Establishment of TDAR Mouse Model
- Experimental Animals: B-hCD40/hCD40L mice , 7-8 weeks old, female
- Modeling reagent: Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH)
- Modeling sites: Intraperitoneal injection (i.p.)
- Modeling method: Intraperitoneal injection : day 0
| Readouts |
| Optional tests |
Molecular levels |
Serum IgG and IgM |
| Protein level (Elisa or Luminex) |
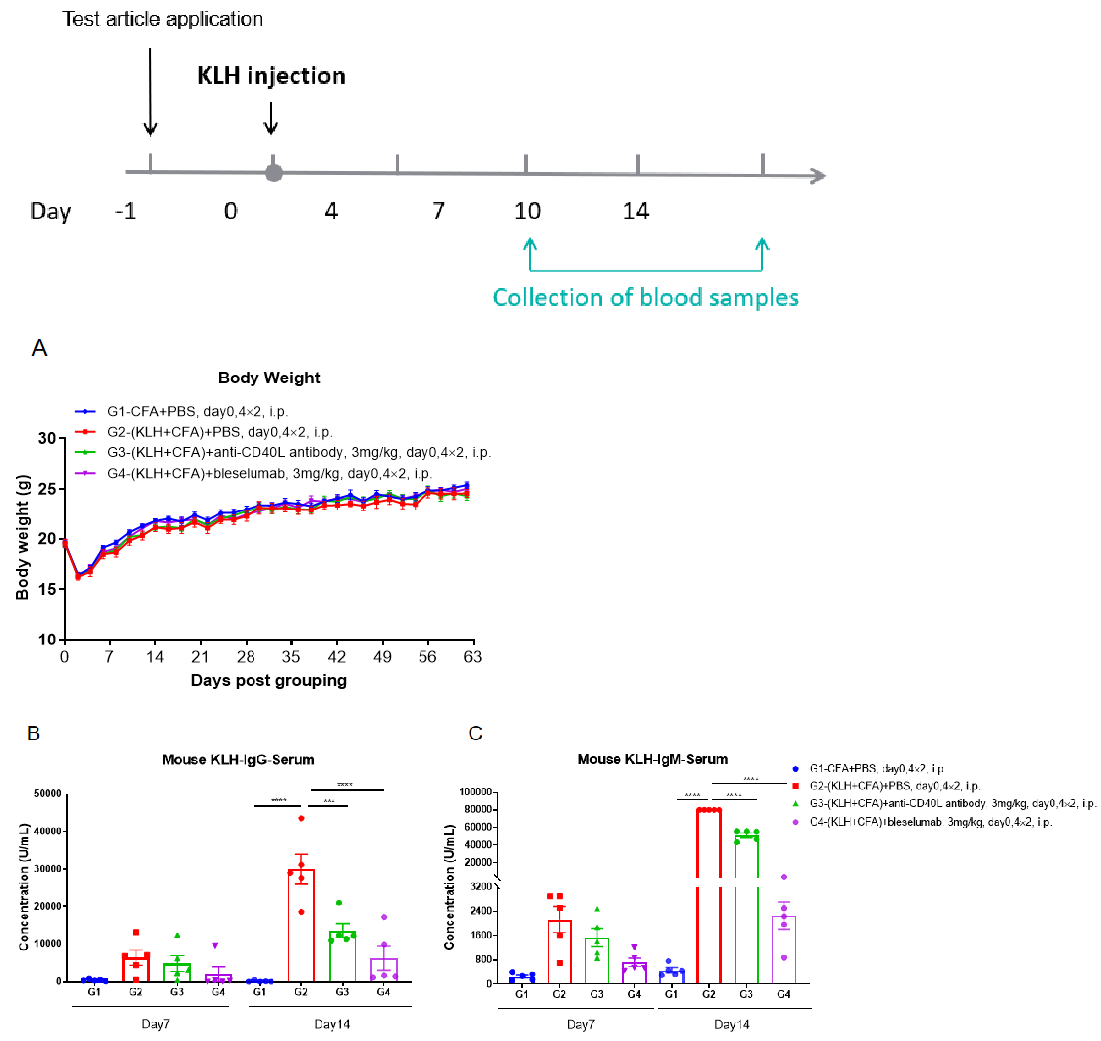
B-hCD40/hCD40L mice was used to establish the T-Dependent Antibody Response assay (TDAR assay) and evaluate the efficacy of anti-CD40 and anti-CD40L antibody. B-hCD40/hCD40L mice were used in a T-Dependent Antibody Response (TDAR) assay to evaluate anti-CD40 (bleselumab, in-house) and anti-CD40L (client-provided) antibody efficacy. Mice were intraperitoneally immunized with 100 μg KLH on Day 1. Blood was collected on Days 7 and 14 for ELISA analysis of KLH-specific IgG and IgM. (A) Body weight increased steadily. (B, C) KLH-specific IgG and IgM levels rose after immunization but were significantly reduced in anti-CD40L and bleselumab (anti-CD40)-treated groups, validating B-hCD40/hCD40L mice as a preclinical model for in vivo anti-CD40/CD40L antibody assessment. CD40 and CD40L antibodies suppress TDAR by blocking the essential CD40–CD40L co-stimulatory interaction required for T cell–dependent B cell activation and antibody production.