


CB17/lcr-PrkdcscidFcgr4tm2(FCGR3A)Bcgen Ncr1tm1(NCR1)Bcgen/Bcgen • 112987
| Product name | B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 112987 |
| Strain name | CB17/lcr-PrkdcscidFcgr4tm2(FCGR3A)Bcgen Ncr1tm1(NCR1)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | CB-17 SCID |
| NCBI gene ID | 246256, 17086 (Human) |
| Aliases | CD16, FCG3, CD16A, FCGR3, IGFR3, IMD20, FCR-10, FCRIII, FCGRIII, FCRIIIA, LY94, CD335, NKP46, NK-p46 |
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
The regulatory region and exons 1~5 of mouse Fcgr4 gene that encode the full-length protein were replaced by human FCGR3A(F158V) exons 1~6 and regulatory region in B-hCD16A /hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) mice.
The exons 1~7 of mouse NKp46 gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human NKP46 exons 1~7 in B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
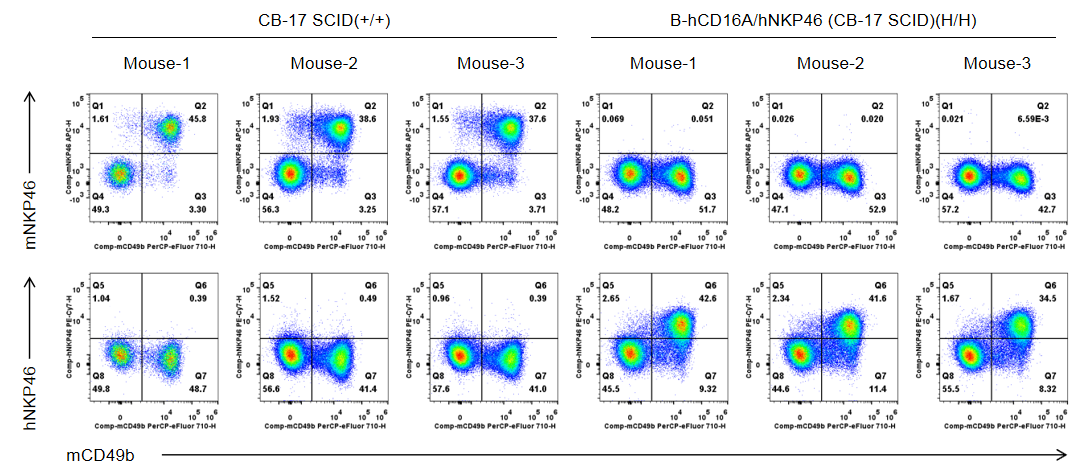
Strain specific NKP46 expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse NKP46 antibody (eBioscience™, 17-3351-82) and anti-human NKP46 antibody (Biolegend, 331916) by flow cytometry. Mouse NKP46 was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human NKP46 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
