

on this page
Immunoglobulin Fc receptors (FcRs) are membrane-bound proteins expressed by various hematopoietic cells, which specifically recognize and bind to the Fc region of different immunoglobulin classes and subclasses. These include FcγRI/CD64, FcγRII/CD32, and FcγRIII/CD16 for IgG; FcεRI for IgE; FcαRI/CD89 for IgA; FcµR for IgM; and Fcα/µR for both IgA and IgM. Additionally, other receptors on different cell types interact with Ig molecules, such as the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) found on intestinal epithelial cells, placenta, and endothelium; the low-affinity FcεRII/CD23 on B cells and macrophages; and the polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR) on mucosal epithelial cells
The efficacy of antibodies is contingent upon their capacity to identify antigenic epitopes and their inherent flexibility, which enables them to engage with their respective Fc receptors. Activation of Fc receptors on leukocytes triggers a cascade of immune responses, including pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. However, evaluating the pharmacodynamic (PD) properties of therapeutic antibodies in preclinical models is challenging because Fcγ receptors differ between mice and humans, as well as their expression patterns.
Biocytogen has developed the FcR-humanized mouse models for the study of human FcRs' function in vivo. In these models, the corresponding endogenous mouse FcR genes have been deleted, and human FcR genes are expressed that accurately replicate the unique pattern of human FcR gene expression. Assessment of the in vivo activities of a range of cytotoxic or therapeutic antibodies through the use of FcR gene humanized mice has yielded significant insights into the effector functions of human immunoglobulin Fc regions. Biocytogen's provision of these models has established them as a vital preclinical resource for the evaluation of therapeutic human antibodies targeting malignancies, autoimmune disorders, inflammatory conditions, and infectious diseases.
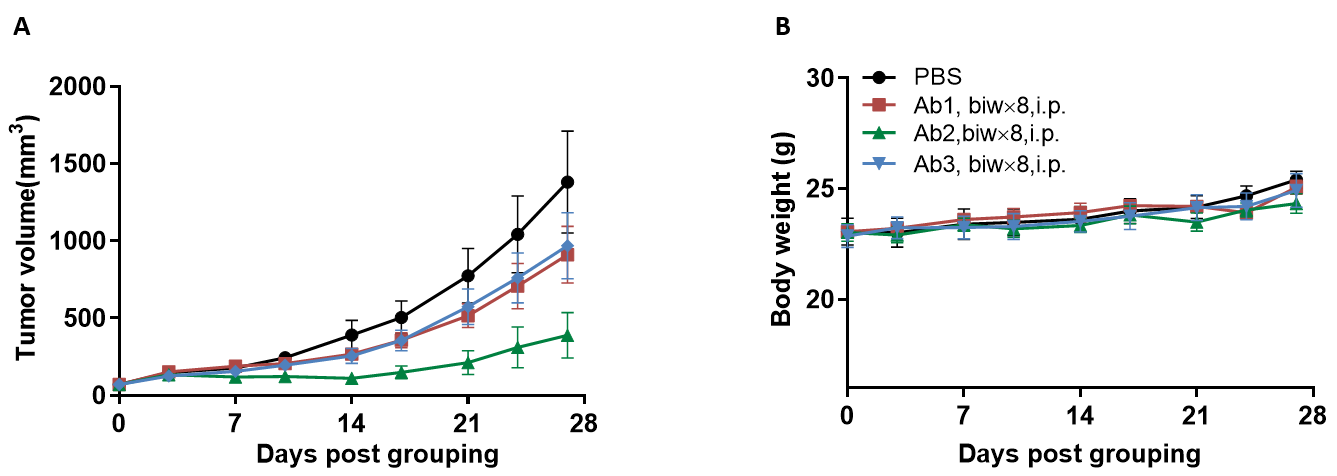
Antitumor activity of anti-human CD16A-based Ab in B-hCD16A mice.
