

• 322286
| Product name | B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 322286 |
| Strain background | BALB/c |
| Aliases | B4; CVID3 |
| Tissue | B lymphocyte |
| Disease | Reticulum cell sarcoma |
| Species | Mouse |
| Application | B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells, both #2-C02 and #1-E04 can be used for efficacy studies in B lymphoma. Another, #1-E04 can also be used for efficacy studies in subcutaneously tumor of hCD19 overexpression, but the drug administration window should be pay attention. |
on this page
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells. The exogenous promoter, human CD19 coding sequence and luciferase-GFP was inserted to replace part of murine Cd19 gene in B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells. Mouse Cd19 transcript was disrupted, the protein no longer be expressed.
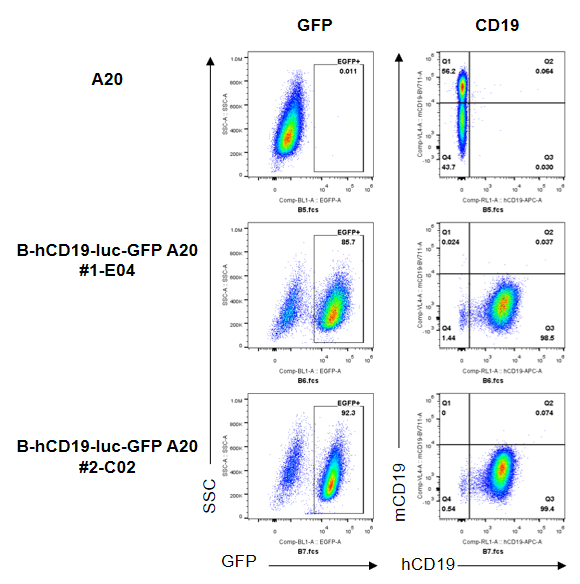
CD19 expression analysis in B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells by flow cytometry. Single cell suspensions from B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 were stained with anti-CD19 antibody (anti-hCD19 antibody BioLegend, Cat.302212; anti-mCD19 antibody, BioLegend, Cat.15555). Human CD19 was detected on the surface of B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells but not wild-type A20 cells. And mouse CD19 was not detected on B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells.
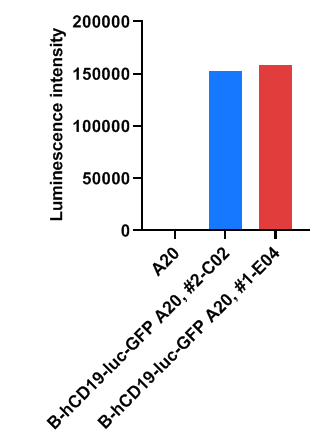
Luminescence signal intensity of B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells. Cell lysates of wild-type A20 and B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells were measured using the Bright-GloTM luciferase Assay (Promega, Catalog No. E4030). B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells have a strong luminescence signal that is not present in wild-type A20 cells.
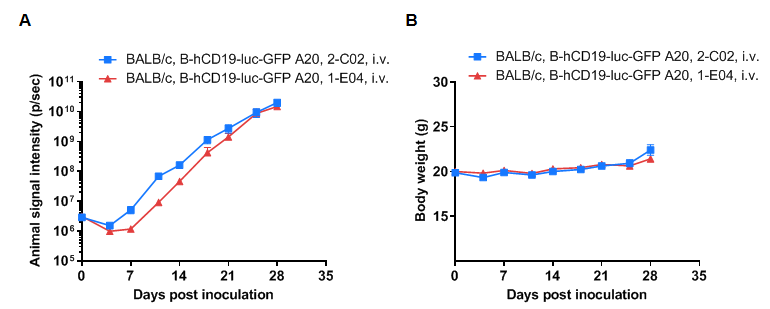
Growth kinetics of B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 tumors determined by bioluminescence imaging (BLI). B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells were injected into the tail vein of wild-type BALB/c mice (9-week-old). Signal intensity and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Signal intensity. (B) Body weight. (C) Raw bioluminescence images. These results indicate that B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy evaluation. