

Biocytogen has established stable rheumatoid arthritis (RA) mouse models in various strains, including C57BL/6, DBA, and BALB/c, ideal for preclinical drug efficacy studies.
We have developed a series of target-humanized mouse models for pharmacodynamic evaluation and research in autoimmune and inflammatory disease studies, supporting RA therapeutic development.
on this page
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases, characterized by joint swelling, pain, and impaired mobility. In severe cases, RA can lead to disability, with pathological features such as synovial hyperplasia, cartilage damage, and bone erosion.
Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA):
Induced by immunization with type II collagen (CII), the primary component of articular cartilage. CIA mice develop autoimmune polyarthritis that mimics the clinical and histological features of human RA.
Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis (CAIA):
Triggered by injection of anti-collagen antibodies. This model has a rapid disease onset and is widely used for studying acute arthritis progression.
Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis (AIA):
Also known as Freund's adjuvant arthritis, reflects many of the clinical features of human RA and is divided into complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) and incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA), with CFA being the most studied autoimmune model of rheumatoid arthritis.
To support the development of RA therapeutics, Biocytogen has established various stable and reliable RA mouse models across multiple strains (C57BL/6, DBA, and BALB/c). These models are suitable for evaluating the preclinical efficacy of drug candidates.
| Readout | ||
| Included tests | Phenotype | Body weight |
| Clinical score | ||
| Histopathology | H&E(Paws) | |
| Optional tests | Tissue homogenate | Cytokines test |
| Peripheral blood flow cytometry | Flow cytometry assay | |
| Mice strains |
| B-hIL6/hIL6R |
| B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 |
| B-hOX40hOX40L |
| B-hCD40 |
| B-hPD1 |
| Clinical score | Symptoms of CIA |
| Score 0 | Normal |
| Score 1 | Redness and swelling of one joint type (A, B, C) |
| Score 2 | Redness and swelling of both joint types (A, B, C) |
| Score 3 | Redness and swelling of the three joint types (A, B, C) |
| Score 4 | The whole paw is red and swollen to the maximum extent |
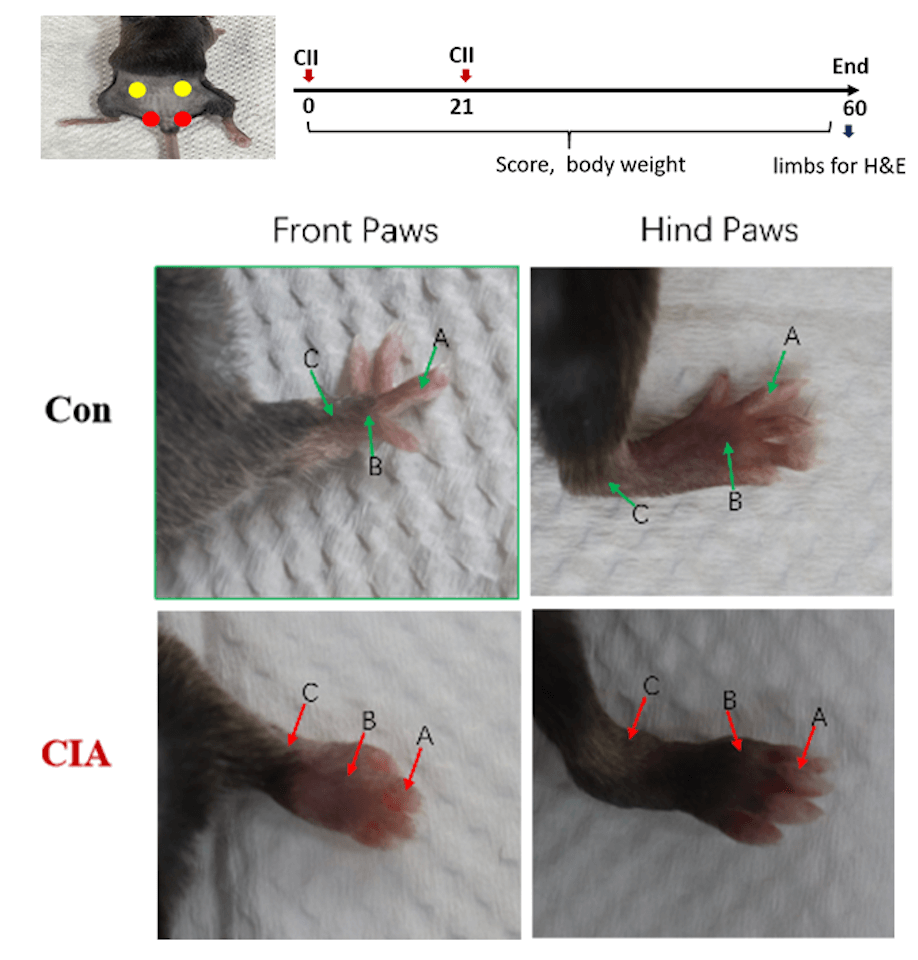
| Joint types: A: interphalangeal joint B: metacarpophalangeal joint C: wrist and tarsal joint | |
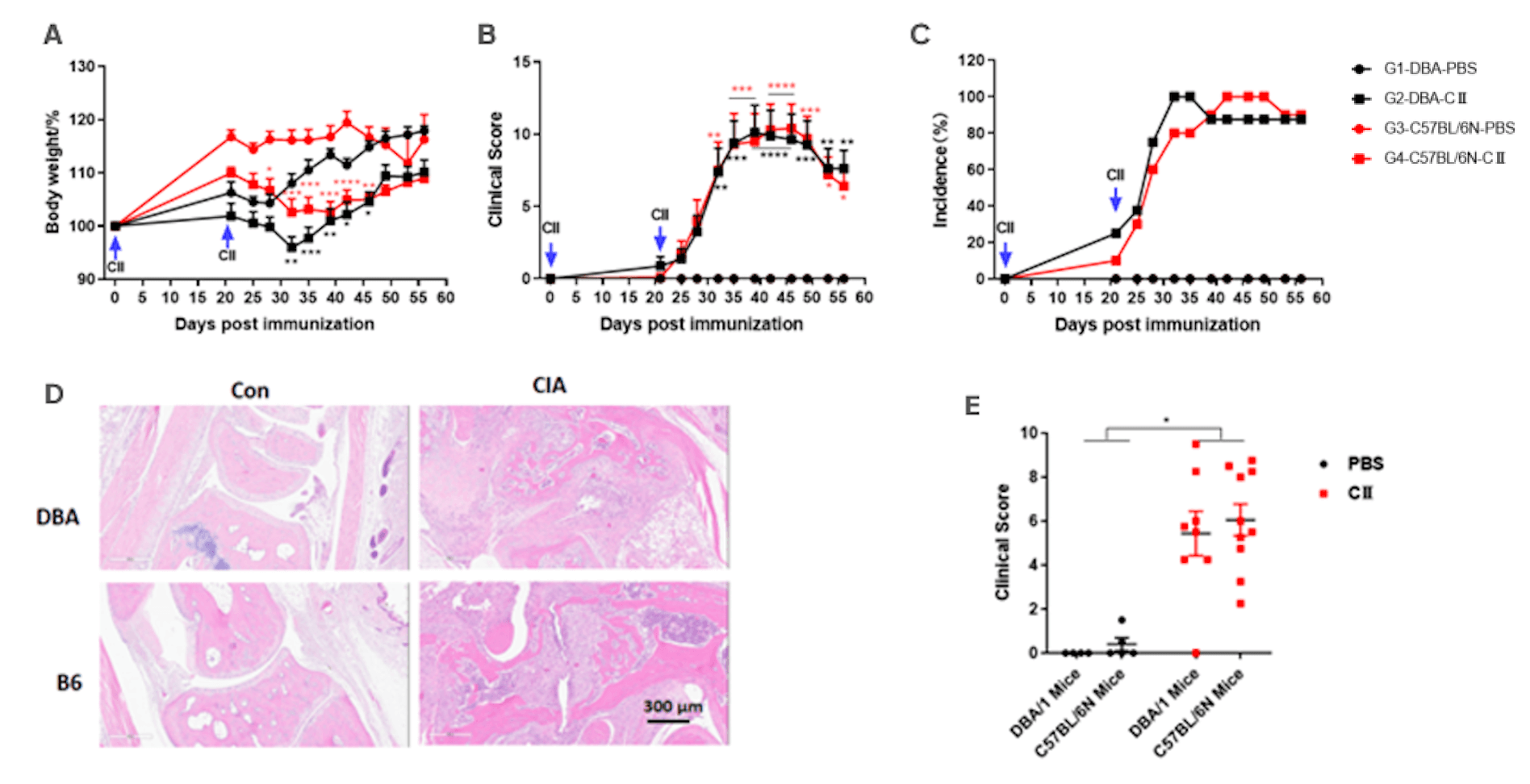
Collagen induced arthritis. DBA/1 mice or C57BL/6 mice received CⅡ emulsion on day 0 (200 μg) and day 21 (200 μg). Body weight (A) and clinical score (B) were recorded twice a week after the second immunization, the incidence (C) of arthritis were calculated. At the endpoint, bone tissue were collected for H&E staining (D, E). Mean ± SEM, n=4-10. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).