(A) Anti-human CD16A-based Ab inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hCD16A mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hCD16A mice (female,13 week-old, n=7). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 70 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human CD16A-based Ab with doses and schedules indicated in panel B. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human CD16A-based Ab was efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hCD16A mice, demonstrating that the B-hCD16A mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human CD16A-based Ab. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
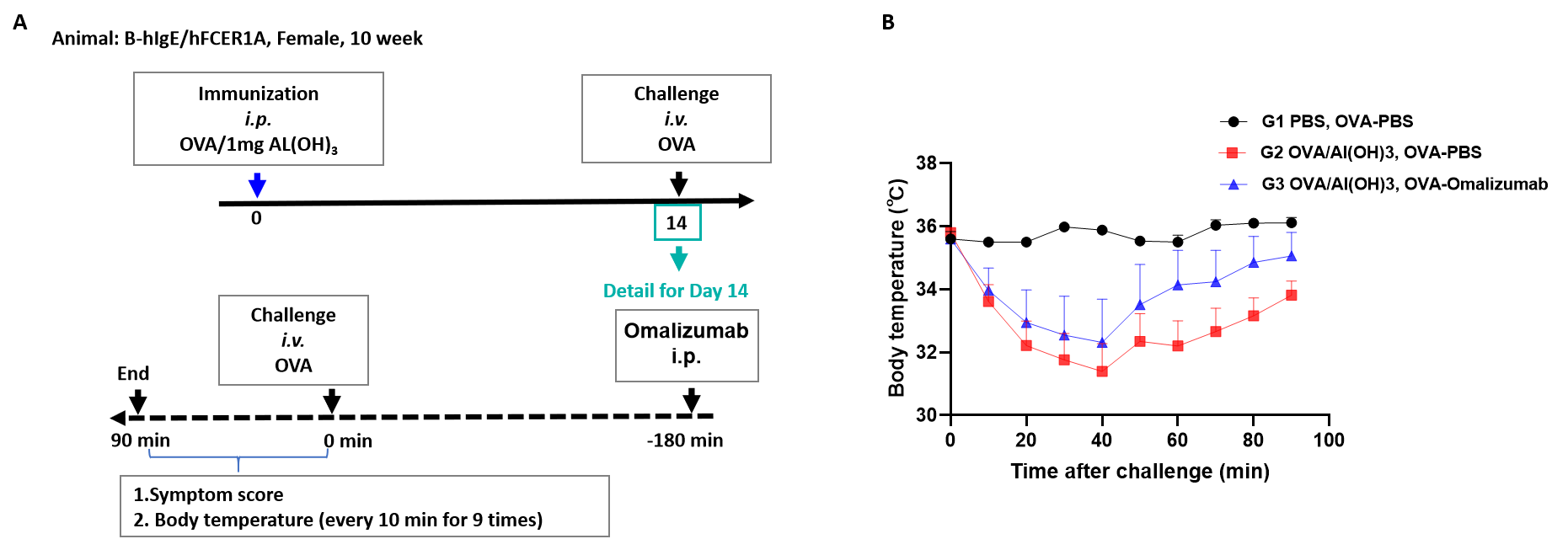
Effects of Omalizumab on OVA induced ASA. B-hIgE/hFCER1A mice (H/H; H/H) received OVA/Al(OH)3 immunization on day 0, and challenge with OVA on day 14. Omalizumab (in house) was injected 3 hour before challenge on day 14. (A) The body temperature of the mice was recorded from 0 to 90 minutes after the challenge. (B) An increasing trend was produced by Omalizumab (in house) in the ASA model. It can be seen that omalizumab (in house) has an inhibitory effect on the decrease in body temperature caused by ASA modeling in B-hIgE/hFCER1A mice (H/H; H/H).
