

Biocytogen offers high-quality in vivo pharmacology services using a diverse array of animal models to assess the efficacy, safety, and early toxicity of novel therapeutics, including small molecules, monoclonal and bispecific antibodies, recombinant proteins, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), peptides, tumor vaccines, CAR-T cell therapies, and oncolytic viruses.
on this page
Biocytogen specializes in conducting high-quality in vivo efficacy studies to evaluate the therapeutic potential of novel drug candidates. These studies leverage genetically modified mouse models that express human targets knocked into the loci of their corresponding mouse genes, severely immunodeficient (B-NDG) mice and their variants, as well as wild-type models. Our approach supports drug discovery and development across oncology, immuno-oncology, autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurological conditions.
With expertise in testing a wide range of biologics, including mono- and bispecific antibodies, recombinant proteins, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), peptides, tumor vaccines, CAR-T cell therapies, and oncolytic viruses, Biocytogen ensures comprehensive evaluation of therapeutic efficacy.
Our in vivo models cover:



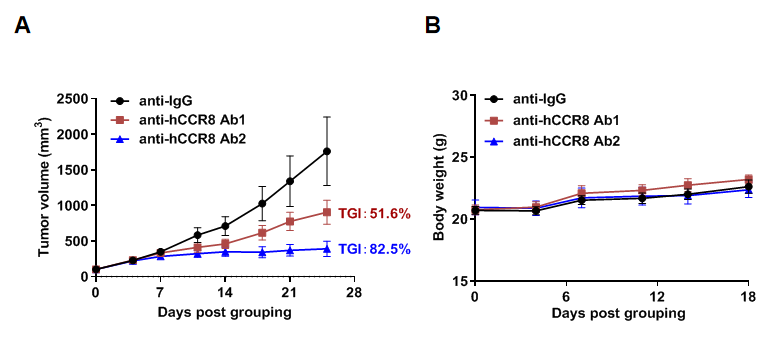
Antitumor activity of anti-human CCR8 antibody in B-hCCR8 mice bearing MC38 cells. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hCCR8 mice (female, 7 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human CCR8 antibodies (in house). (A) Tumor growth curve. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown, anti-human CCR8 antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hCCR8 mice. B-hCCR8 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human CCR8 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
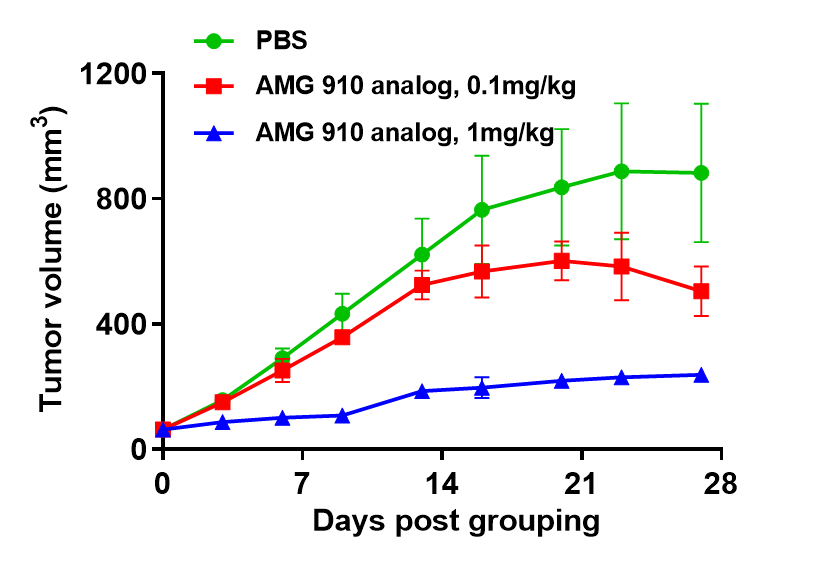
Efficacy evaluation of bispecific antibody on human immune system reconstitution models.(A) Human immune system reconstitution models for CD3-based bispecific antibody study. NUGC4 cells (5E6) were subcutaneously implanted after human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenously implanted into B-NDG mice. Anti-human CD3×Claudin18.2 bispecific antibody (AMG 910 analog) inhibited significantly NUGC4 tumor growth in human PBMC reconstituted B-NDG mice.