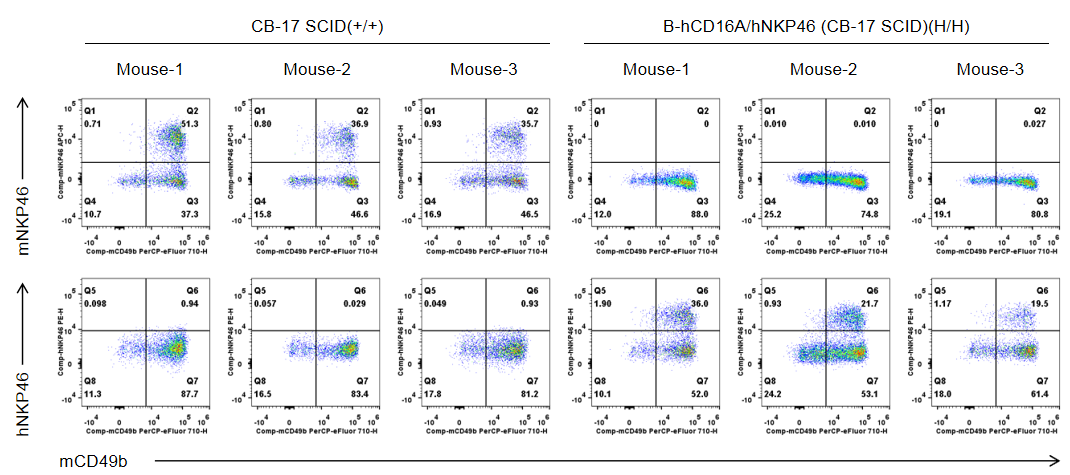
Strain specific NKP46 expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Blood were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse NKP46 antibody (eBioscience™, 17-3351-82) and anti-human NKP46 antibody (Biolegend, 331916) by flow cytometry. Mouse NKP46 was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human NKP46 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
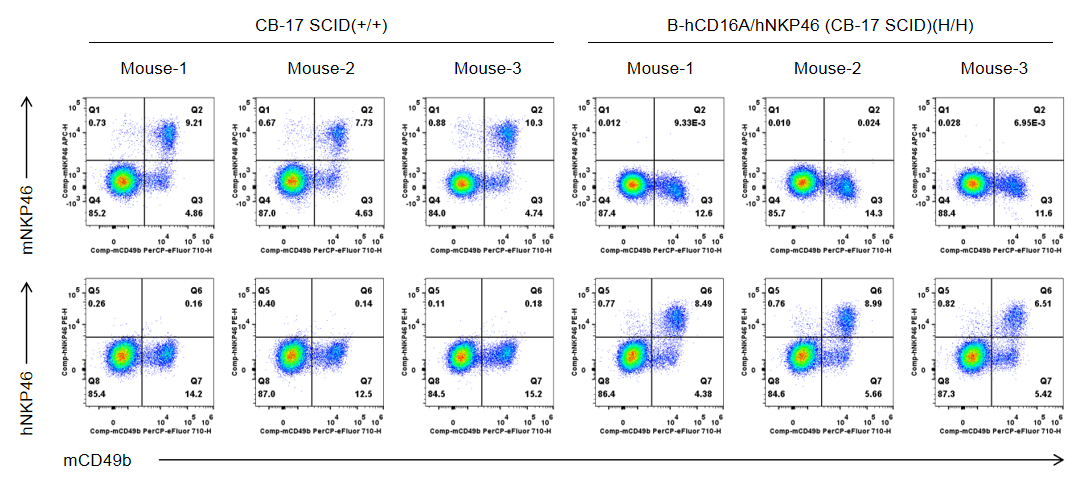
Strain specific NKP46 expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse NKP46 antibody (eBioscience™, 17-3351-82) and anti-human