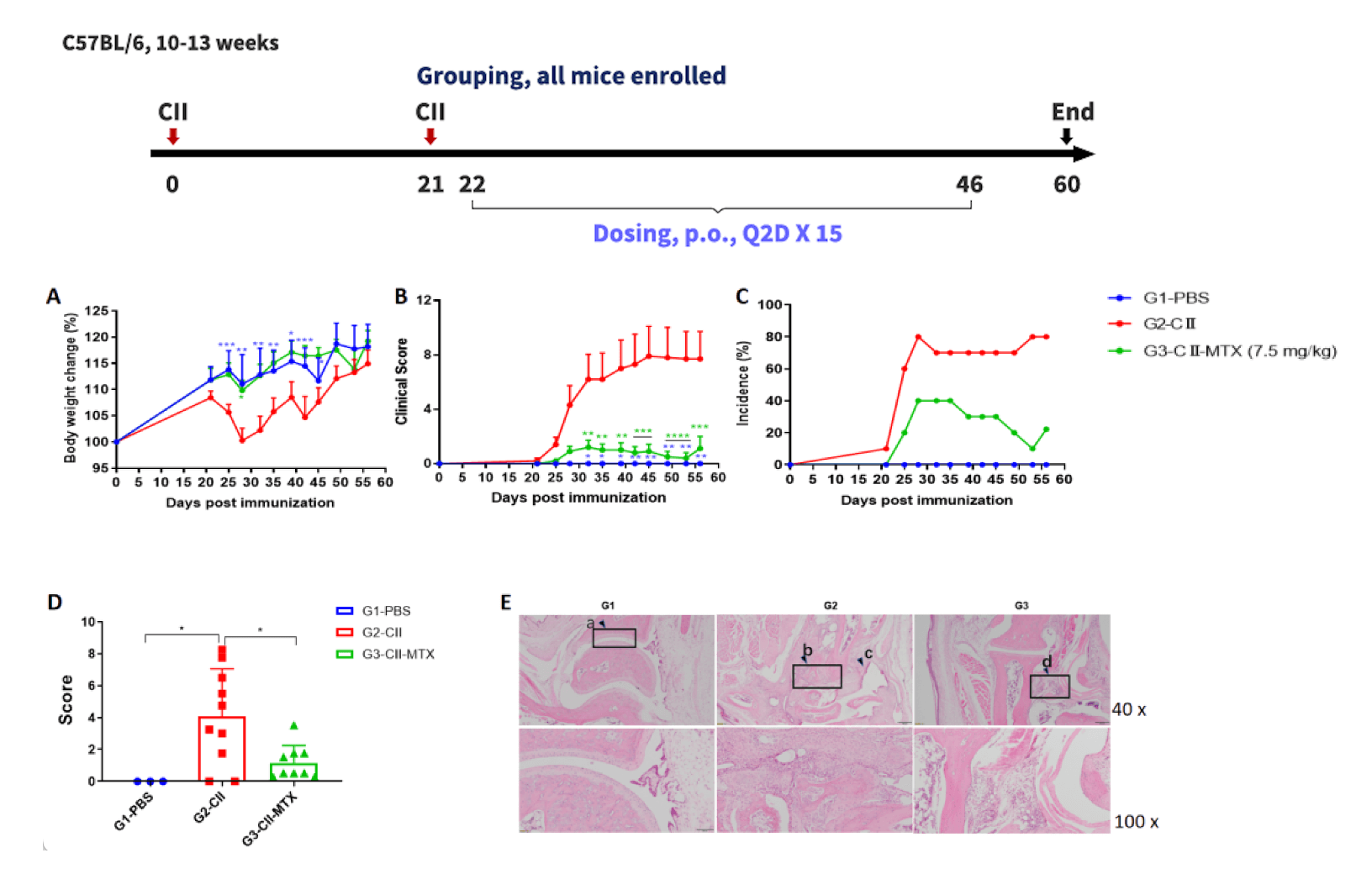
Effects of methotrexate on CIA mouse model.
(A) mouse body weight change; (B) clinical score; (3) mouse morbidity. (D) pathological score; (E) H&E staining of pathological sections. Mean ± SEM (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).