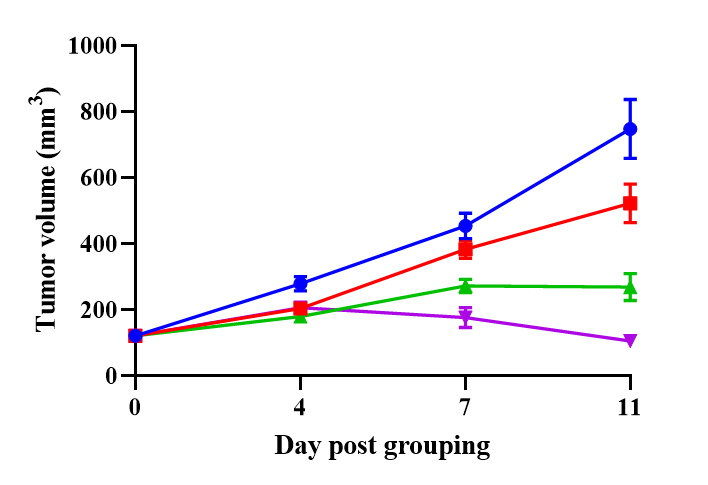
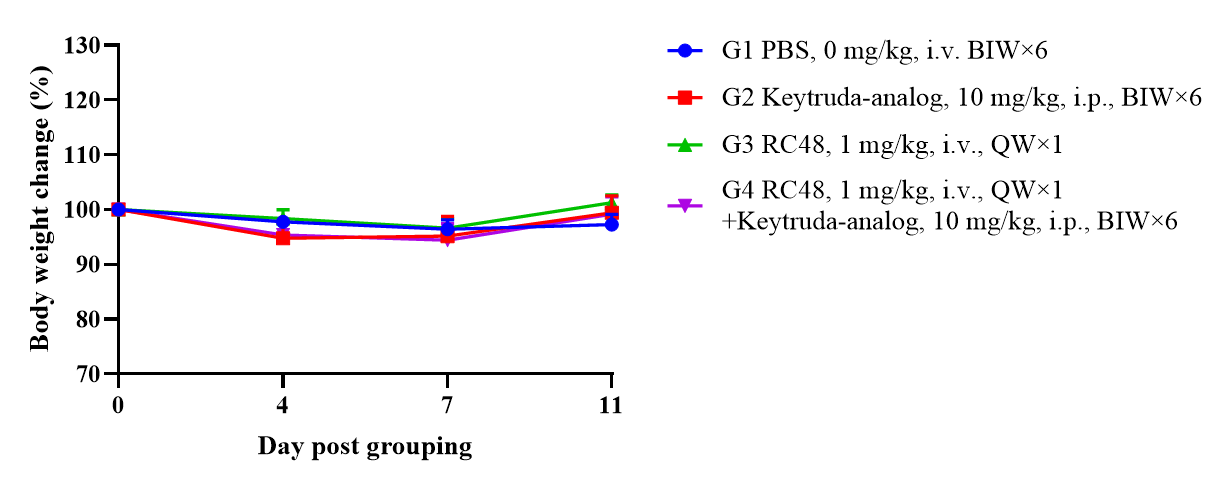
B-NDG mice reconstituted with PBMCs were used for HER2-ADC efficacy studies
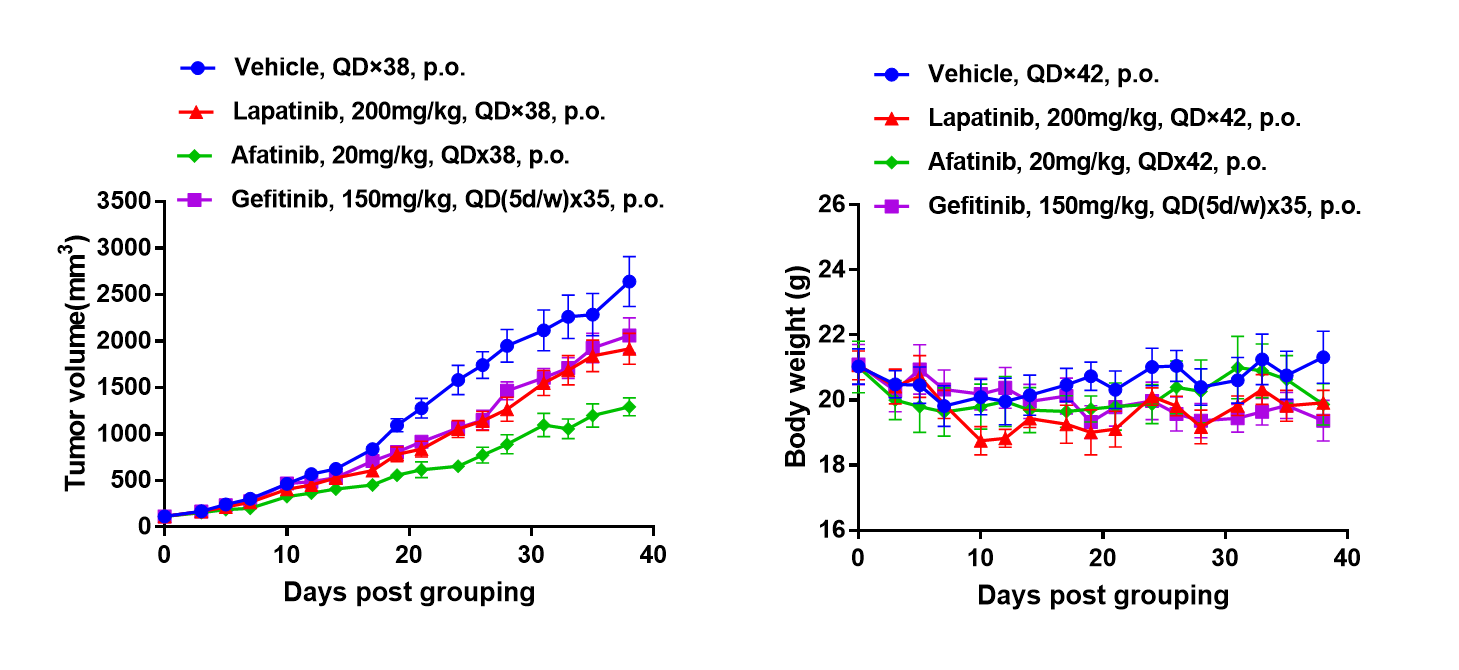
Antitumor activity of Drugs target EGFR in B-NDG mice. (A) Molecular targeted small-molecule anti-cancer drugs slightly inhibited tumor growth of BP0062 in B-NDG mice. PDX model of BP0062 was subcutaneously implanted into B-NDG mice (female, 6 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with different targeted drugs and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, Molecular targeted small-molecule anti-cancer drugs were efficacious, demonstrating that PDX model of BP0062 can be used to establish tumor model and provide a powerful preclinical pancreatic tumor model with EGFR positive cells. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