NKP46 antibody (Biolegend, 331916) by flow cytometry. Mouse NKP46 was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human NKP46 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
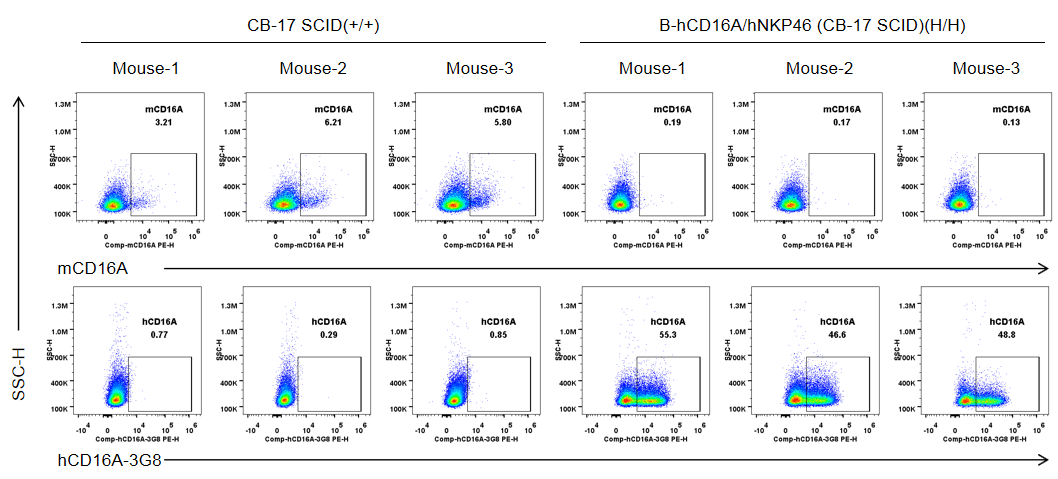
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
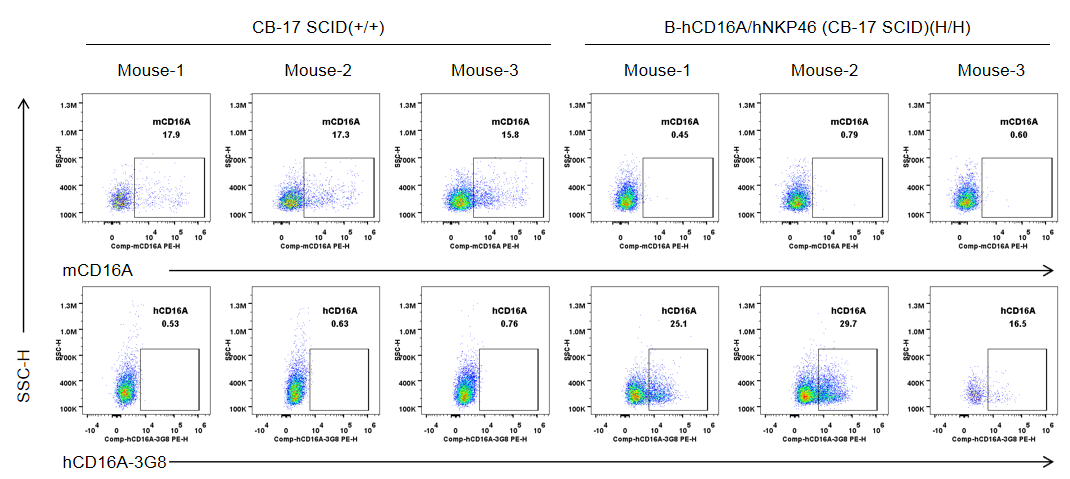
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
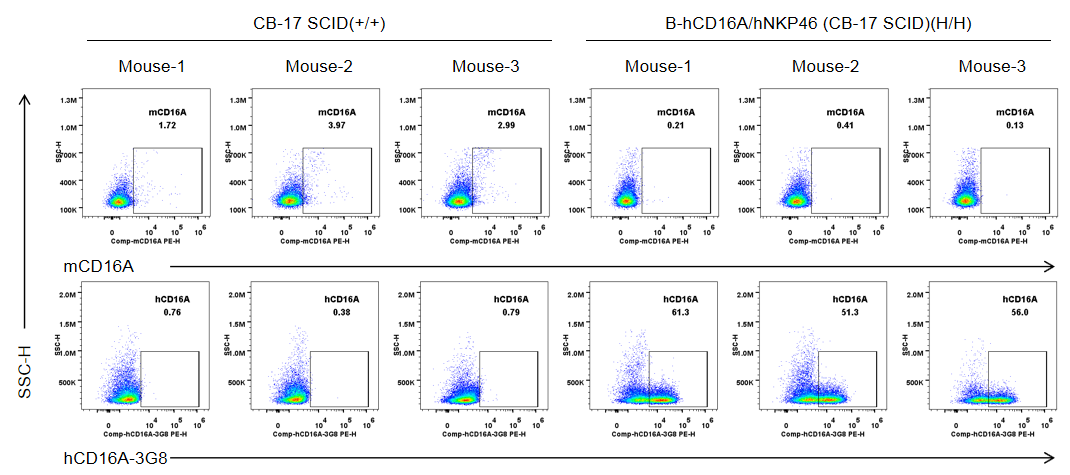
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
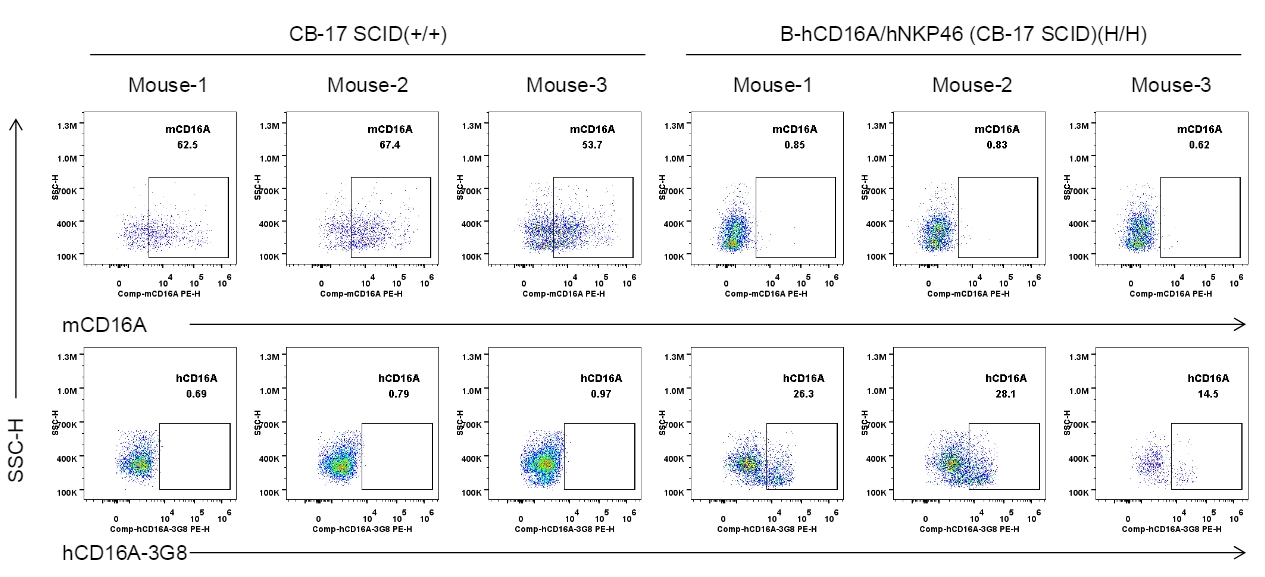
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
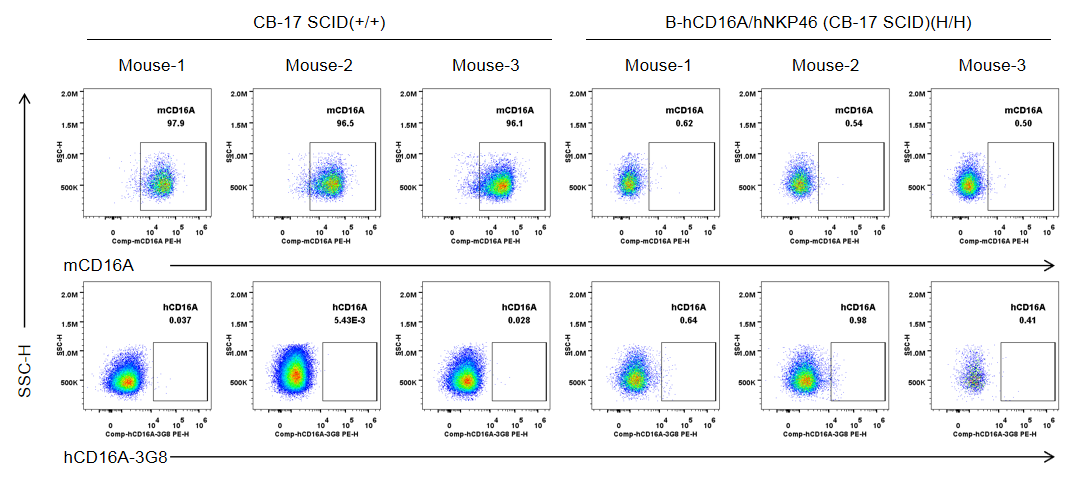
