


C57BL/6-Vegfatm1(VEGFA)Bcgen Angpt2tm2(ANGPT2)Bcgen/Bcgen • 113125
| Product name | B-hVEGFA/hANG2 mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 113125 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Vegfatm1(VEGFA)Bcgen Angpt2tm2(ANGPT2)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| NCBI gene ID | 14960, 14961 (Human) |
| Aliases | DPA1, HLA-DPA, HLA-DP1A; DPB1, HLA-DP, HLA-DPB, HLA-DP1B |
Gene targeting strategy for B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice. The exons 1-6 of mouse I-Ab1 gene that encodes the full-length protein of I-Ab1 was replaced by a chimeric CDS sequence encoding the α chain of HLA-DP and a chimeric CDS sequence encoding the β chain of HLA-DP in B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice. The promoter sequence was derived from I-Ea gene. The following sequences were the chimeric CDS of humanized β chain including the β1 domain of human HLA-DPB1*03:01 and the β2, transmembrane, cytoplasmic domains of mouse I-Ab1 gene. The last sequences were the chimeric CDS of humanized α chain including the α1 domain of human HLA-DPA*02:02 and the α2, transmembrane, cytoplasmic domains of mouse I-Aa gene. The mouse I-A protein was not detectable in the B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice because the mouse I-Ab1 gene was disrupted.
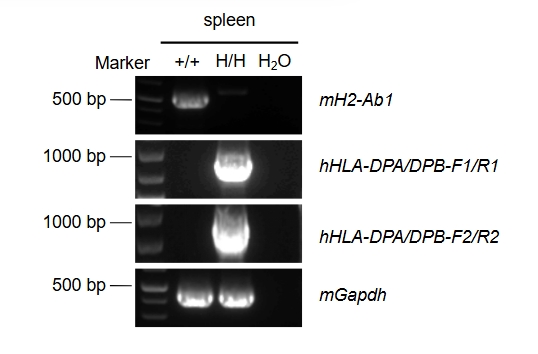