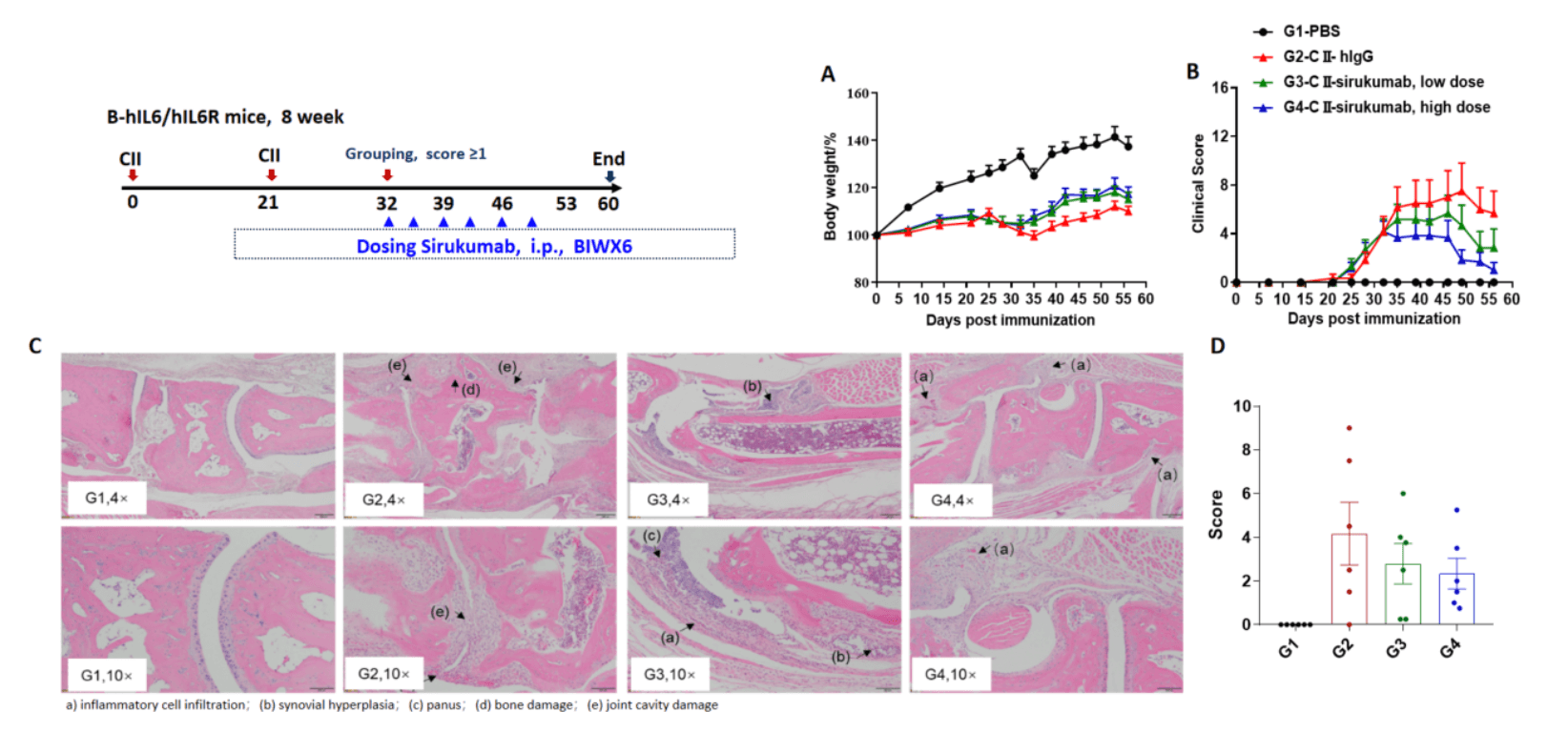
Effects of anti-human IL-6 antibody sirukumab in CIA mouse model. (A) mouse body weight change; (B) clinical score. The results showed that after the model was successfully established, mice in the treatment group (G3, G4) treated with sirukumab antibody showed improved clinical scores in a dose-dependent manner. Histopathological examination was performed on the joints of the extremities at endpoint. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. (D) Score of arthritis histology. Mean ± SEM
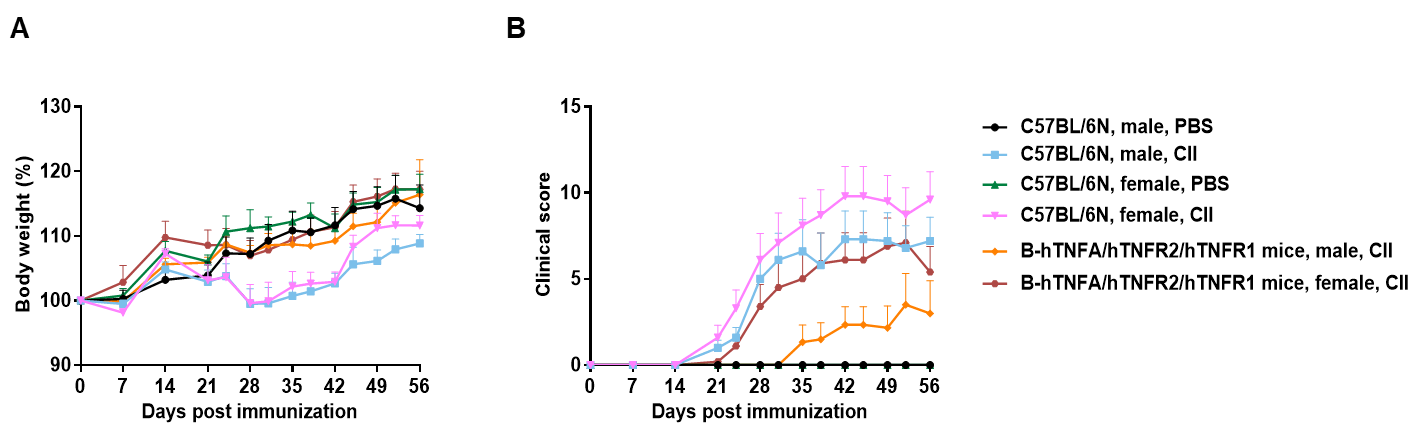
The arthritis model was induced in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice and C57BL/6 mice using collagen (CII).
(A) mouse body weight change; (B) clinical score. The results showed that the clinical score of B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice was significantly increased, suggesting that the arthritis model was successfully established. Mean ± SEM.
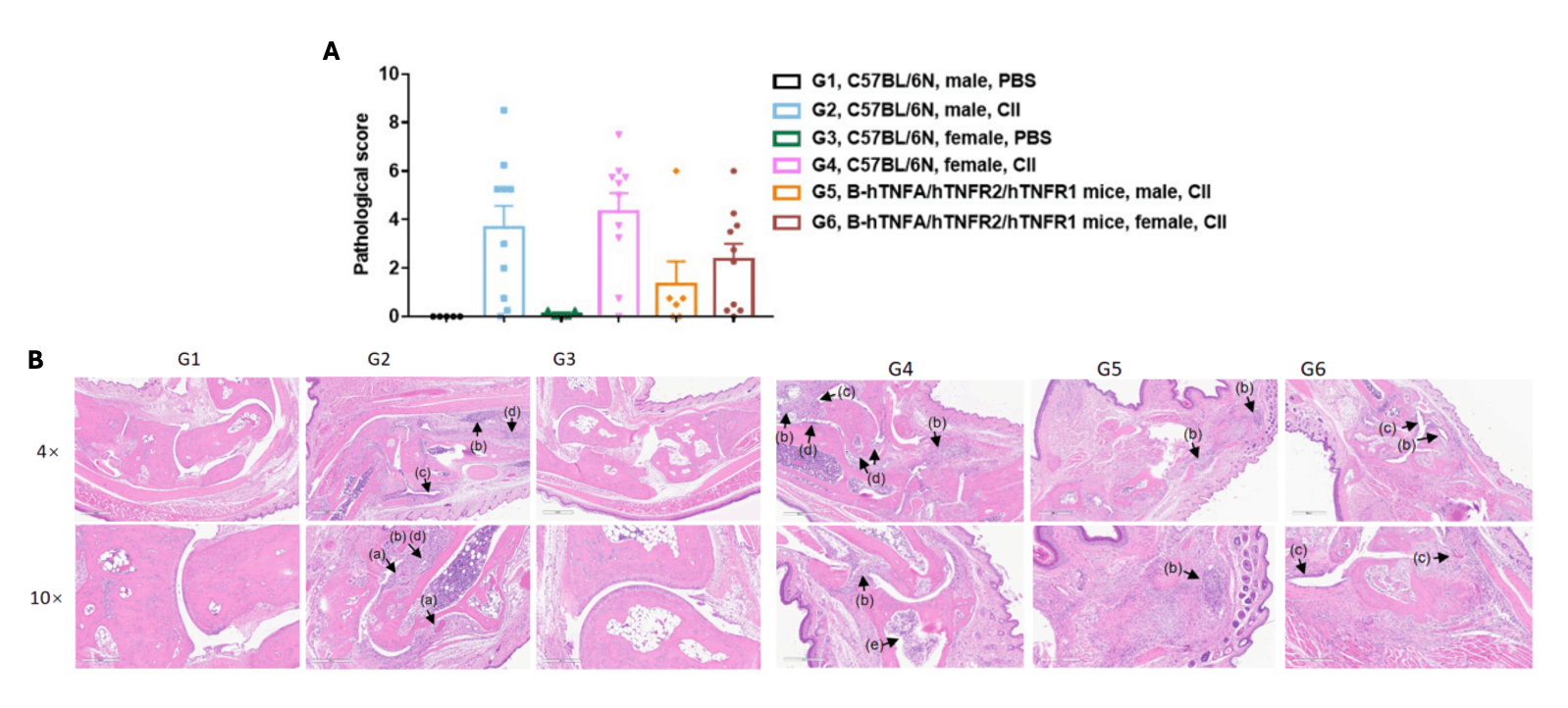
Pathological analysis after the establishment of arthritis in B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice and C57BL/6 mice.
