

on this page
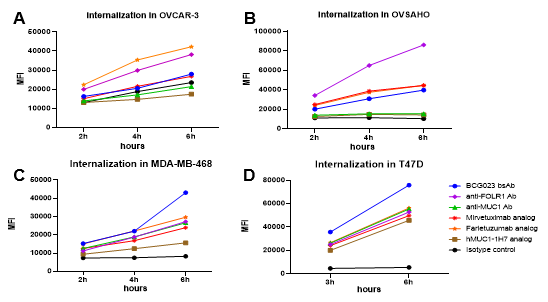
(A-D) Internalization of BCG023 bsAb in four mammalian cell lines. Internalization was measured with a pH sensitive dye by FACS. BCG023 bsAb showed superior to benchmarks internalization activity, and enhanced internalization compared to parental Abs in MDA-MB-468 (C) and T47D (D) tumor cell lines. The anti-FOLR1 Ab showed stronger or comparable activity to benchmarks in all cell lines.
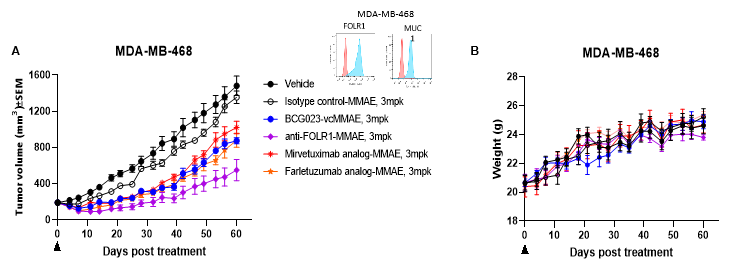
(A) Efficacy study of BCG023 bsADC in a TNBC MDA-MB-468 xenograft model. All ADCs were conjugated to vcMMAE with the same DAR (~4). The anti-FOLR1-MMAE demonstrated stronger anti-tumor efficacy compared to the two FOLR1 benchmark ADCs, and the BCG023-vcMMAE showed comparable efficacy to that of the FOLR1 benchmark ADCs. The body weight of the mice did not decrease over the period of study. (B).
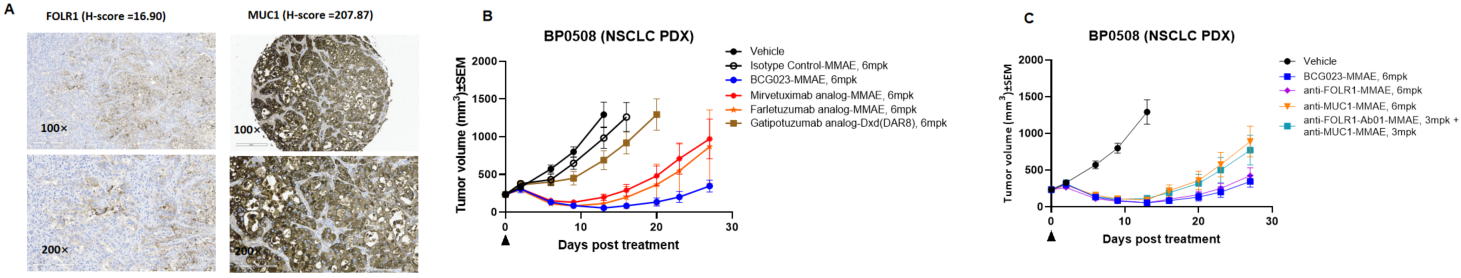
BCG023 bsADC exhibited potent anti-tumor efficacy in a FOLR1-low NSCLC PDX model.
(A) Expression of FOLR1 and MUC1 in the PDX.
(B, C) Efficacy studies of BCG023-vcMMAE. All ADCs carried the same payload (vcMMAE) with the same DAR of ~4, except for Gatipotuzumab analog-Dxd (DAR ~8). The BCG023-MMAE was more effective in the PDX model than the benchmark ADCs, and showed increased efficacy compared to the parental MUC-1 ADC alone or MUC-1 and FOLR1 ADCs in combination.
Folate receptor alpha (FOLR1) is specifically overexpressed in malignant tumors of epithelial origin, including ovarian, lung and breast cancers. While antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) therapies targeting FOLR1 have shown promise in clinical trials, there is still a large proportion of patients, particularly those with low FOLR1 expression, who do not respond, indicating new therapeutic strategies are needed. MUC1 is another tumor-associated antigen that is likewise overexpressed in epithelial ovarian cancer, breast cancer, and NSCLC, among other cancers; analysis of ovarian PDX tumors by immunohistochemistry (IHC) suggests that FOLR1 and MUC1 are both highly expressed in this cancer type.
Learn more about the RenLite and ADC platform.