Biocytogen offers advanced platforms to support the development of diverse cell therapies, including CAR-T, CAR-Macrophages, CAR-NK, TILs, and TCR-T, providing both in vitro services and in vivo models for comprehensive research.
on this page
Cell therapy involves transferring live cells into a patient to treat or cure diseases, using either the patient’s own cells (autologous) or donor cells (allogeneic). Immune cell therapies, especially CAR-T therapy, have revolutionized cancer treatment, achieving remarkable success in hematological malignancies. CAR-T cells are engineered T-cells modified to express chimeric antigen receptors that recognize and attack tumor antigens.
Biocytogen offers advanced platforms to support the development of diverse cell therapies, including CAR-T, CAR-Macrophages, CAR-NK, TILs, and TCR-T, providing both in vitro services and in vivo models for comprehensive research. We have developed a series of immunodeficient mice and established CDX models along with immune reconstitution models to facilitate the evaluation of cell therapies.
| Efficacy | MOA | Safety |
|
|
|
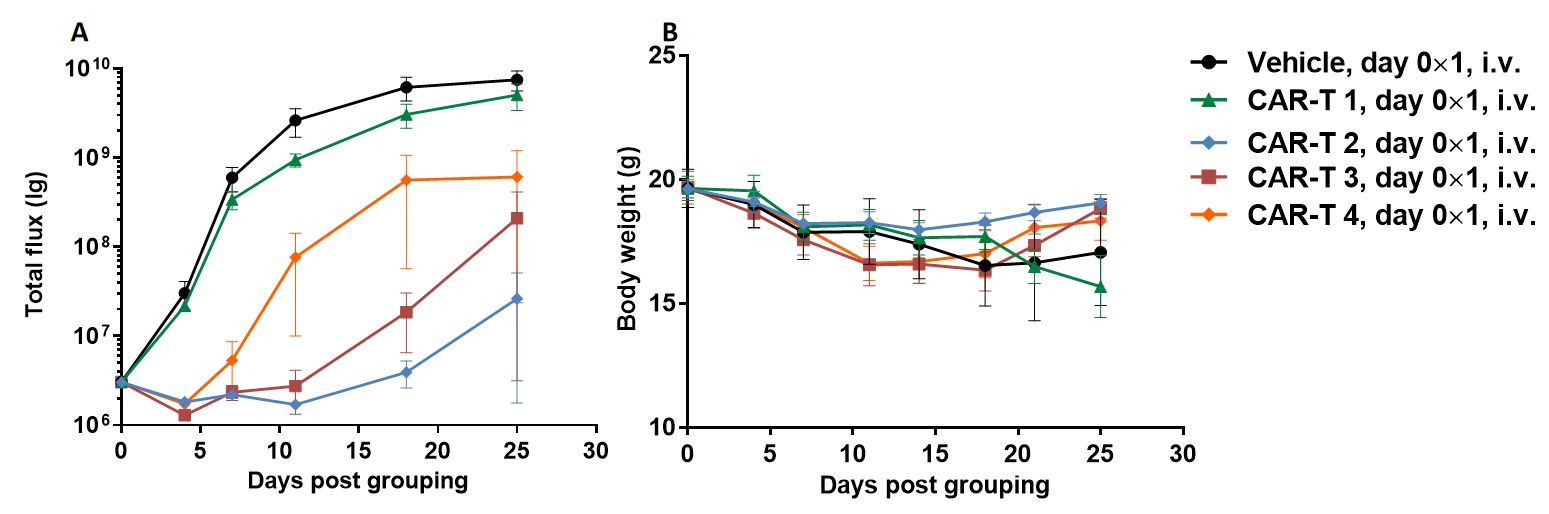
A Raji lymphoma mouse model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human CD47 antibodies were verified. B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice. In vivo imaging systems (IVIS) was used to observe tumor growth. When the fluorescence intensity of the tumor reaches about 1×106 p/sec, the animals were divided into one control group and three treatment group (n=6). (A) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells; (B) Body weight. The results showed that all three anti-human CD47 antibodies could significantly inhibit tumor growth. B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Severe xenogeneic graft versus host disease (xeno-GVHD) would shorten treatment window and hamper efficacy evaluation of transplanted cell therapy. β2 microglobulin (B2M) is a small protein as a component of MHC class I molecules, which are present on all nucleated cells, and that are involved in self-recognition and in defense against micro-organisms. So knockout MHC class I β2-microglobulin (β2m) is an effective way to decrease GVHD.