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was only detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was not detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
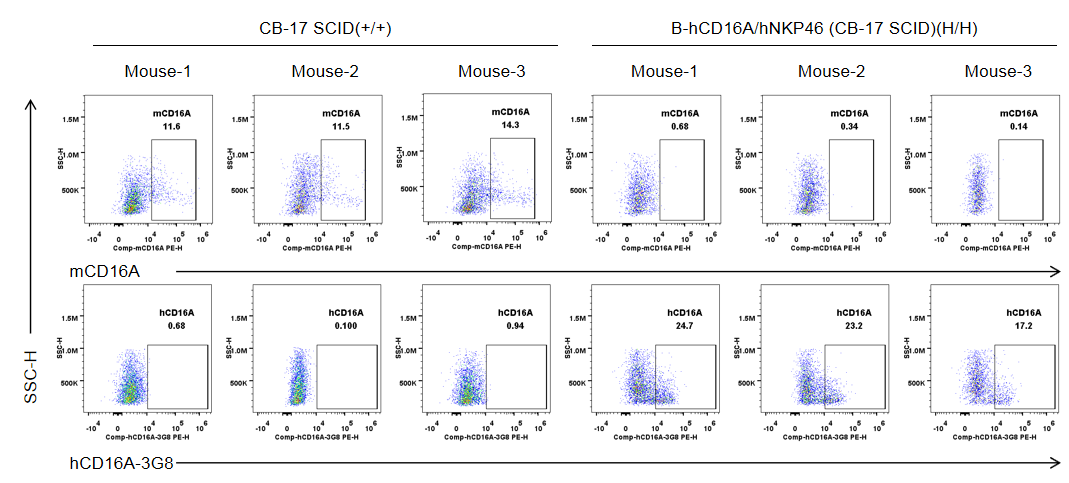
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Blood were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
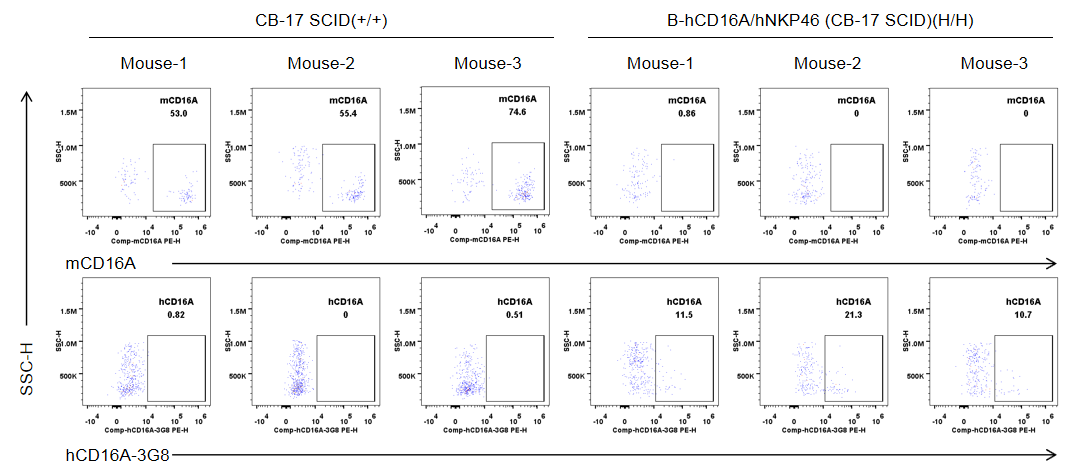
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Blood were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
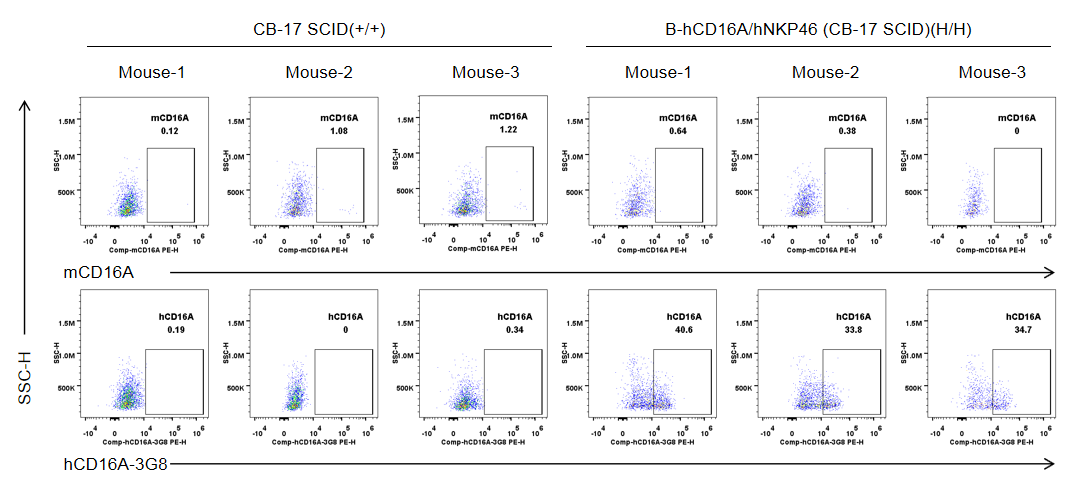
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Blood were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was weakly detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
