

Biocytogen provides a series of EGFP-DTR-Luciferase mouse models that allow researchers to directly observe the dynamic changes and functions of specific cells or tissues expressing the EGFP-DTR-Luciferase gene in mice.
on this page
The cytotoxicity of the heterodimeric corynebacterium diphtheriae exotoxin diphtheria toxin(DTx) had previously been shown to strictly depend on receptor-mediated endocytosis by the heparin-binding EGFlike growth factor precursor (proHB-EGF, also referred to as the DTR).DTR binds the B subunit of DTx and promotes DTx endocytosis. Upon entry into the cytoplasm, the DTx A subunit catalyzes the inactivation of elongation factor 2,resulting in the termination of protein synthesis and leading to the apoptotic death of the target cell.DTx-mediated cell ablation is highly sensitive and efficient, as a single molecule of active DTx A in the cytoplasm is sufficient to kill a eukaryotic cell. Human cells are naturally sensitive to DTx, but murine cells harbor an HB-EGF polymorphism that impairs DTx binding and makes them insensitive to killing by the toxin. Conversely, transgenic expression of a primate proHB-EGF/DTR renders resistant mouse cells DTx sensitive, providing a system for a versatile toxin-induced cell ablation in vivo.The specificity and timing of cell ablation in DTR transgenic mice can be determined by cell type-restricted promoter/enhancer elements and by the regimen of the toxin administration, Immune cell depletion is a powerful method for determining the functional contributions of different immune system components. The technique is particularly useful for studying underlying mechanisms of cancer immunotherapies, since they often work through multiple mechanisms mediated by different immune cell subsets.
Biocytogen provides a series of DTR mouse models. The introduction of the reporter genes EGFP (Enhanced green fluorescent protein) and luciferase can significantly enhance the visualization and quantitative analysis capabilities of the experiment. With this strategy, researchers can directly observe the dynamic changes and functions of specific cells or tissues expressing the EGFP-DTR-Luciferase gene in mice. And with in vivo imaging techniques such as bioluminescence imaging, researchers can noninvasively monitor the expression and cellular activity of specific genes in live mice. This versatile integration makes the EGFP-DTR-Luciferase mouse model a powerful tool for understanding cellular function, disease mechanisms, and drug action mechanisms. These DTR strains have been playing an increasingly important role in studies requiring the targeted depletion of specific immune cell populations. These DTR models are particularly useful for depleting lineages that lack cell surface markers typically targeted by monoclonal antibodies and represent a very efficient and powerful immune cell depletion option, used to better understand and improve the response to immunotherapy.
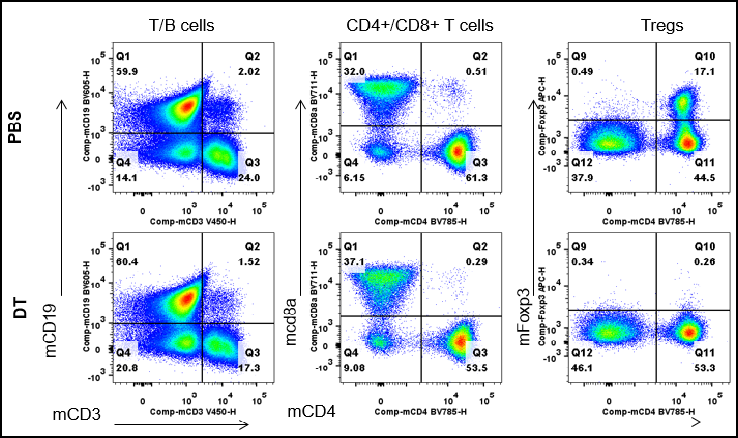
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from male B-Foxp3-EGFP-DTR-Luc mice (n=3, 7-month-old) injected with PBS or DT (30 ng per g body weight) for two consecutive days. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. After DT injection, Tregs were dramatically decreased in spleen.
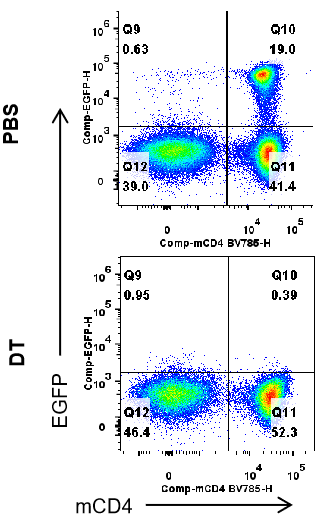
Analysis of EGFP expression in spleen of B-Fxop3-EGFP-DTR-Luc mice by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from B-Foxp3-EGFP-DTR-Luc mice mice(n=3, 7-month-old) injected with PBS or DT (30ng per g body weight) for two consecutive days. Flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess EGFP expression in T cells. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for CD3+;CD19- T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. After DT injection, EGFP signal was dramatically decreased in spleen.