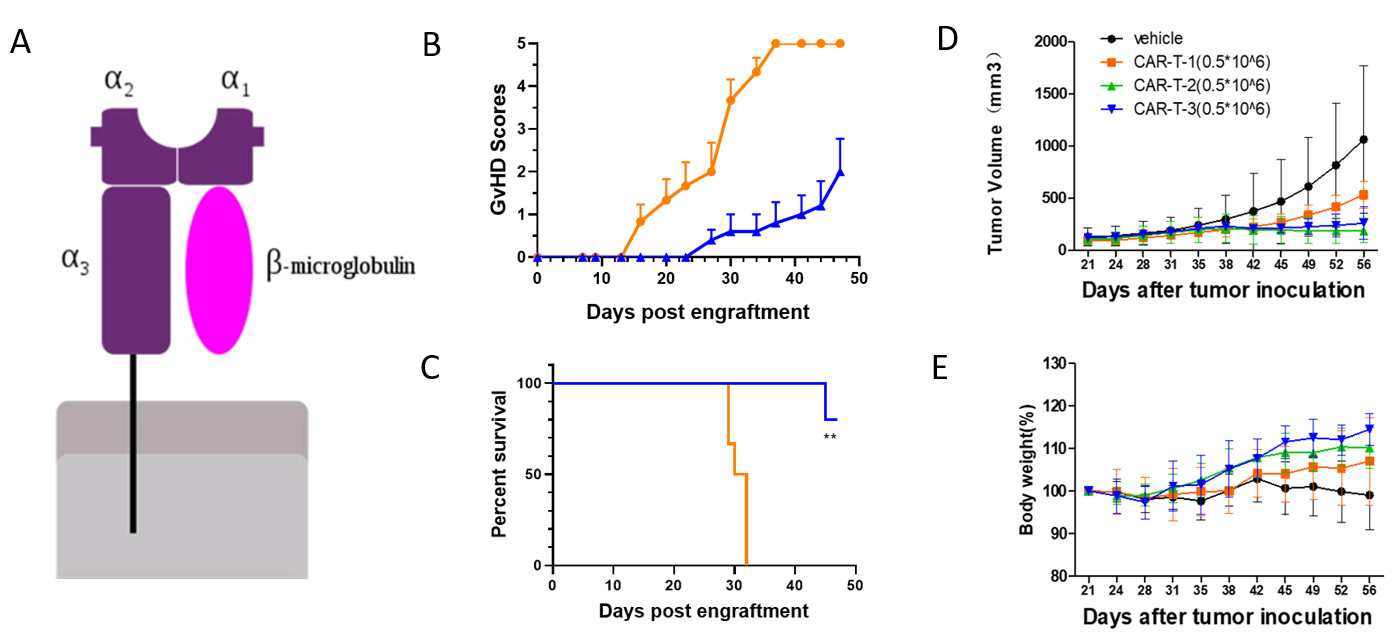
(A) B2M is involved in the composition of MHCI molecules; (B-C) B-NDG B2m KO plus mice (blue line) showed decreased GVHD scores and prolonged survival compared to WT B-NDG mice(orange line) after implanted PBMCs; (D-E) CAR-T