


C57BL/6-Cd274tm2(CD274)Bcgen/Bcgen • 113045
| Product name | B-hPD-L1 mice plus |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 113045 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Cd274tm2(CD274)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| NCBI gene ID | 29126 |
| Aliases | B7-H, B7H1, PD-L1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, PDL1, hPD-L1 |
on this page
Gene targeting strategy for B-hPD-L1 mice plus. The exons 1-7 of mouse Pdl1 gene that encode the whole molecule were replaced by human counterparts in B-hPD-L1 mice plus. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene were replaced by human counterparts.
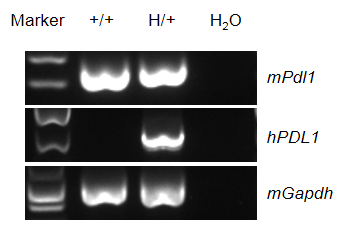
Species specific analysis of PDL1 gene expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and heterozygous humanized B-hPD-L1 mice plus by RT-PCR. Spleen were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and heterozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus (H/+). Mouse Pdl1 mRNA was detectable in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and heterozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus. Human PDL1 mRNA was detectable only in heterozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
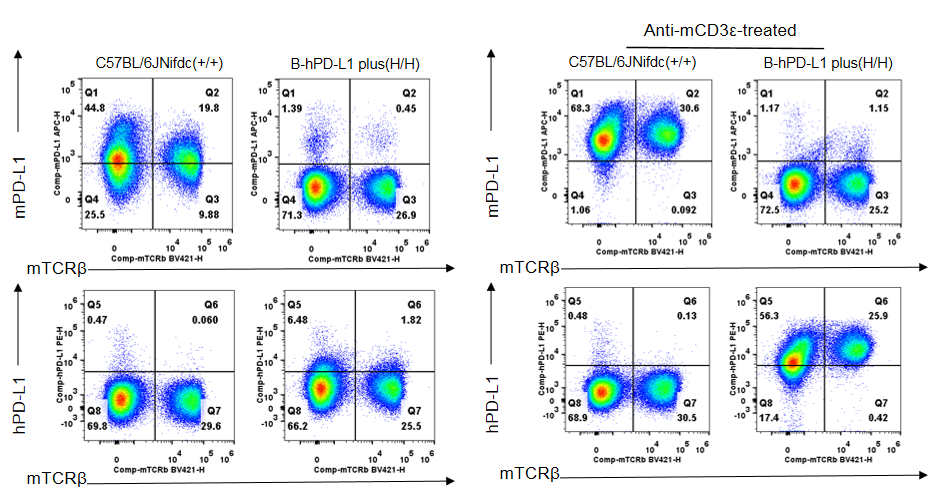
Strain specific PD-L1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus (H/H) stimulated with anti-mouse CD3ε antibody (7.5 μg, i.p.) in vivo for 24 hrs (male, 10-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody (Biolegend, 124312) and anti-human PD-L1 antibody (Biolegend, 329706) by flow cytometry. Mouse PD-L1 was detectable in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice. Human PD-L1 was only detectable in homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus, but not in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice.