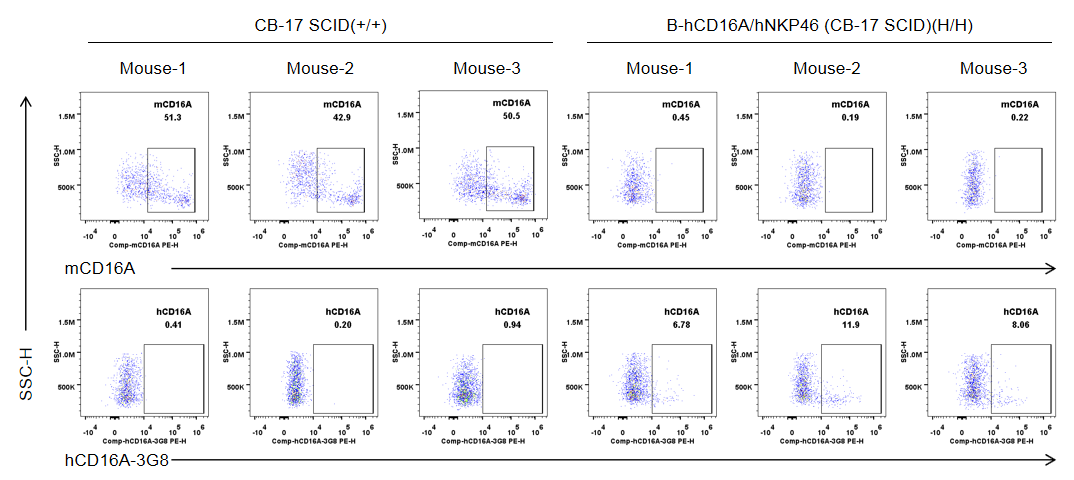
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Blood were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was not detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was weekly detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
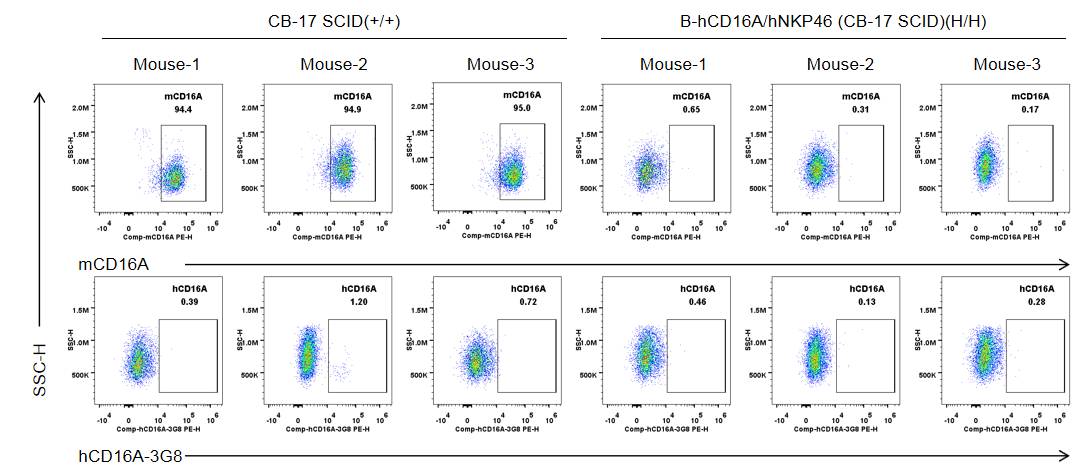
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Blood were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was not detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
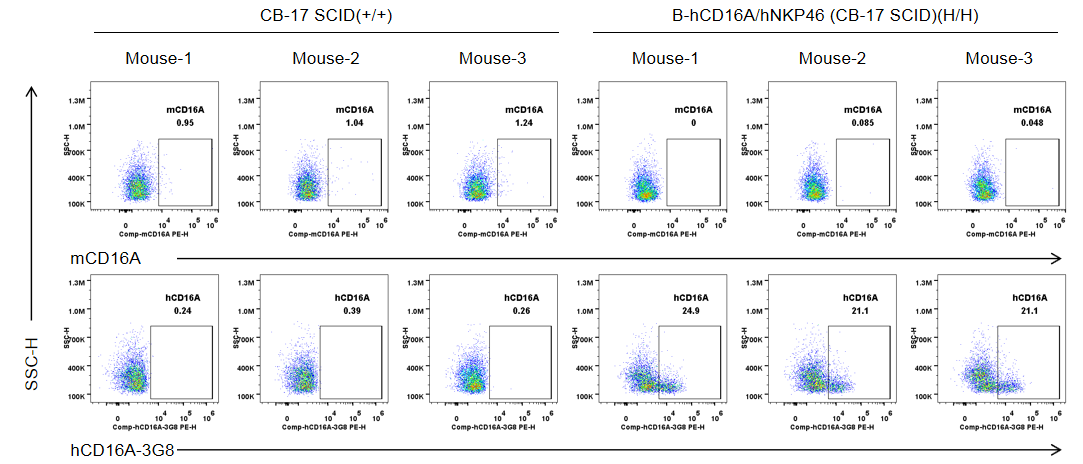