| T1/2 (day) | CL (mL/day) | |||
| B-hFcRn | C57BL/6 | B-hFcRn | C57BL/6 | |
| Ab1 | 8.9 | 10.4 | 0.312 | 0.264 |
| Ab1-YTE | 12.7 | 4.1 | 0.072 | 0.36 |
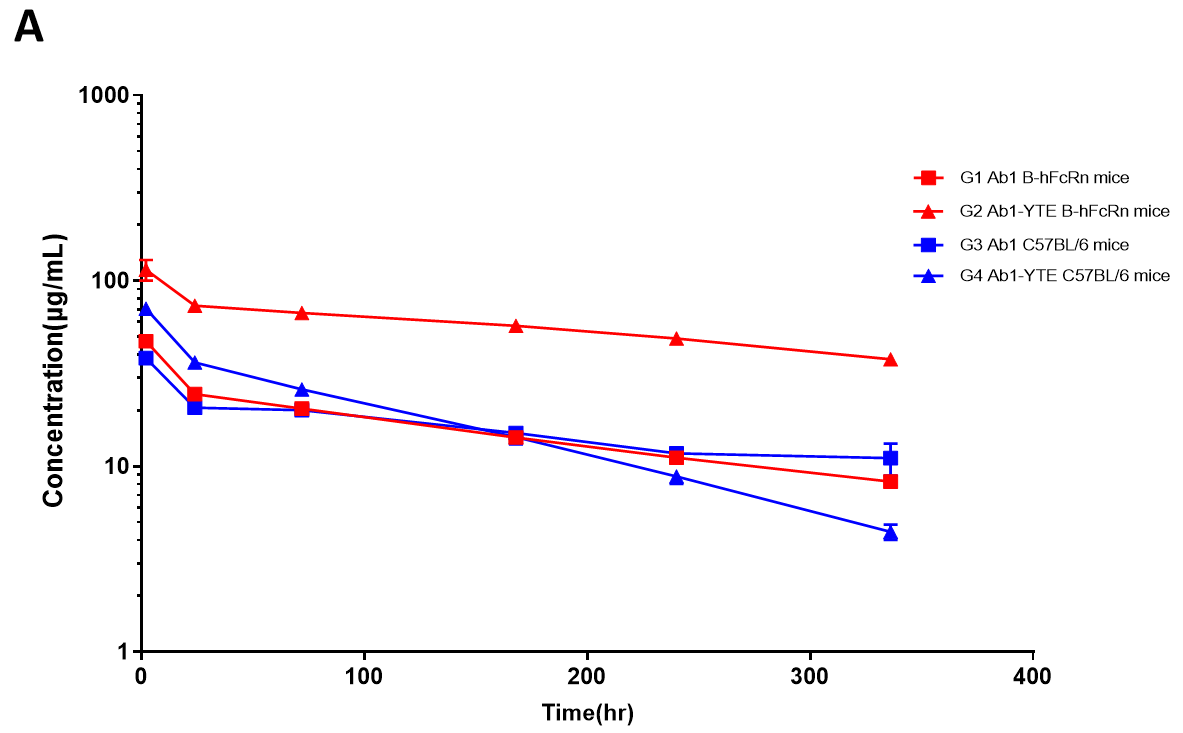
The serum pharmacokinetics profiles for Ab1 and Ab1-YTE are shown. The effect of YTE in prolonging the half-life of antibodies is only observed in B-hFcRn mice but not in wild-type mice.
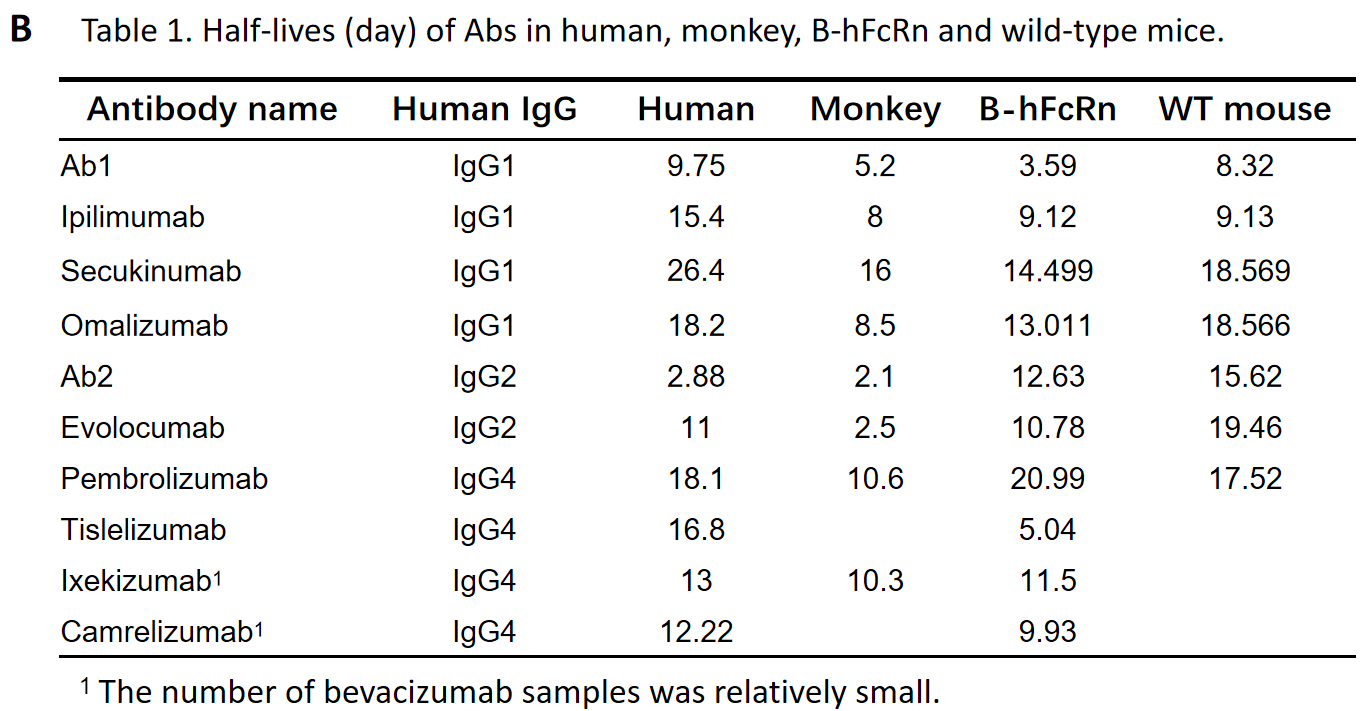
