

Biocytogen has established a hyperuricemia model induced by potassium oxonate and uric acid, widely used to study the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and assess the efficacy of therapeutic interventions.
on this page
Hyperuricemia is a risk factor for diabetes, cardiovascular complications, metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease. The increasing trend of hyperuricemia in the last past decades has attracted much attention. Hyperuricemia is closely related to the overproduction and under-excretion of uric acid (UA) in patients. In the formation of uric acid, xanthine oxidase (XOD) is a key enzyme involved in the conversion of xanthine. Responsible for the conversion of xanthine and hypoxanthine into uric acid Excessive consumption of purine foods and lack of the genetic enzyme can lead to uric acidemia and hyperuricemia.
Biocytogen has established a hyperuricemia model induced by potassium oxonate and uric acid, widely used to study the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and assess the efficacy of therapeutic interventions.
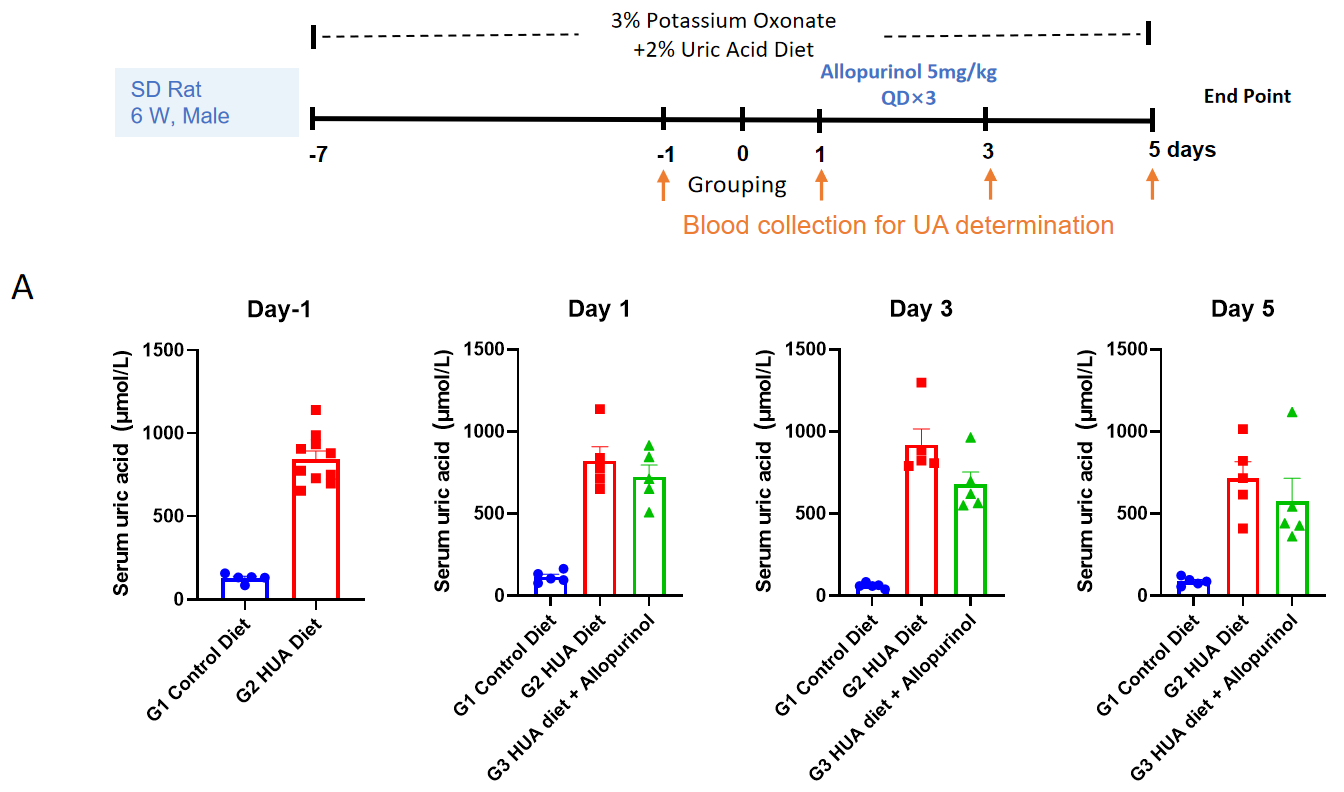
Establishment of hyperuricemia model induced by special diet containing 3% potassium oxonate and 2% uric acid. A, Serum uric acid change before and after allopurinol treatment. N = 5 mice per group, **p <0.01,****p <0.0001 vs. G2 group.