in vivo efficacy study in B-NDG B2m KO plus mice, tumor volume(D) and body weight(E).
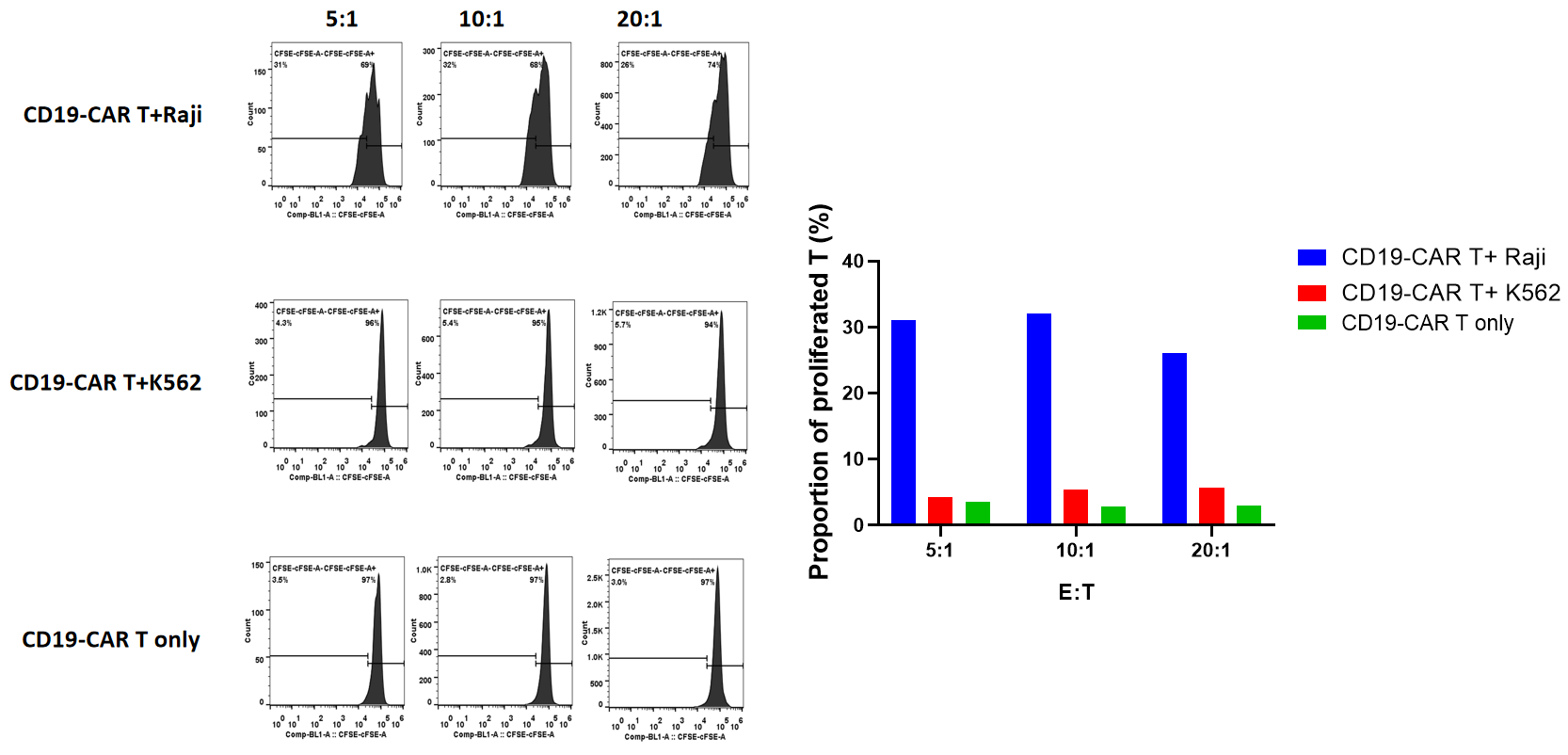
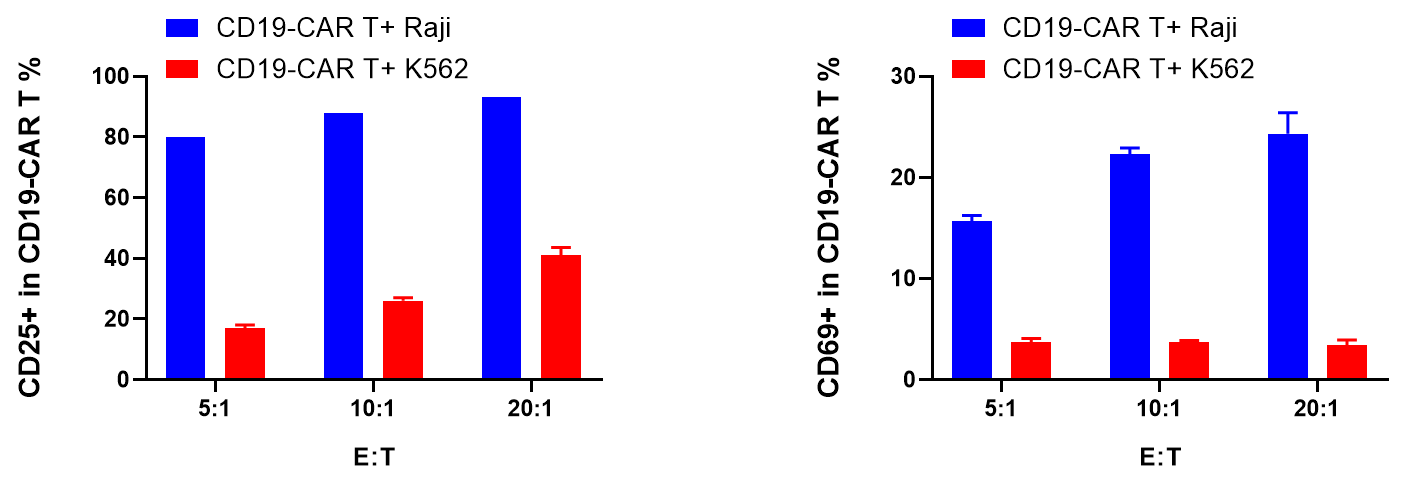
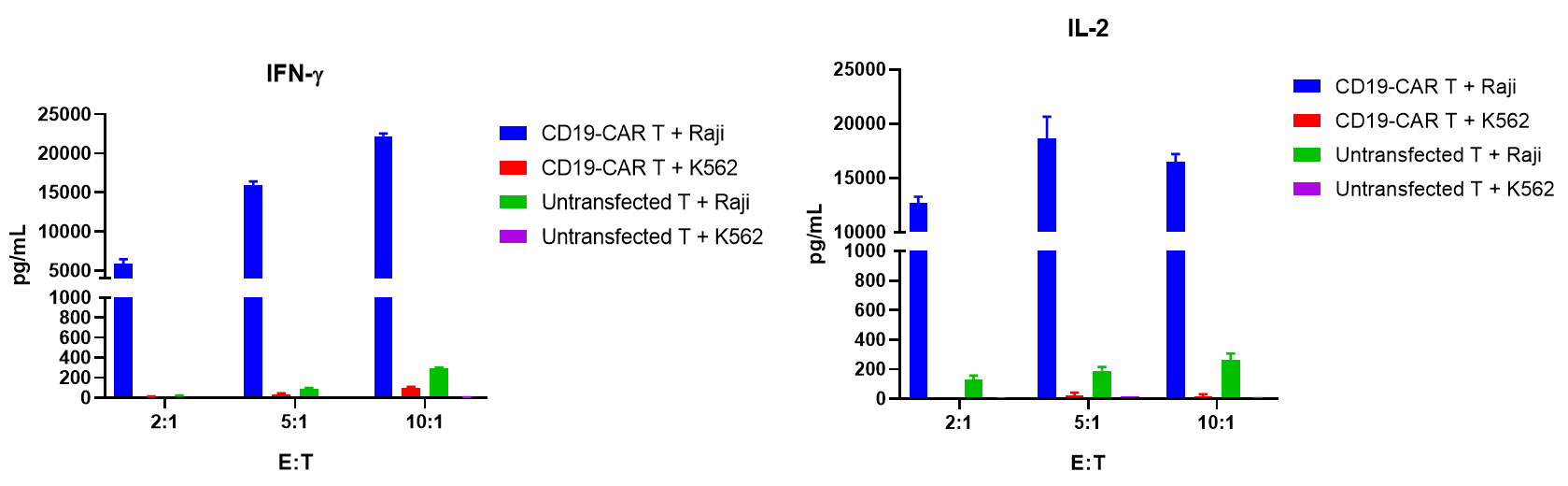
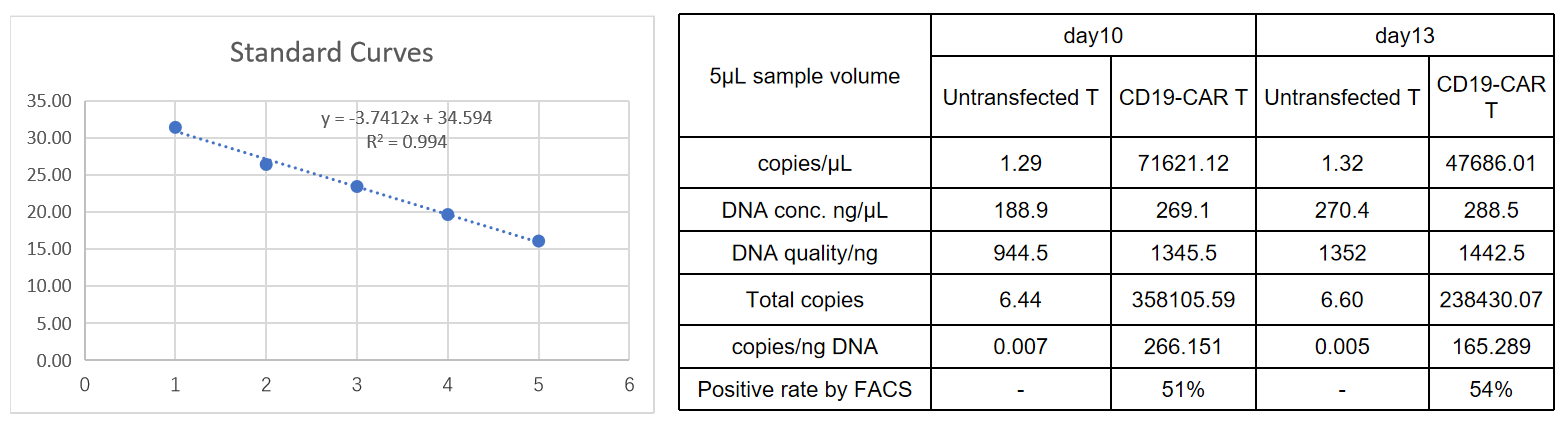
The y-axis represents the Ct value, the x-axis represents the logarithm (base 10) of the concentration of standard copies. The slope of the standard curve represents the efficiency of real-time PCR amplification. When the amplification efficiency is 100%, the slope is -3.32.