(A) Pathological score; (B) H&E staining of pathological sections, (a)pannus; (b)inflammatory cell infiltration (c)synovial hyperplasia; (d)bone structure damage; (e) inflammatory cell in bone marrow. In the model group, subcutaneous mixed inflammatory cell infiltration, periarticular stenosis, articular cartilage and bone tissue destruction and other arthritic lesions were observed in all or part of the limb joints, suggesting that the arthritis model was successfully established. Mean ± SEM.
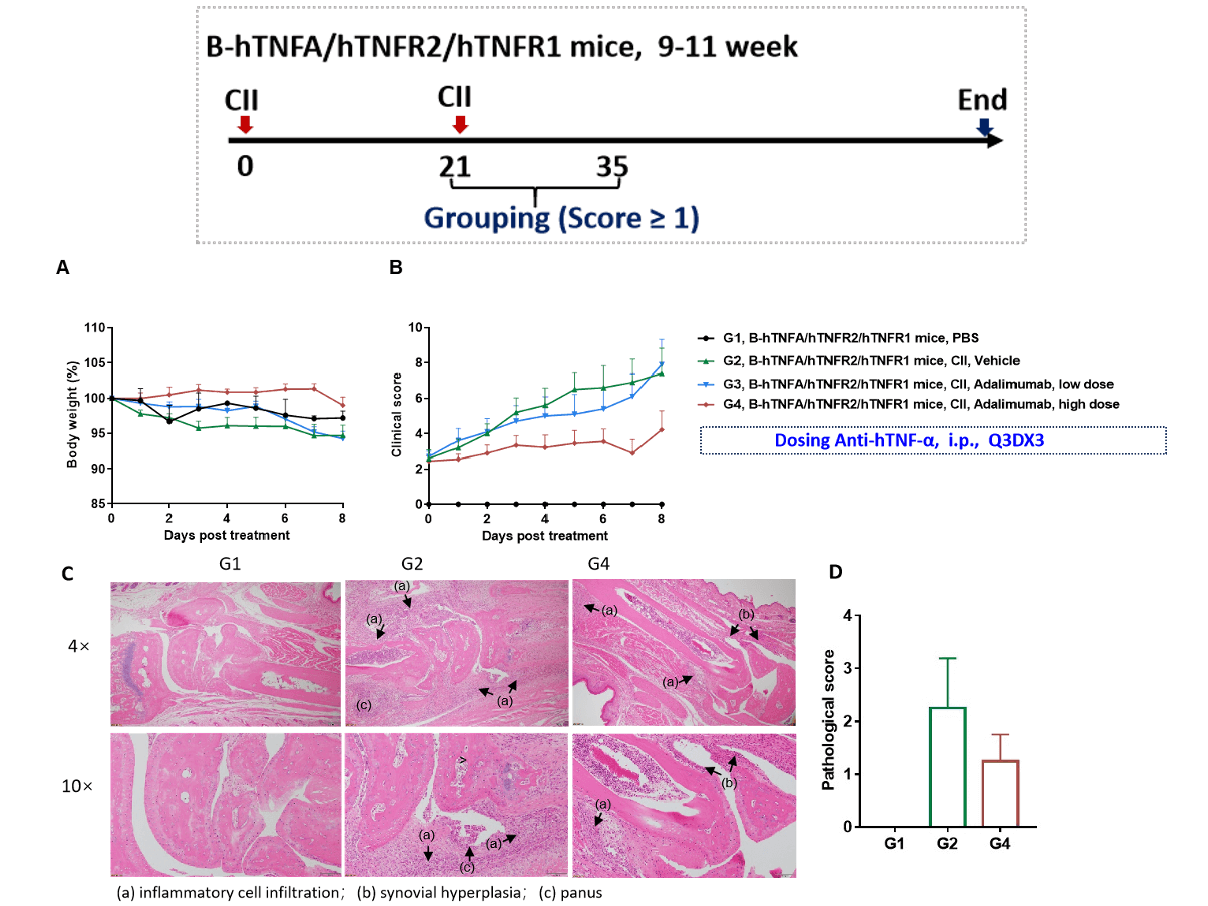
Effects of anti-human TNF-α antibody Adalimumab in CIA mouse model. (A)mouse body weight change; (B) clinical score. High dose of adalimumab treated animal in G4 had reduced clinical score compared to G2. (C) Joints of the animals were collected at study endpoint and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and pathological score were shown (D). Mean ± SEM.
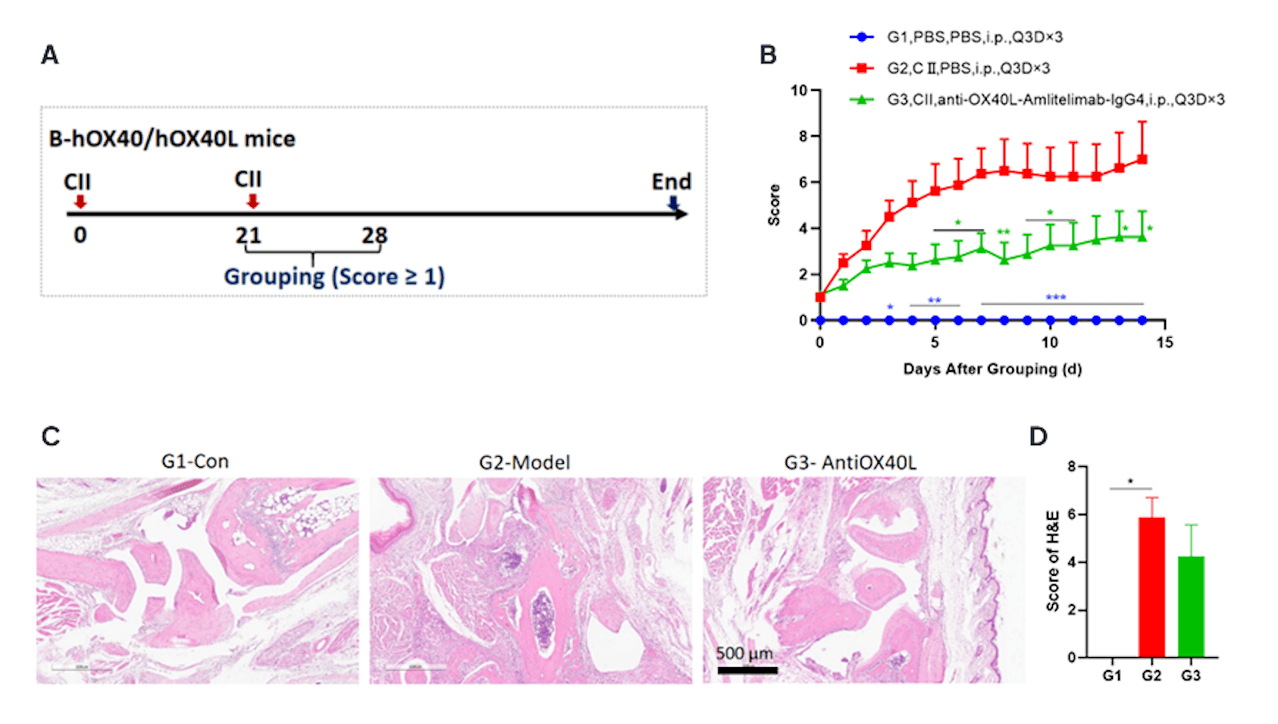
Effects of anti-human OX40L antibody Amlitelimab on CIA mouse model.