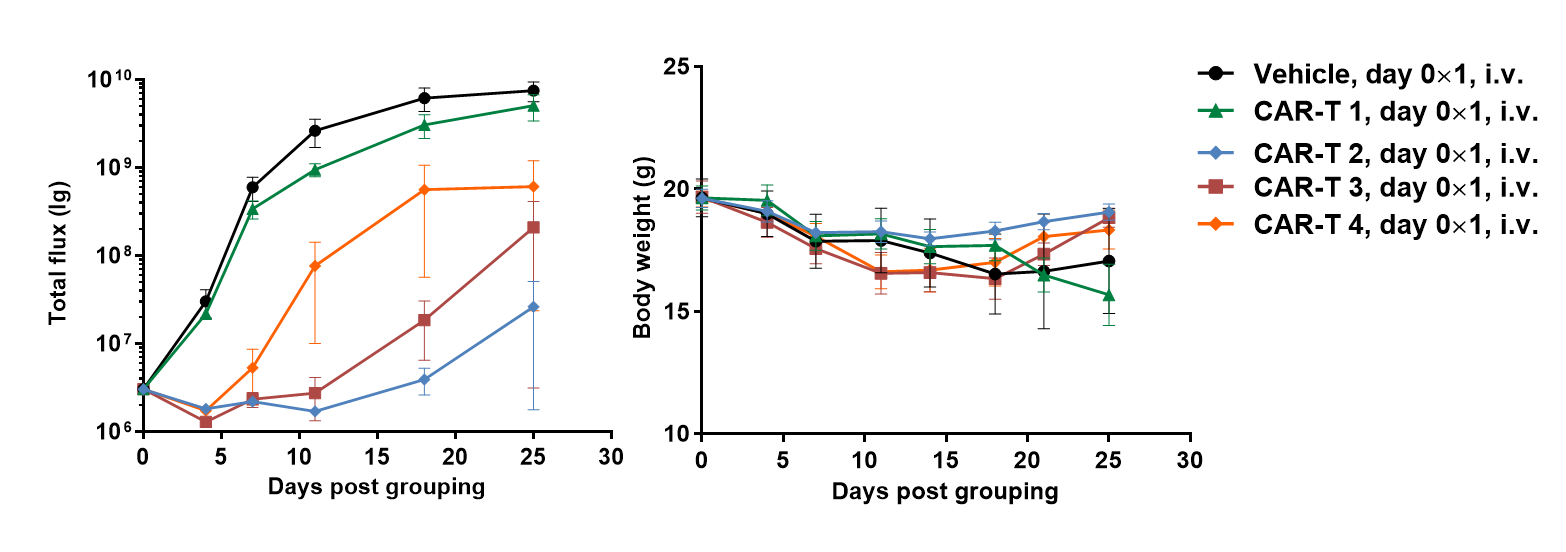
A Raji lymphoma mouse model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human CD47 antibodies were verified. B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice. In vivo imaging systems (IVIS) was used to observe tumor growth. When the fluorescence intensity of the tumor reaches about 1×106 p/sec, the animals were divided into one control group and three treatment group (n=6). (A) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells; (B) Body weight. The results showed that all three anti-human CD47 antibodies could significantly inhibit tumor growth. B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.