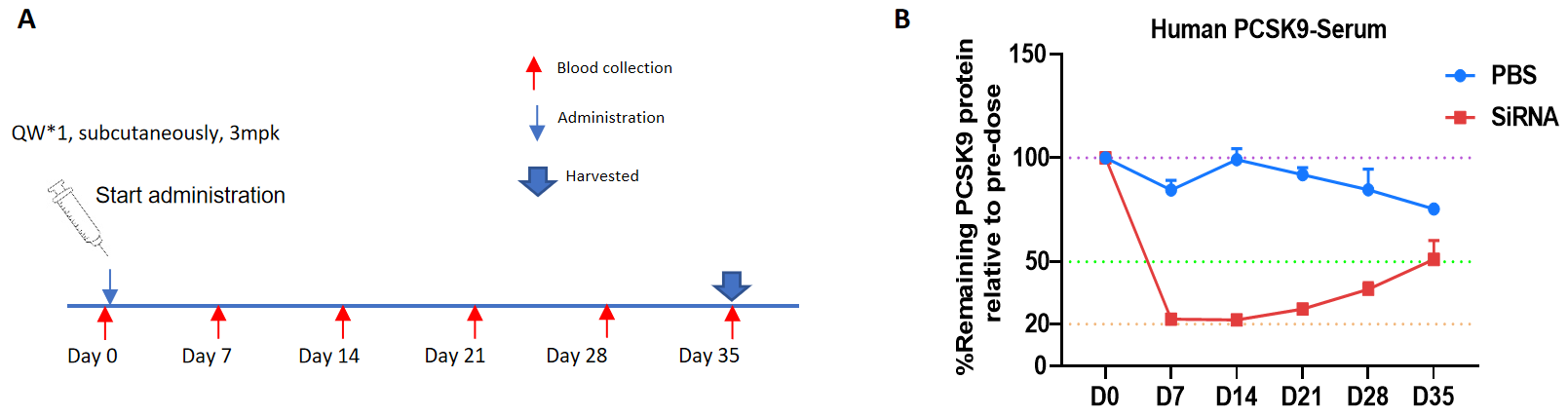
The inhibitory efficiency of the PCSK9 targeted nucleic acid drugs in homozygous B-hPCSK9 mice plus. B-hPCSK9 mice plus were randomly divided into two groups (10-week-old, male). The human PCSK9-targeted nucleic acid drug Inclisiran (synthesized according to patents) and PBS were administered to the mice individually. The nucleic acid drug was administered in the form of PBS aqueous solution. The mice were sacrificed on day 35. (A) The schematic diagram of experimental processing. (B) The changes in PCSK9 protein expression levels in serum on days 7, 14, 21, 28 and 35 after administration, compared to the levels before administration. The human PCSK9 levels in the treatment group (G2) were reduced compared to the control group (G1), demonstrating that B-hPCSK9 mice plus provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of human PCSK9-targeted nucleic acid drugs. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.