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was not detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
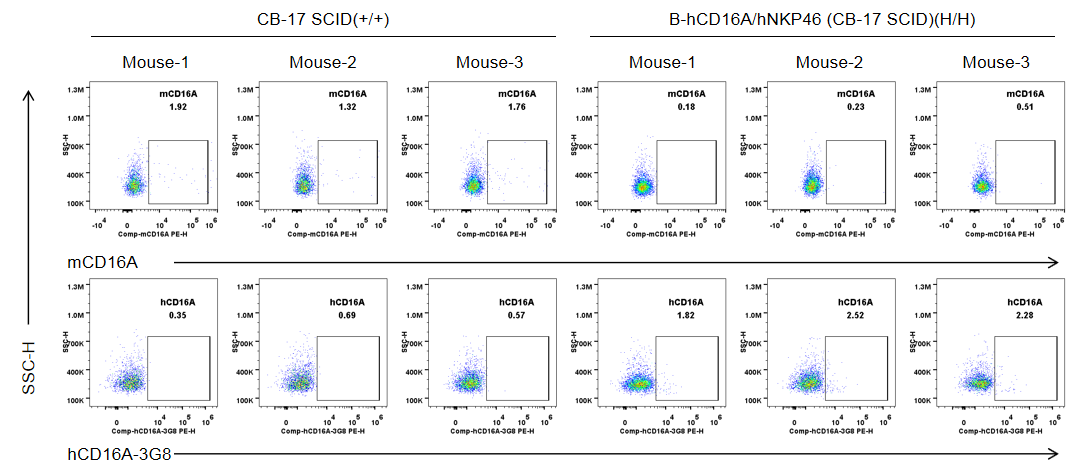
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was weakly detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was weakly detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
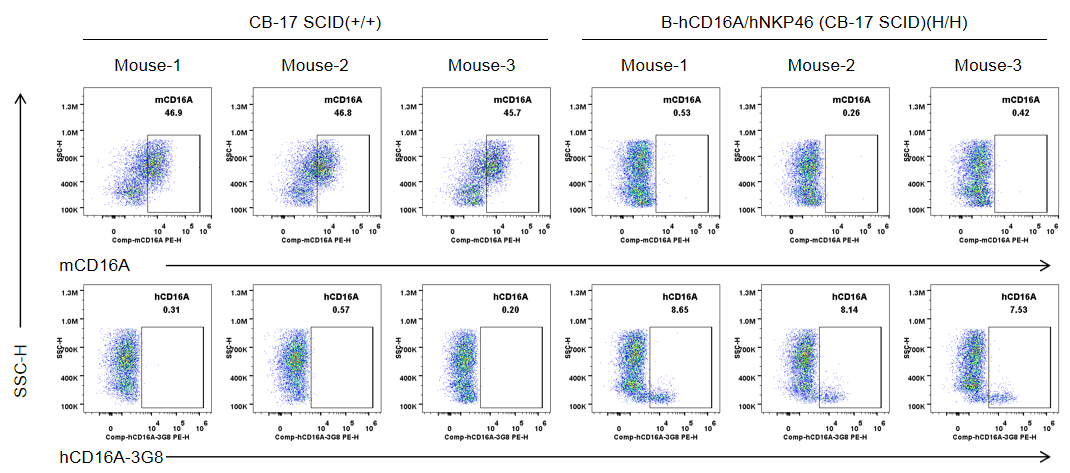
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
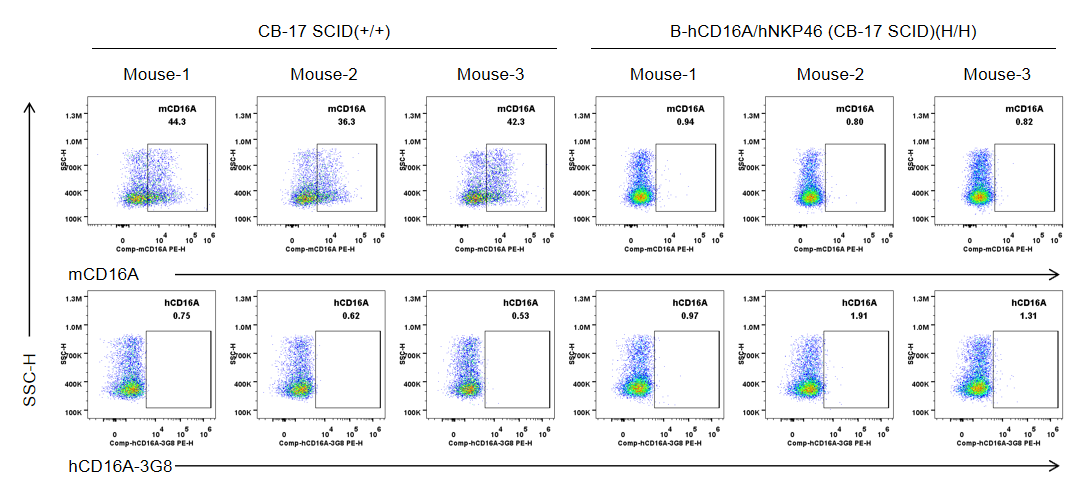
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID), but not in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice.