(A)Schematic diagram of experiment design;
(B)clinical scores. Amlitelimab treatment(G3) reduced clinical score in CIA models. Data was shown as Mean±SEM, and analyzed using Two way ANOVA followed Dunnett compared with G2. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).(C) Joints of the animals were collected at study endpoint and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and pathological score were shown (D). Data was shown as Mean±SEM, and analyzed using One way ANOVA followed Dunnett compared with G2. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).
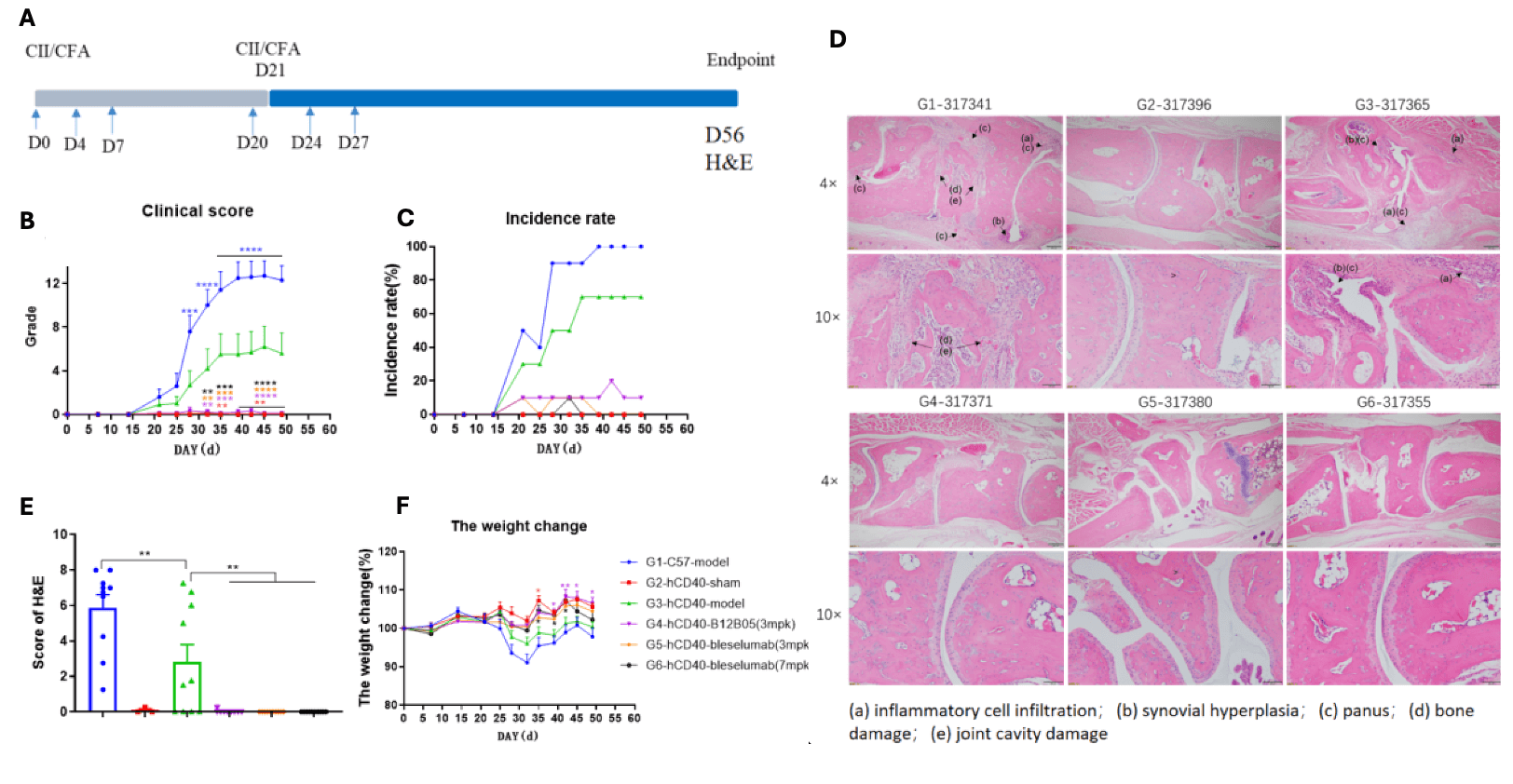
Effects of anti-human CD40 antibody in CIA mouse model.
(A)Schematic diagram of experiment design; (B) clinical scores. (C) Incidence rate (D) Joints of the animals were collected at study endpoint and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and pathological score were shown. Anti-CD40 treatment reduced incidence rate and clinical score in CIA animals (G4-G6). Data was shown as Mean±SEM, and analyzed using One way ANOVA followed Dunnett compared with G3. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001). (E) Score of arthritis histology. (F) Animals body weight change. Data was shown as Mean±SEM, and analyzed using One way ANOVA followed multiple comparison with G3. (*p<0.0...
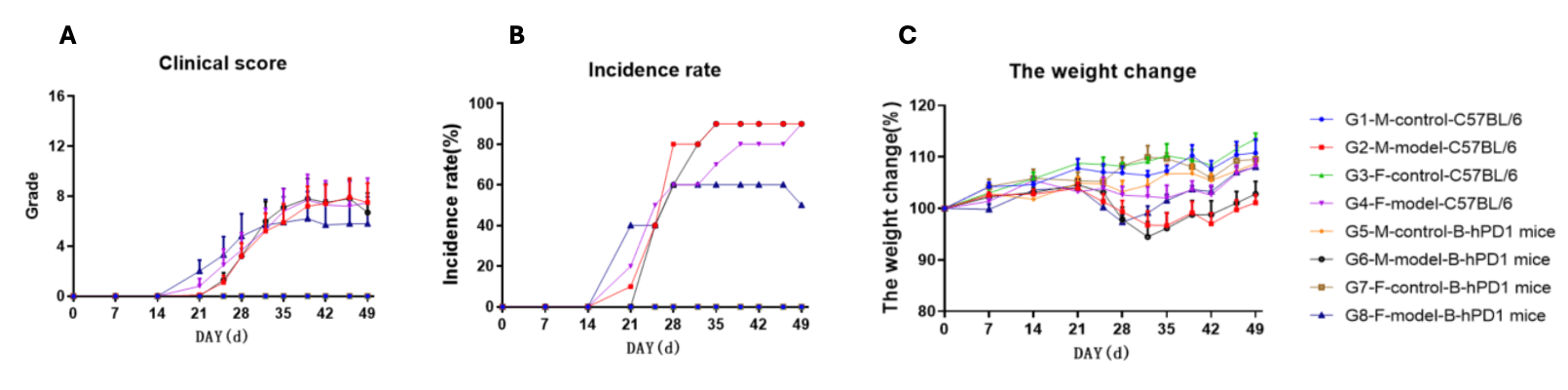
Collagen induced arthritis in B-hPD-1 mice. (A) clinical scores. (B) Incidence rate (C)Animals body weight change of B-hPD-1 mice after CIA modeling. Mean ± SEM.