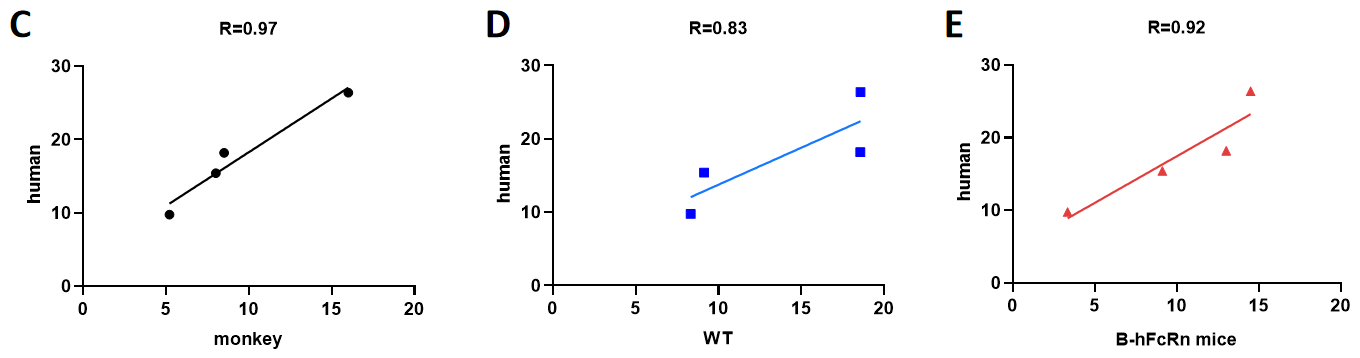
Correlations of half-lives between human and monkey (C), Wild-type mice (WT) (D), B-hFcRn mice (E) (only including human IgG1 mAbs).
| Product Name | Product No. | Background | Action |
| B-hC1Q mice | 111990 | C57BL/6 | |
| B-NDG FcγR KO mice | 112839 | B-NDG | |
| B-NDG hIL15, FcγR KO mice | 112653 | B-NDG | |
| huHSC-B-NDG hIL15, FcγR KO mice | 114031 | B-NDG | |
| MORE >> | |||