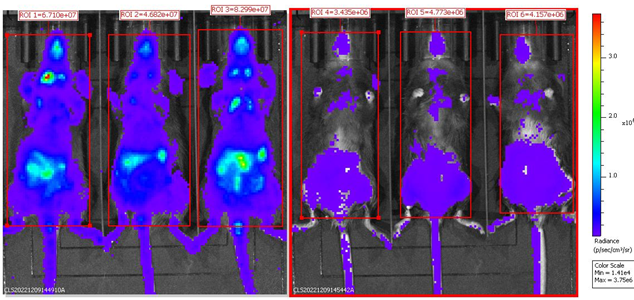
BLI analysis of homozygous B-Foxp3-EGFP-DTR-Luc mice after DT injection. Homozygous B-Foxp3-EGFP-DTR-Luc mice i.p. injected with PBS (n=3) or DT (n=3) for two consecutive days were anaesthetized for the bioluminescence imaging.Mice were imaged 10 min after i.p. injection of 150mg/kg D-Lucifenrin potassium salt using IVIS Lumina LT Inst Series III imaging system. Bioluminescence imaging could also be used for tracing Tregs cells
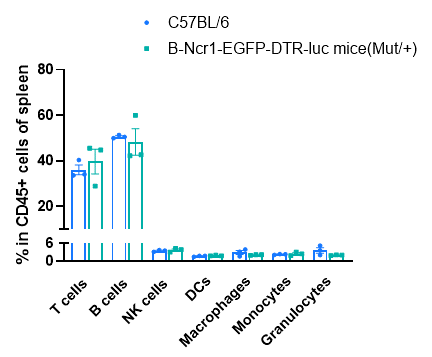
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from C57BL/6 and B-Ncr1-EGFP-DTR-luc mice (n=3, 9-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. Percentages of T cell, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages in heterozygous B-Ncr1-EGFP-DTR-luc mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice. The frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in blood and lymph node of B-Ncr1-EGFP-DTR-luc mice were also comparable to wild-type C57BL/6 mice (Data not shown). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
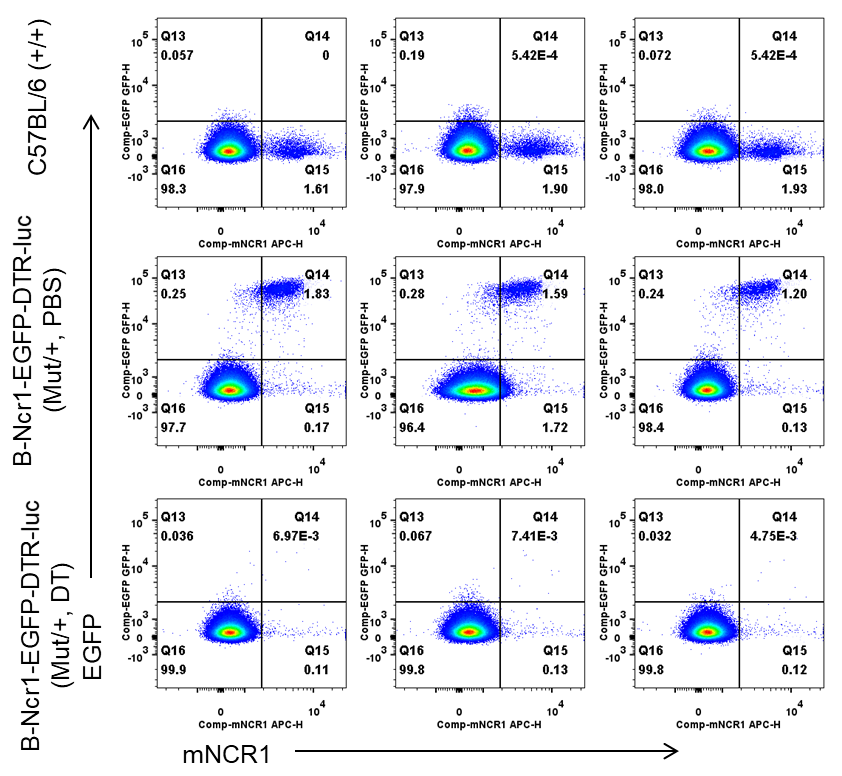
Frequency of EGFP+ cells in NK cells from spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and heterozygous B-Ncr1 EGFP-DTR-luciferase mice(Mut/+) (n=3, 8-9-week-old) injected with PBS or DT (50ng per g body weight) for four consecutive days. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of EGFP+ cells in NK cells. The frequency of EGFP in NK cells was decreased in heterozygous mice after DT injection.
| Product Name | Product No. | Background | Action |
| B-Cd8a-EGFP-DTR-luciferase mice | 112814 | C57BL/6JNifdc | |
| MORE >> | |||