

on this page
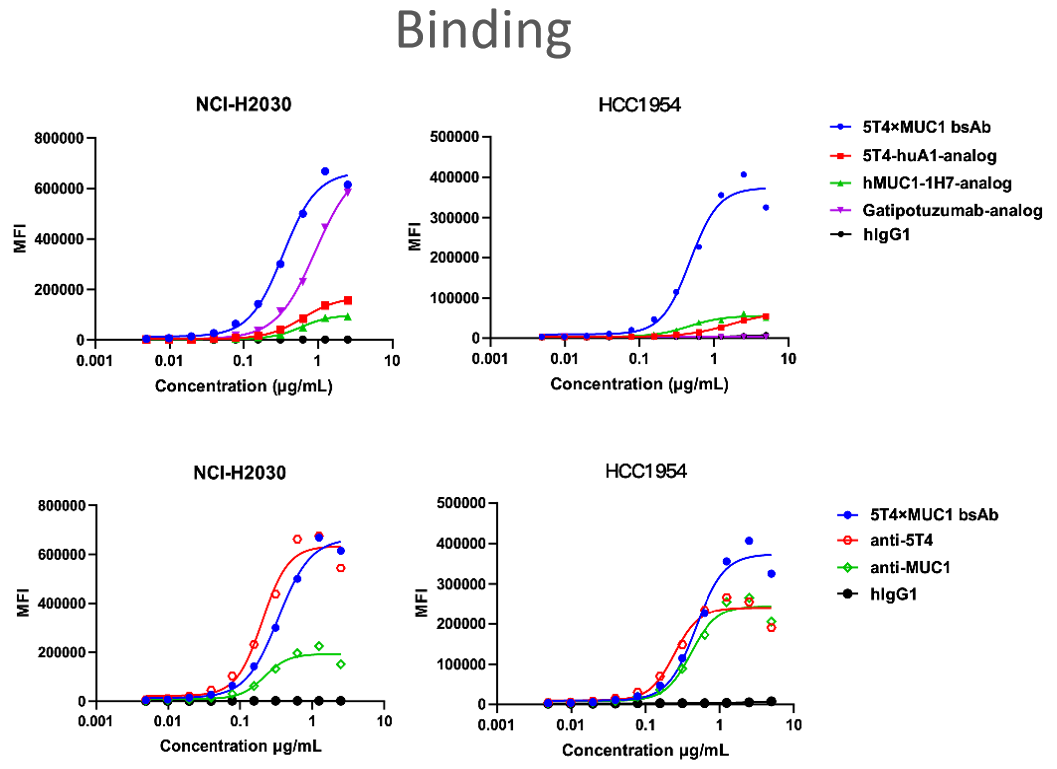
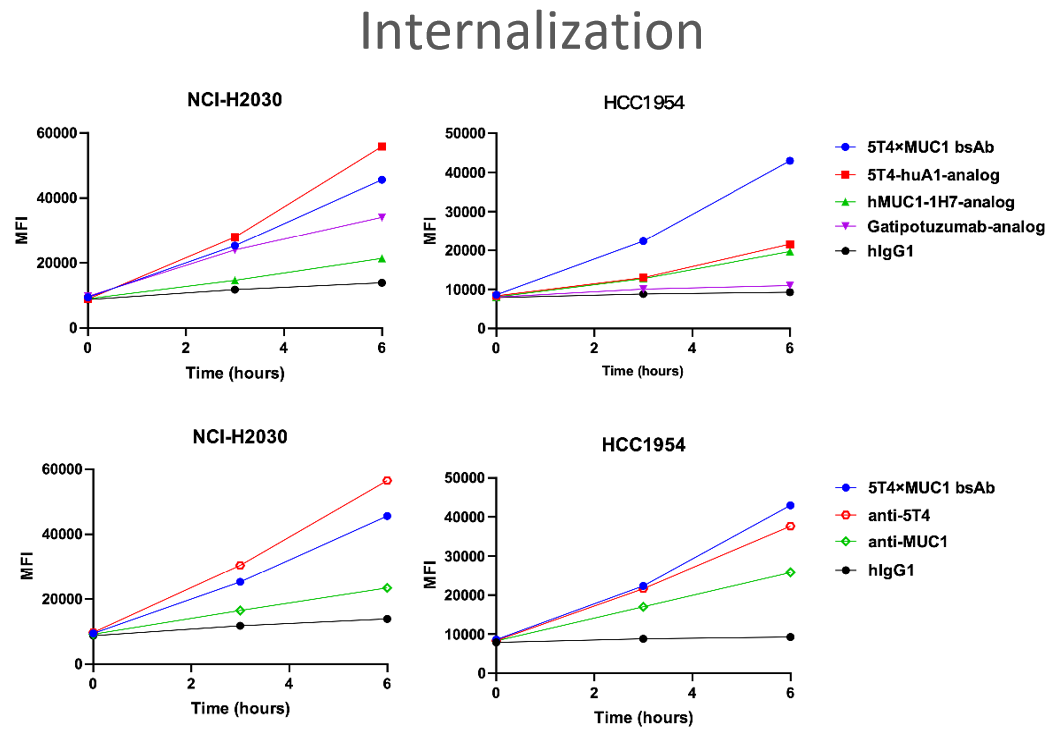
(A-D) The 5T4×MUC1 bsAb with binding and internalization in two cell lines. The 5T4×MUC1 bsAb showed stronger binding than benchmarks in two cell lines and with higher binding activity than its parental antibodies in HCC1954 (A,B). Accordingly, the endocytosis activity in two cell lines reflects consistent results with binding (C,D).