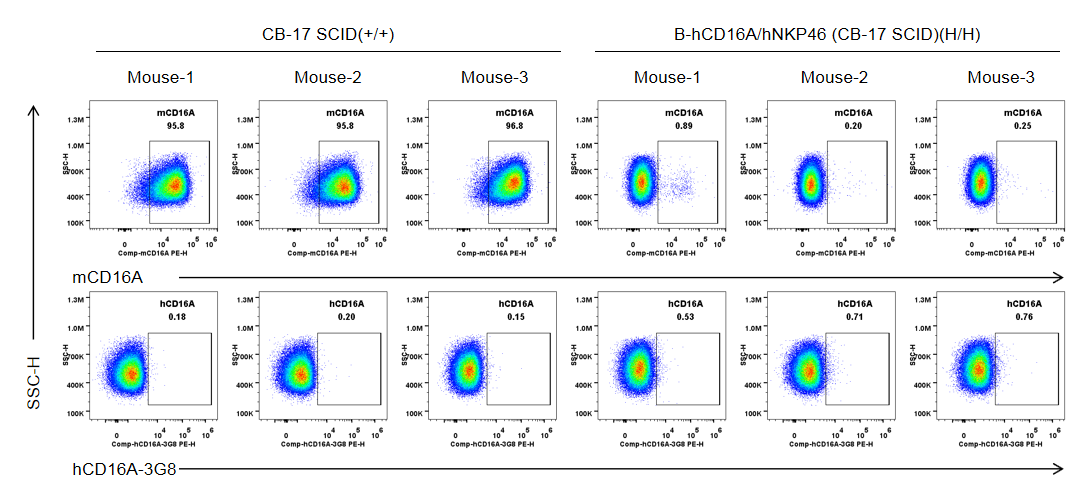
Strain specific CD16A expression analysis in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H) (n=3, 6-week old). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-mouse CD16.2 (FcγRIV) antibody (Biolegend, 149503) and anti-human CD16 antibody (Biolegend, 302008) by flow cytometry. Mouse CD16A was detectable in wild-type CB-17 SCID mice. Human CD16A was not detectable in homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
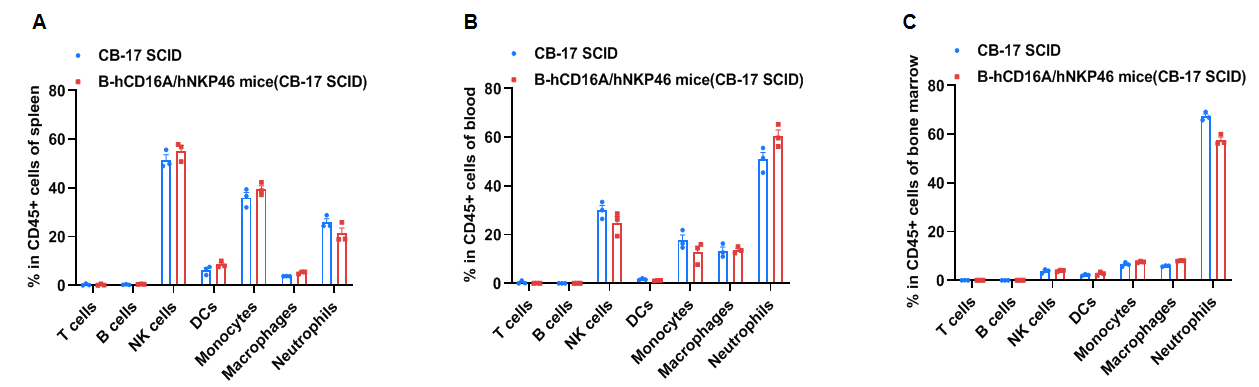
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes (A), blood (B) and bone marrow (C) were isolated from wild-type CB-17 SCID mice and homozygous B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (n=3, 7-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. Percentages of NK cells, DCs, monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils in B-hCD16A/hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) were similar to those in CB-17 SCID mice, demonstrating that humanization of CD16A and NKP46 does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in spleen, blood and bone marrow. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.