| Mice | Gender | Incidence on Day28 | Incidence on Day32 |
| B-hIL6/hIL6R mice | M | 34% | 40% |
| B-hTLR8 mice | F | 60% | 50% |
| B-hCD40 mice | F | 50% | 50% |
| B-hOX40/OX40L mice | M | 20% | 60% |
| B-hPD1 mice | F | 60% | 60% |
| M | 60% | 80% | |
| B-hTNFA/hTNFR2/hTNFR1 mice | F | 48% | 55% |
| M | 80% | 80% |
| Readout | ||
| Included tests | Phenotype | Body weight |
| Clinical score | ||
| Histopathology | H&E(Paws) | |
| Optional tests | Tissue homogenate | Cytokines test |
| Peripheral blood flow cytometry | FACS test | |
| Mice strains |
| C57BL/6 |
| BALB/c |
| B-hTNFA |
| Clinical score | Symptoms of CIA |
| Score 0 | Normal |
| Score 1 | Redness and swelling of one joint type (A, B, C) |
| Score 2 | Redness and swelling of both joint types (A, B, C) |
| Score 3 | Redness and swelling of the three joint types (A, B, C) |
| Score 4 | The whole paw is red and swollen to the maximum extent |
| Joint types: A: interphalangeal joint B: metacarpophalangeal joint C: wrist and tarsal joint | |
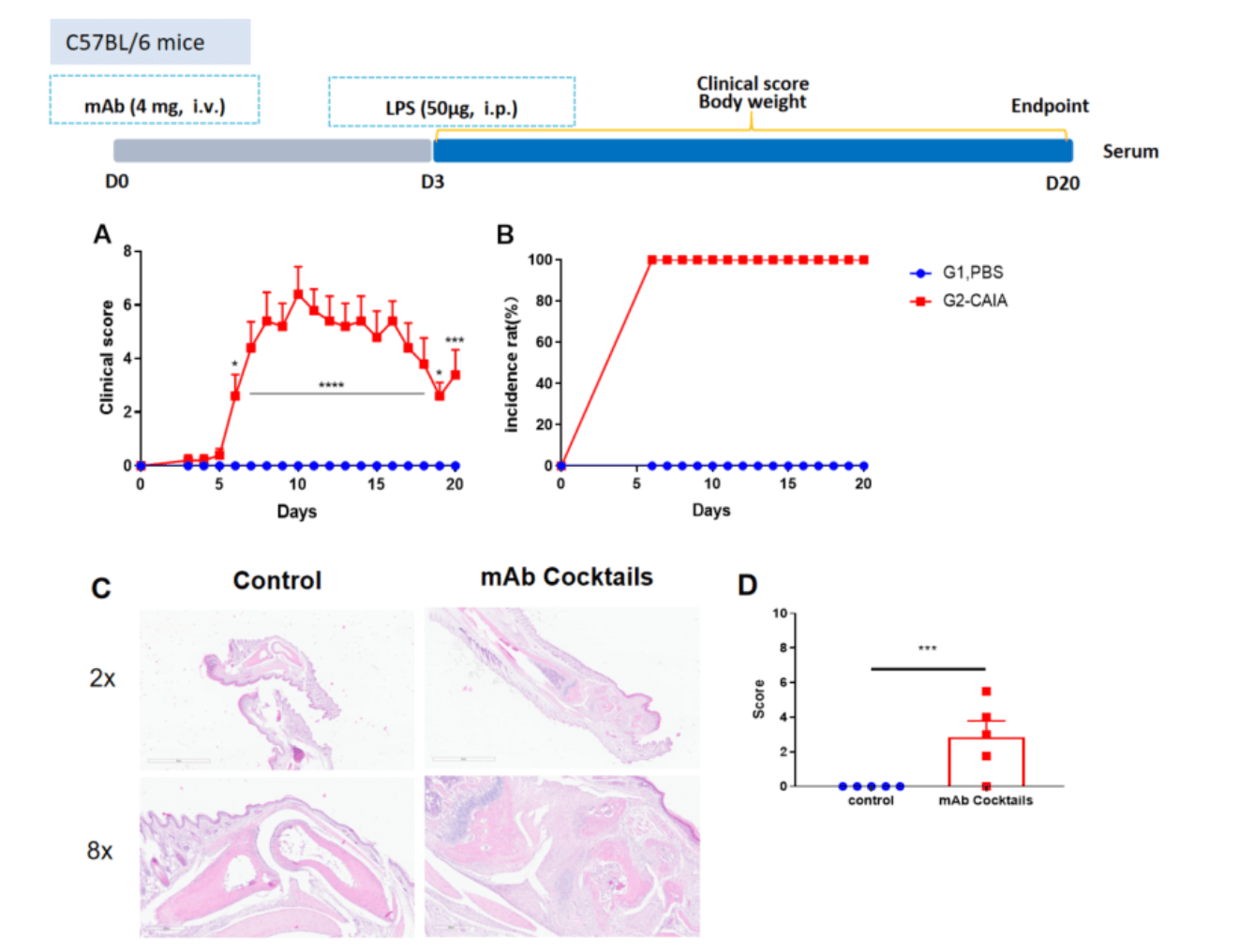
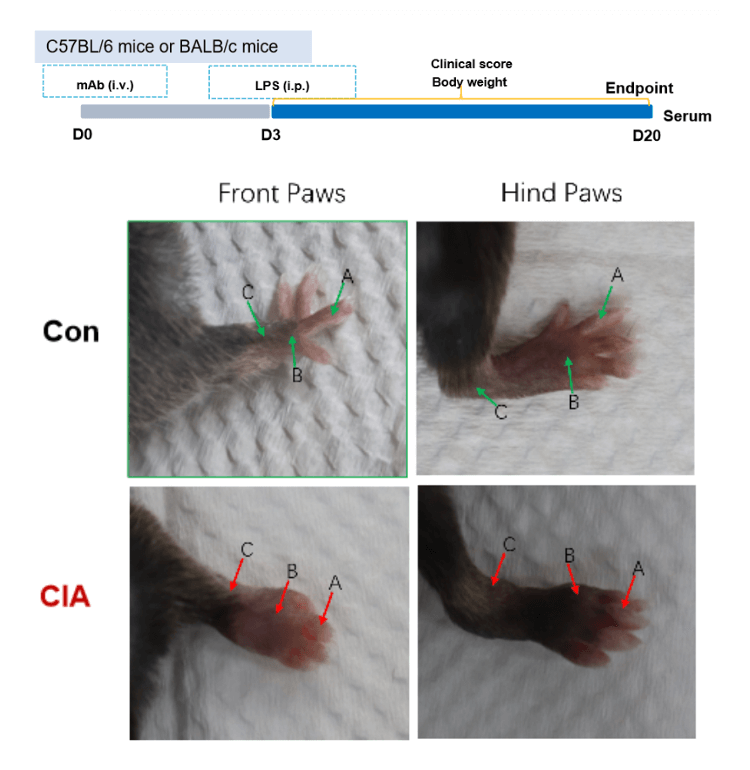
Collagen antibody induced arthritis. Clinical score (A) and incidence rates (B) of CAIA model in C57BL/6 mice. Two way-ANOVA followed by multiple comparison. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05. (C) Joints of the animals were collected at study endpoint and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and pathological score were shown (D).