Strain specific analysis of HLA-DPA/DPB mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice by RT-PCR. Spleen RNA was isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice(+/+) and homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice(H/H), and then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse H2-Ab1 or human HLA-DPA/DPB primers. Mouse H2-Ab1 mRNA was detectable only in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human HLA-DPA/DPB mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice but not in wild-type mice.
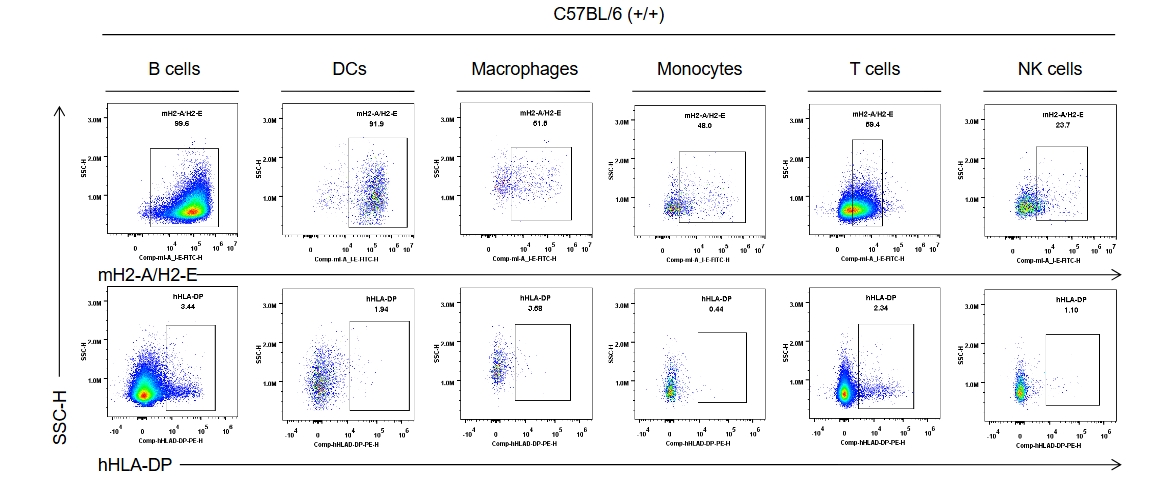
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Mouse H2-A/H2-E was only detectable in wild-type mice. Human HLA-DP was not detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
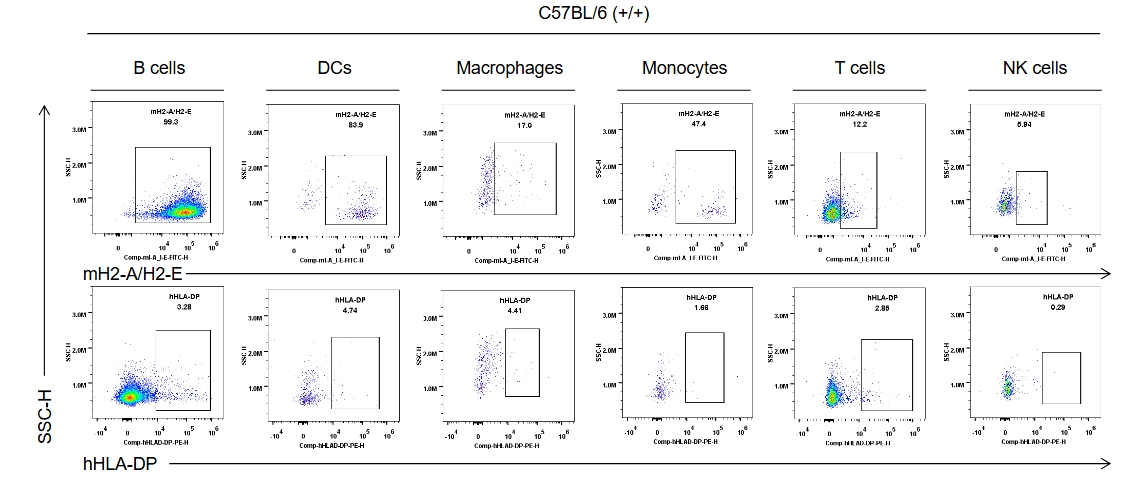
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Mouse H2-A/H2-E was only detectable in wild-type mice. Human HLA-DP was not detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
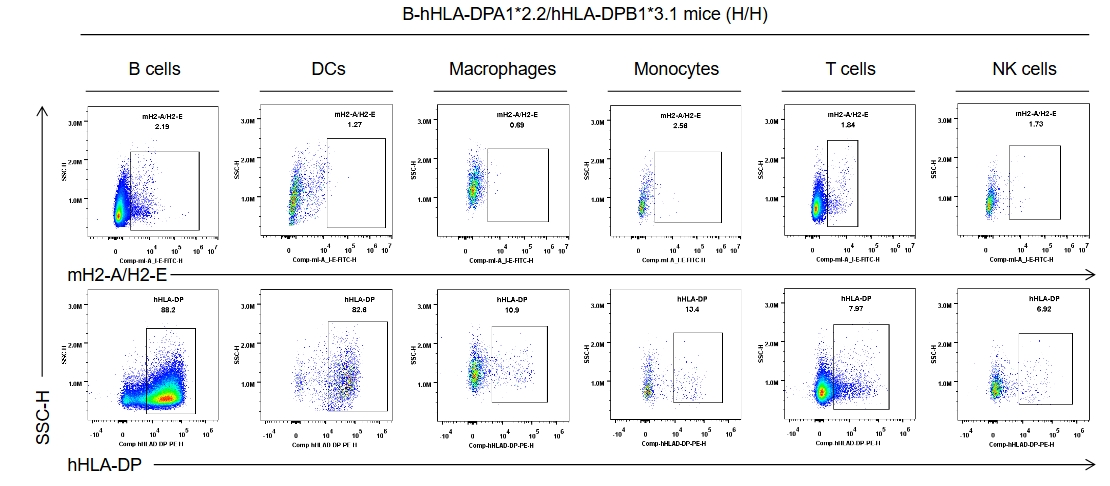
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Human HLA-DP was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
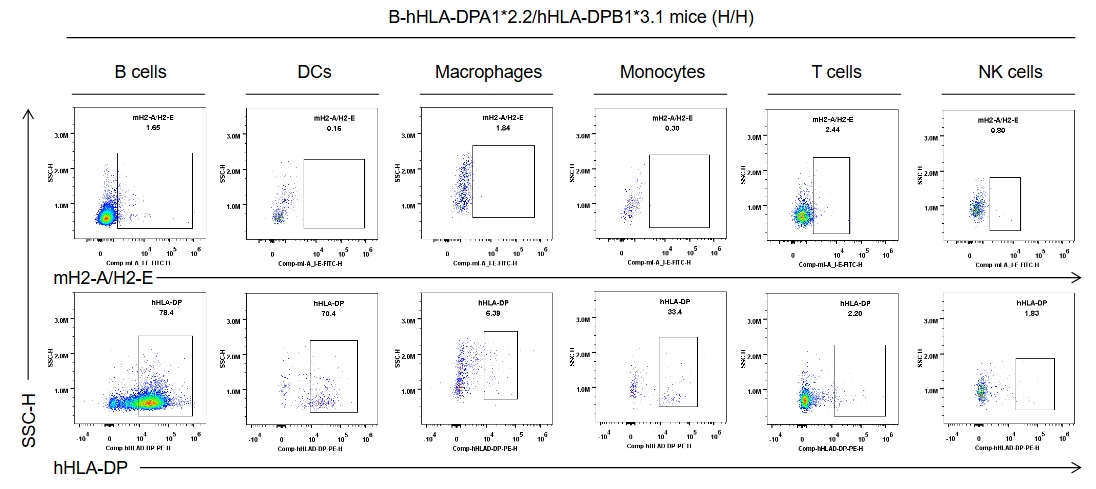
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Human HLA-DP was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