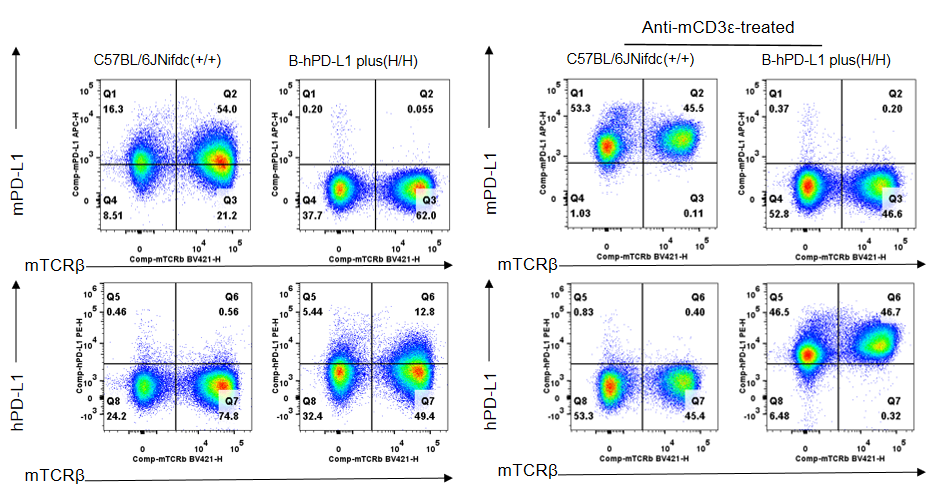
Strain specific PD-L1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus by flow cytometry. Lymph nodes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus (H/H) stimulated with anti-mouse CD3ε antibody (7.5 μg, i.p.) in vivo for 24 hrs (male, 10-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody (Biolegend, 124312) and anti-human PD-L1 antibody (Biolegend, 329706) by flow cytometry. Mouse PD-L1 was detectable in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice. Human PD-L1 was only detectable in homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus, but not in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice.
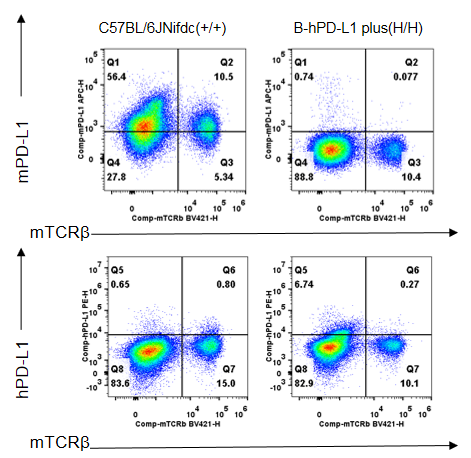
Strain specific PD-L1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus by flow cytometry. Blood was collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus (H/H) (male, 10-week-old, n=1). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody (Biolegend, 124312) and anti-human PD-L1 antibody (Biolegend, 329706) by flow cytometry. Mouse PD-L1 was detectable in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice. Human PD-L1 was only detectable in homozygous B-hPD-L1 mice plus, but not in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice.
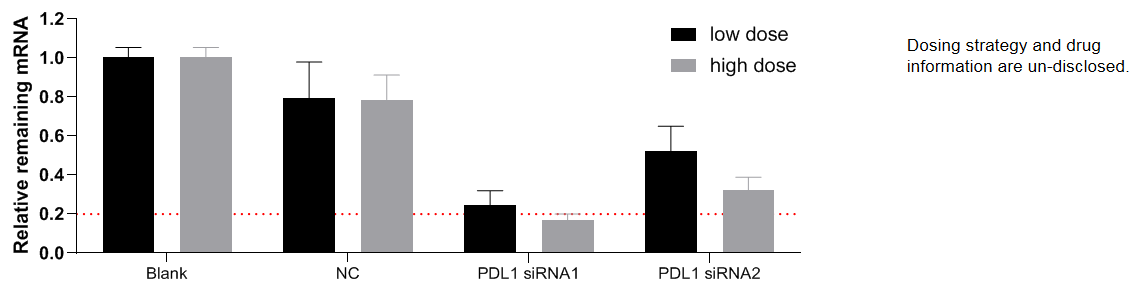
The inhibitory efficiency of the nucleic acid drugs against human PDL1 in B-hPD-L1 mice plus. B-hPD-L1 mice plus were euthanized, and primary hepatocytes were cultured, which were then randomly divided into 8 groups. After treatment with human PD-L1 targeted nucleic acid drugs (provided by the client) for 48 hours, the expression level of human PDL1 mRNA was detected by qPCR. The human PDL1 mRNA in the treatment group (PDL1 siRNA1) was significantly reduced compared to the control group (NC), demonstrating that B-hPD-L1 mice plus provide a powerful preclinical model for in vitro evaluation of human PD-L1 targeted nucleic acid drugs. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Note: This experiment was performed by the client using B-hPD-L1 mice plus. All the other materials were provided by the client.