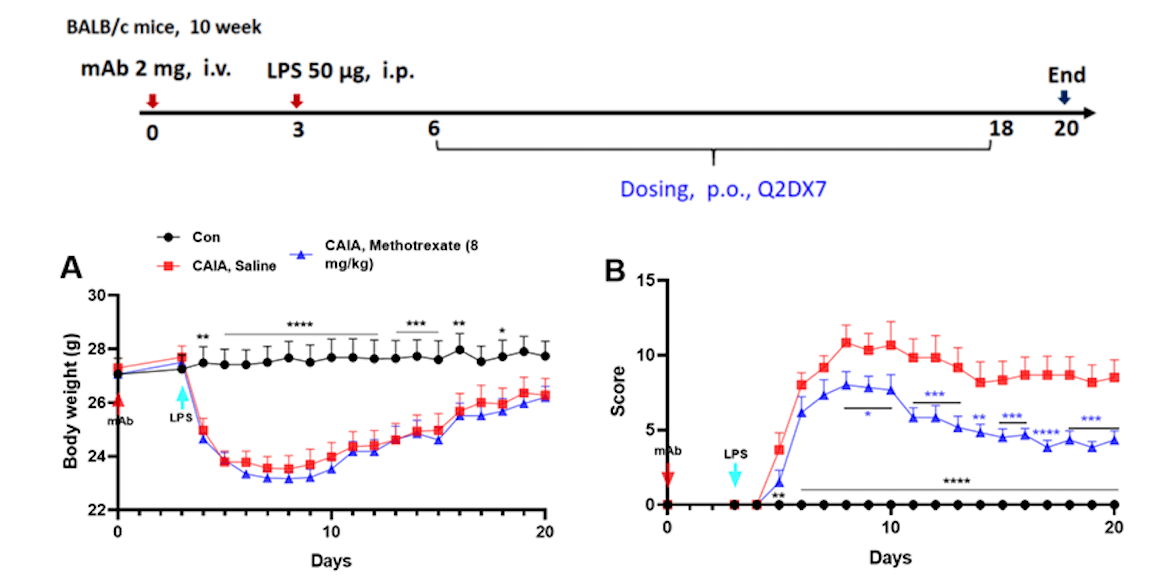
Effects of methotrexate on collagen antibody induced arthritis. Mice received mAb injection on day 0, LPS injection on day 3. Body weight (A) and clinical score (B) were recorded every day from day 3Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.
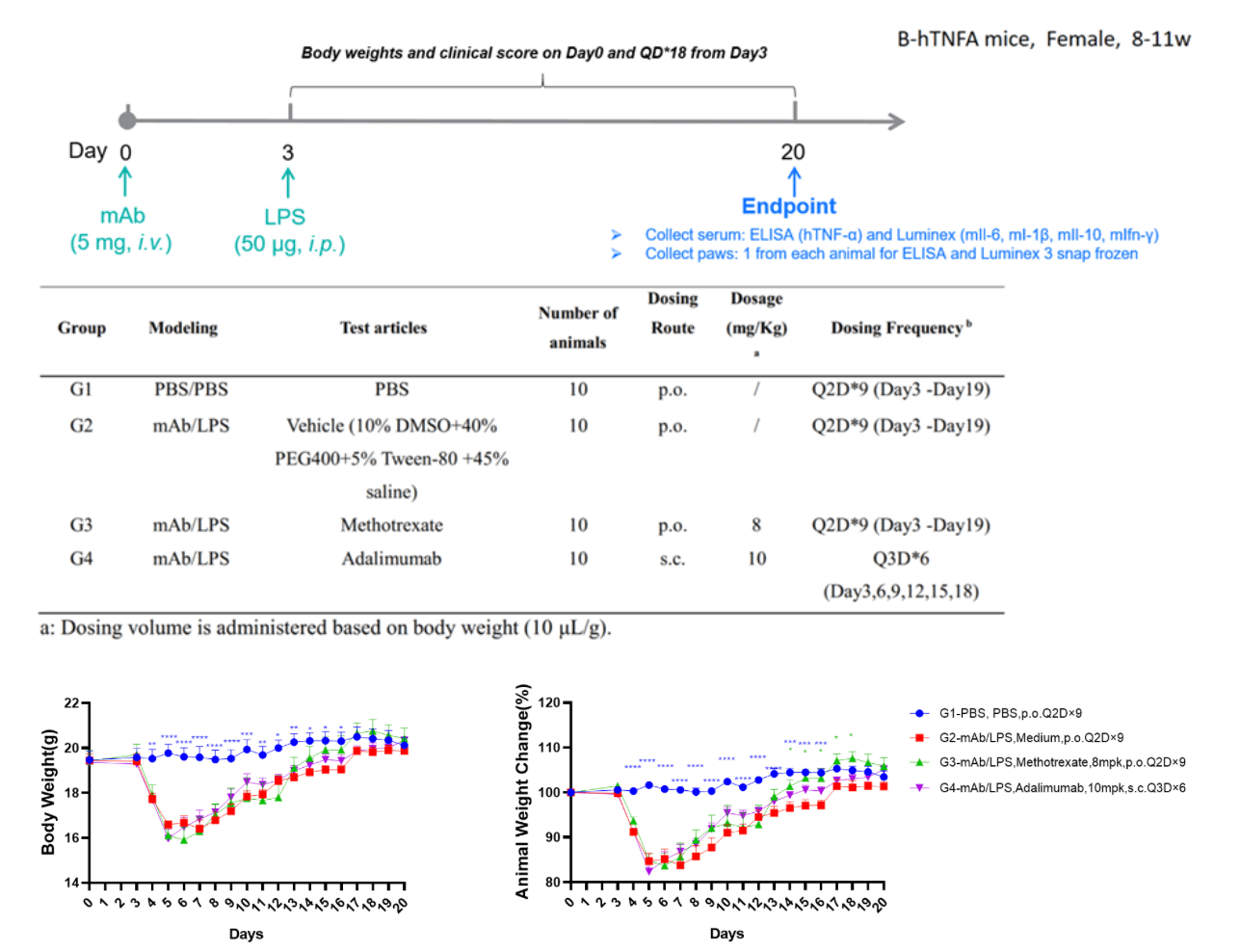
Fig1. Effects of test article on body weight changes of B-hTNFA mice in CAIA. Significant decrease in body weight post CAIA induction was observed in G2 modeled group compared with G1 non-modeled control group (A, B). Test articles, methotrexate (G3) and Adalimumab (G4) did not lead to significant drop in body weights compared modeled group G2. Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparison test, all groups compared with G2, Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.
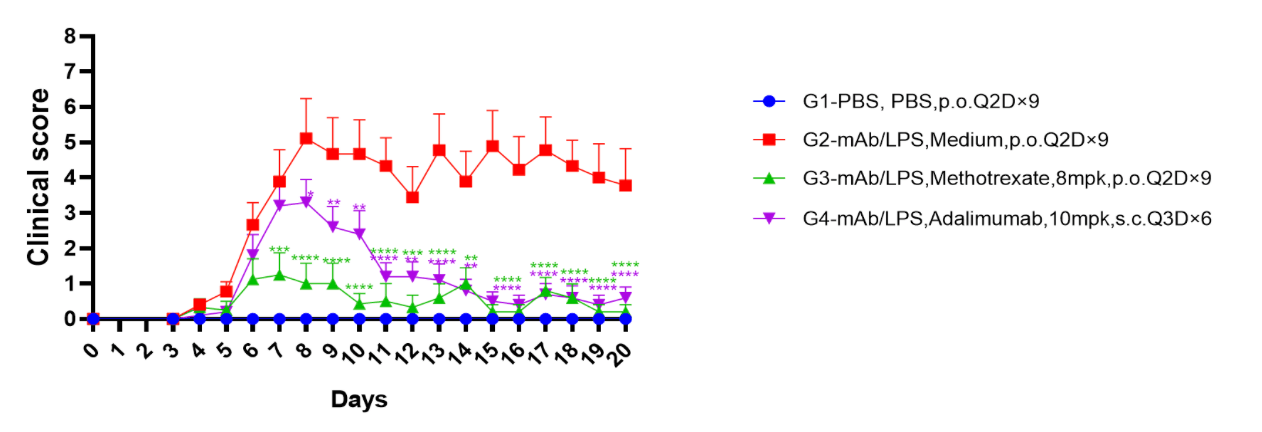
Fig2. Effects of test article on clinical scores of B-hTNFA mice in CAIA. Significant increase in clinical scores post CAIA induction was observed in G2 modeled group compared with G1 non-modeled control group. Both methotrexate (G3) and adalimumab (G4) treated groups showed decreased clinical scores compared to G2, indicating efficacy. Two way ANOVA with multiple comparison test, all groups compared with G2, Mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 (G1 significance not shown).