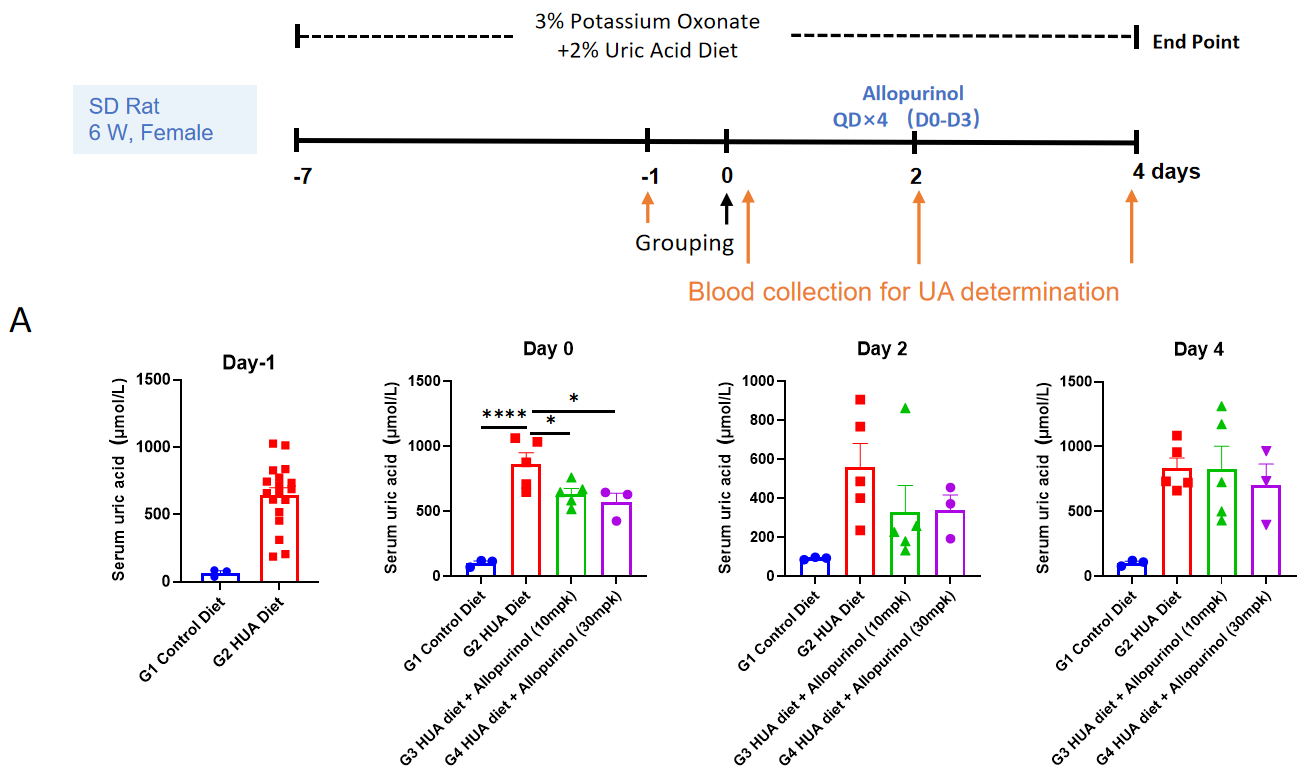
Establishment of hyperuricemia model induced by special diet containing 3% potassium oxonate and 2% uric acid. A, Serum uric acid change before and after allopurinol treatment. N = 5 mice per group, *p <0.05,****p <0.0001 vs. G2 group.