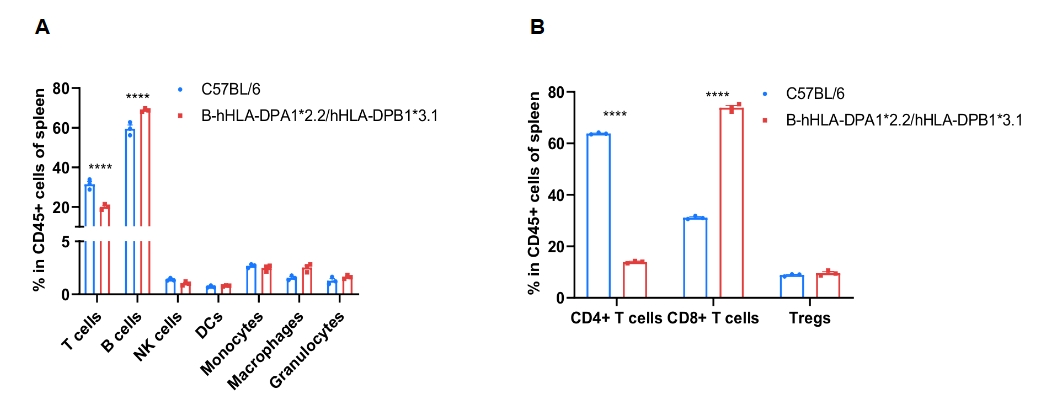
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) (male, n=3, 6-week-old) and homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H) (male, n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Percentages of NK cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of T cells and CD4+ T cells in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were lower than those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of B cells and CD8+ T cells in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were higher than those in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
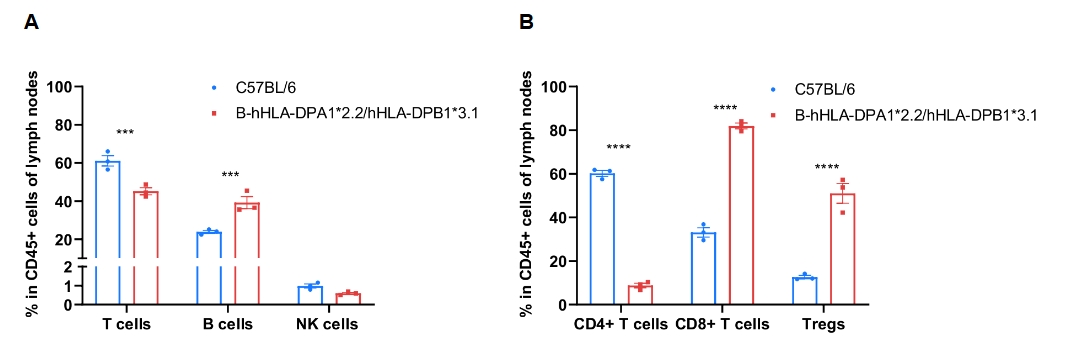
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the lymph node by flow cytometry. The lymph node cells were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) (male, n=3, 6-week-old) and homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H) (male, n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Percentages of NK cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of T cells and CD4+ T cells in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were lower than those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of B cells, CD8+ T cells, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were higher than those in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.