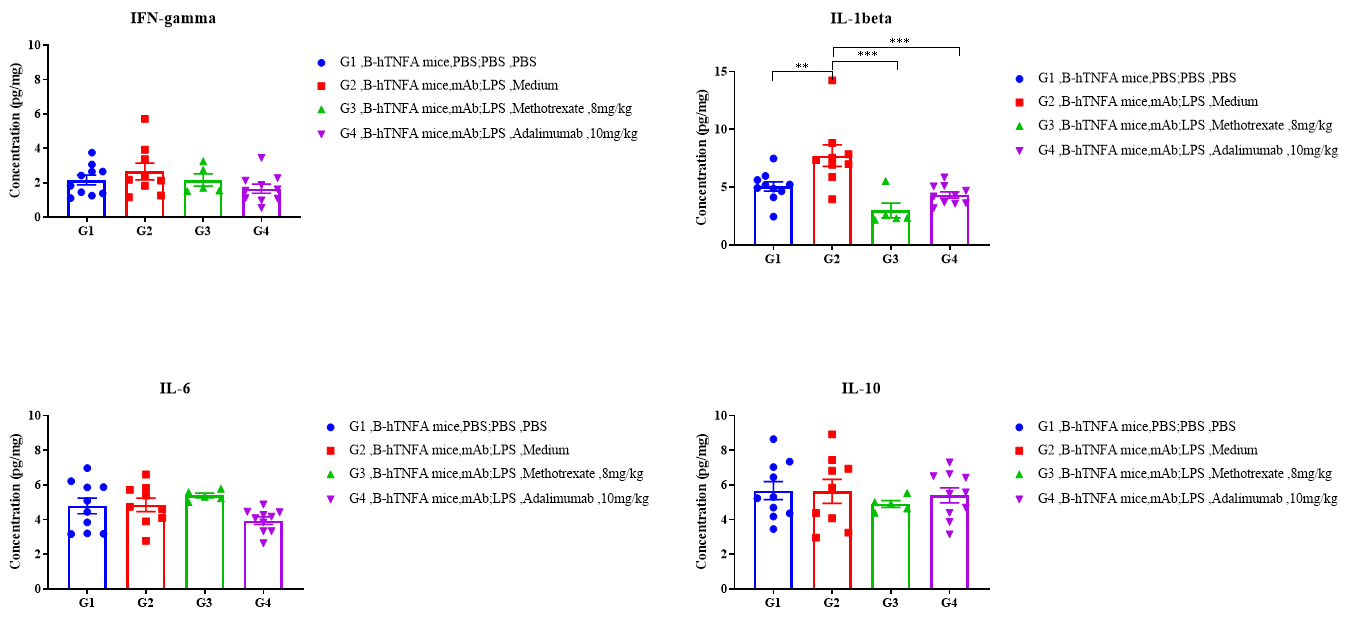
Fig3. Effects of test article on cytokine levels in left hindlimb tissue of B-hTNFA mice in CAIA. No significant differences in the expression level of IL-6, IL-10, IFN-gamma in mouse left hindlimb was observed between G2 modeled group compared with G2 non-modeled group, while significant increase in IL-1beta was found between G1 and G2, which was reversed in G3 and G4, test articles treated groups. Data was shown as Mean±SEM, and analyzed using One way ANOVA followed Dunnett compared with G2 . Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.

Adjuvant arthritis in the rat.
doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im1504s19
T cells against the pathogenic and protective epitopes of heat-shock protein 65 are cross-reactive and display functional similarity: novel aspect of regulation of autoimmune arthritis
| Readout | ||
| Included tests | Phenotype | Body weight |
| Clinical score | ||
| Histopathology | H&E(Paws) | |
| Optional tests | Tissue homogenate | Cytokines test |
| Peripheral blood flow cytometry | FACS test | |
| Mice strains |
| SD rat |
| Score | Symptom |
| Score 0 | No erythema or swelling |
| Score 1 | Slight erythema or swelling of one of the toes or fingers |
| Score 2 | Erythema and swelling of more than one toe or finger |
| Score 3 | Erythema and swelling of the ankle or wrist |
| Score 4 | Complete erythema and swelling of toes or fingers and ankle or wrist, and inability to bend the ankle or wrist |
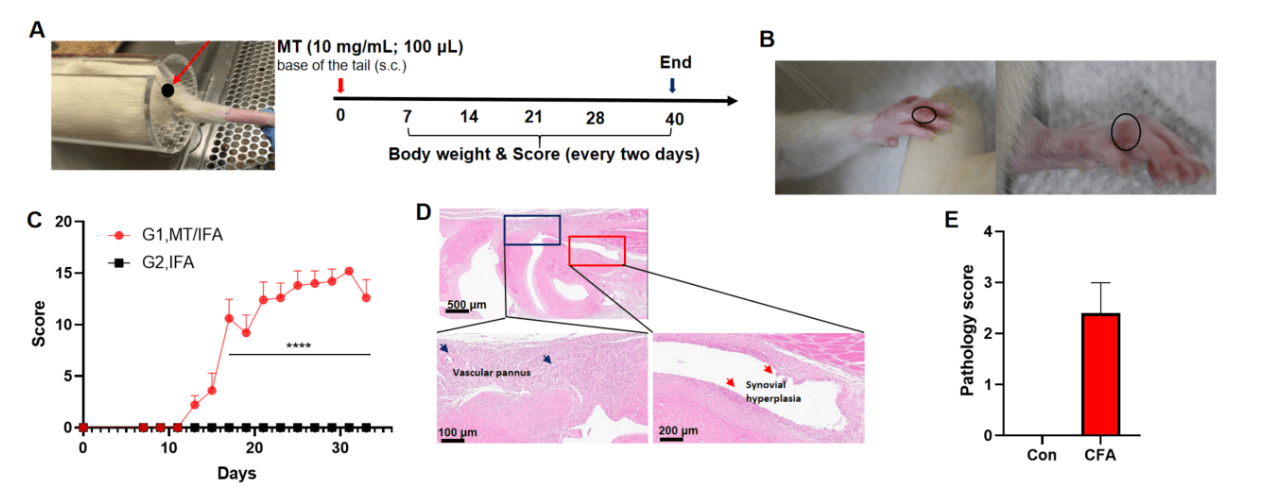
Adjuvant induced arthritis in rat. Rat (7 week, male) receive subcutaneous injection of MT/IFA (10 mg/mL; 100 μL) suspension on day 0 at the base of tail(G1, n=5; G2, n=3), body weight and score were recorded every two days from day 7 to the end (A). Adjuvant produced swelling and redness in paws of rat (B), all paws of AIA rat were scored (C). H&E staining showed that inflammation, vascular pannus, synovial hyperplasia were observed in AIA rat (D, E). Values were expressed as mean ± SEM, ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.0...