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Growth kinetics of B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 tumors determined by bioluminescence imaging (BLI). B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells were injected into the tail vein of wild-type BALB/c mice (9-week-old). Signal intensity and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Signal intensity. (B) Body weight. (C) Raw bioluminescence images. These results indicate that B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy evaluation. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
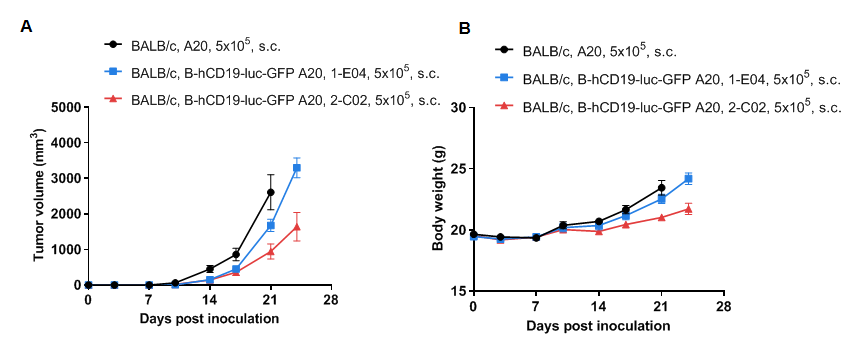
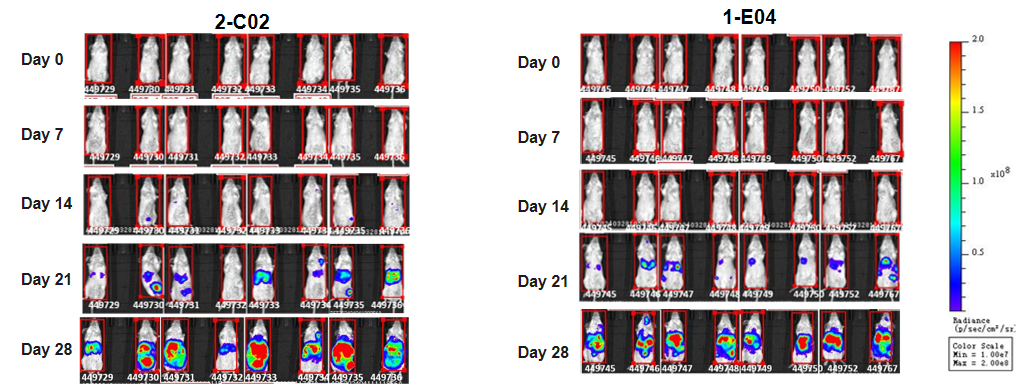
Subcutaneous homograft tumor growth of B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells. B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells and wild-type A20 cells were subcutaneously implanted into BALB/c mice (7-9 weeks old). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume ± SEM. (B) Body weight (Mean± SEM). Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 × long diameter × short diameter2. As shown in panel A, B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies. The consistency of the #1-E04 tumor is good, but the drug administration window is short.
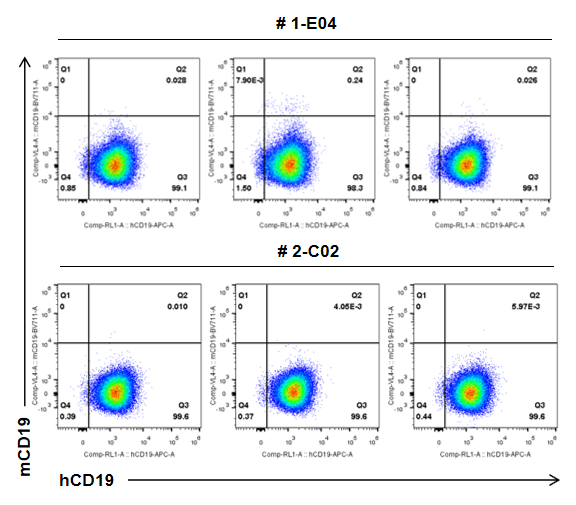
B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells (5x105) and wild-type A20 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into BALB/c mice (female, 7-9 weeks old, n=8), and on 24 days post inoculation, tumor cells were harvested and assessed for human CD19 expression by flow cytometry. As shown, human CD19 was highly expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Therefore, B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy studies of novel CD19 therapeutics.
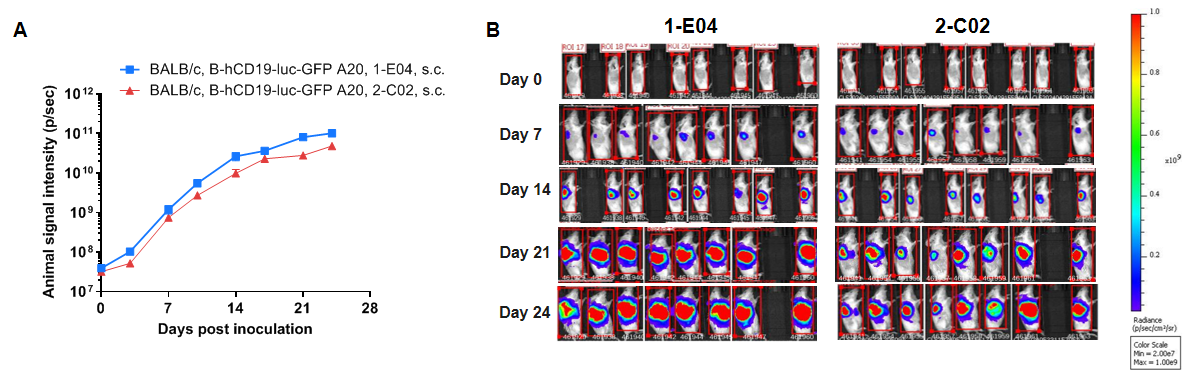
Growth kinetics of B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 tumors determined by bioluminescence imaging (BLI). B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells and wild-type A20 cells were subcutaneously implanted into BALB/c mice (7-9 weeks old). Signal intensity and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Signal intensity. (B) Raw bioluminescence images. These results indicate that B-hCD19-luc-GFP A20 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy evaluation. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.