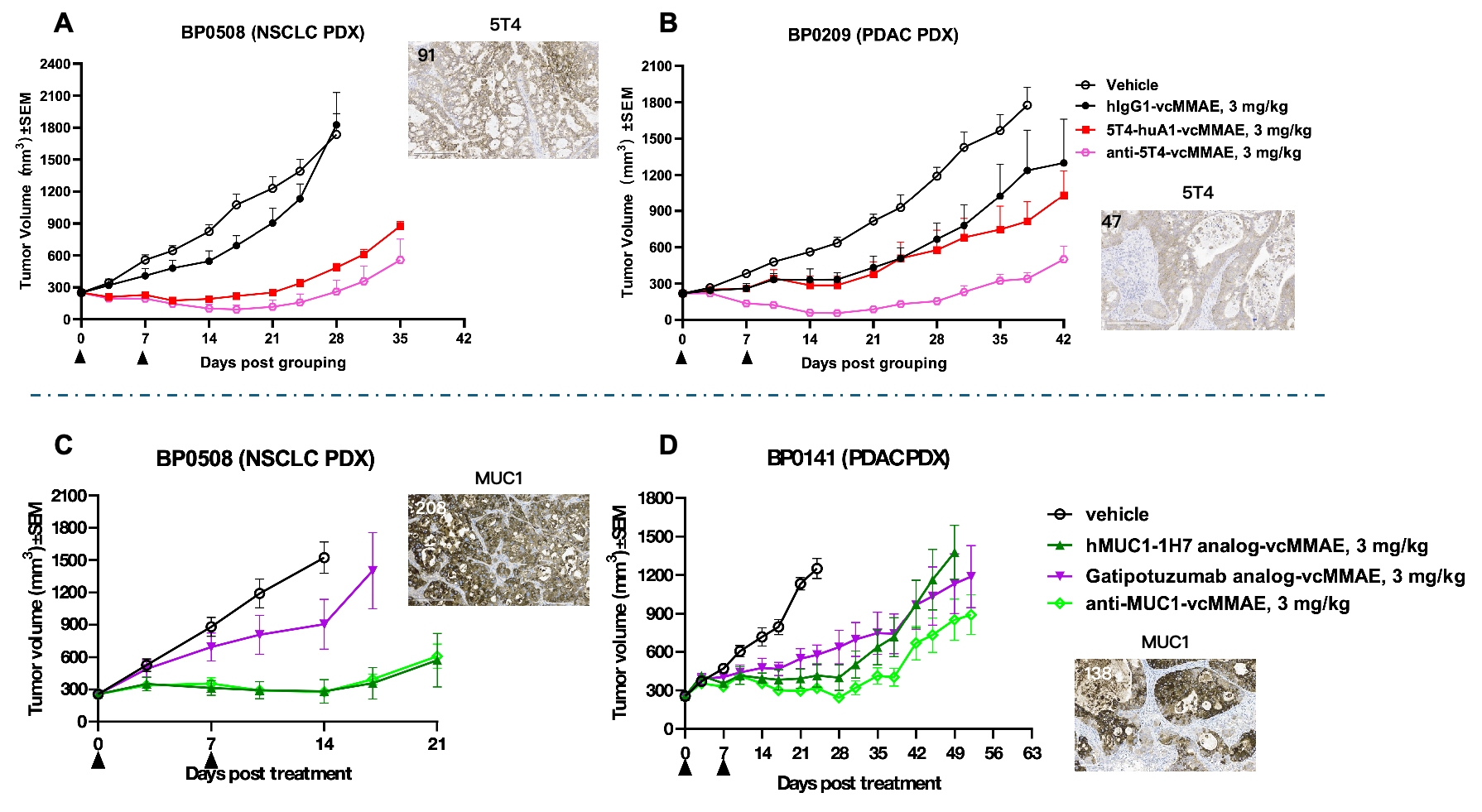
The anti-5T4 vcMMAE and anti-MUC1 vcMMAE exhibit superior, or at least comparable, efficacy relative to the 5T4 and MUC1 benchmark ADCs, respectively. Both show more potent activity than their benchmark ADC in PDX models with low 5T4 and moderate MUC1 expression, respectively. All ADCs carried the same payload (vcMMAE) with the same DAR of ~4. The 5T4 and MUC1 expression in the PDX model are shown and the H-score is labeled.
5T4 is an oncofetal antigen that is frequently overexpressed in solid tumors with adverse clinical outcomes and is an attractive therapeutic target due to its low expression in normal adult tissues. While several therapeutic agents targeting 5T4 antigen are currently being evaluated in human clinical trials, none have yet entered the market. Another target, MUC1, is currently under clinical investigation, with most drugs in clinical trials showing limited efficacy due to the shedding of the target antigen MUC1-N. 5T4 and MUC1 are commonly co-expressed in various solid tumors, including lung, breast, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers, suggesting that targeting both antigens with a bispecific ADC (bsADC) could be a promising therapeutic strategy.
Learn more about the RenLite and BsADC assets.