


NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen B2mtm1Bcgen Fcgrttm1(B2m/Fcgrt)Bcgen H2-Ab1tm1Bcgen/Bcgen • 111895
| Product name | B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 111895 |
| Strain name | NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen B2mtm1Bcgen Fcgrttm1(B2m/Fcgrt)Bcgen H2-Ab1tm1Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | B-NDG |
| Aliases | H2-Ab1: AI845868, Abeta, H-2Ab, H2-Ab, I-Abeta, IAb, Ia-2, Ia2, Rmcs1; B2m: Ly-m11, beta2-m, beta2m; Fcgrt: FcRn |
| Application | No MHC class I/II molecule expression;Reduce GVHD and prolong the experimental window period;Improve the accuracy of efficacy verification |
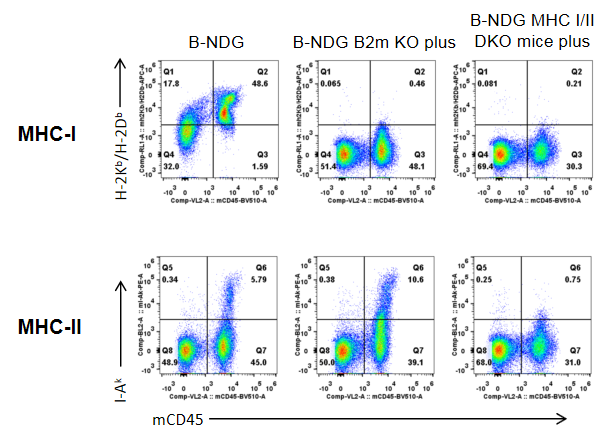
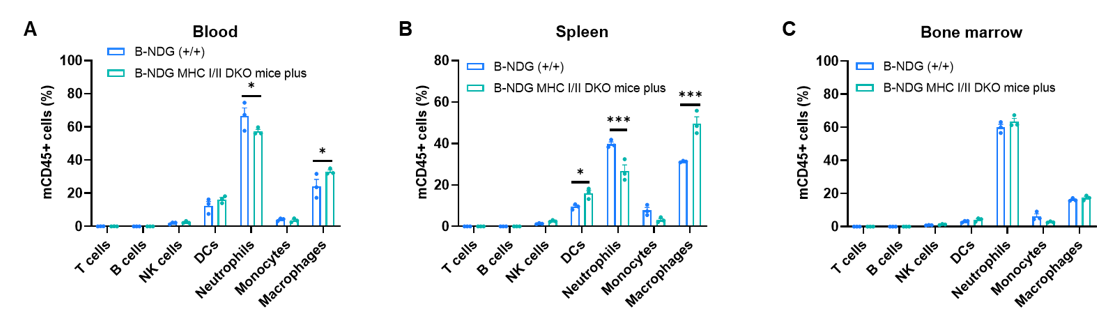
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen, blood and bone marrow by flow cytometry. Blood, spleen and bone marrow were collected from B-NDG mice and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus (male, 9-week-old, n=3). Leukocyte subpopulations were analyzed by flow cytometry analysis. Results showed that T cells, B cells and NK cells were not detectable in all tissues of B-NDG mice and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
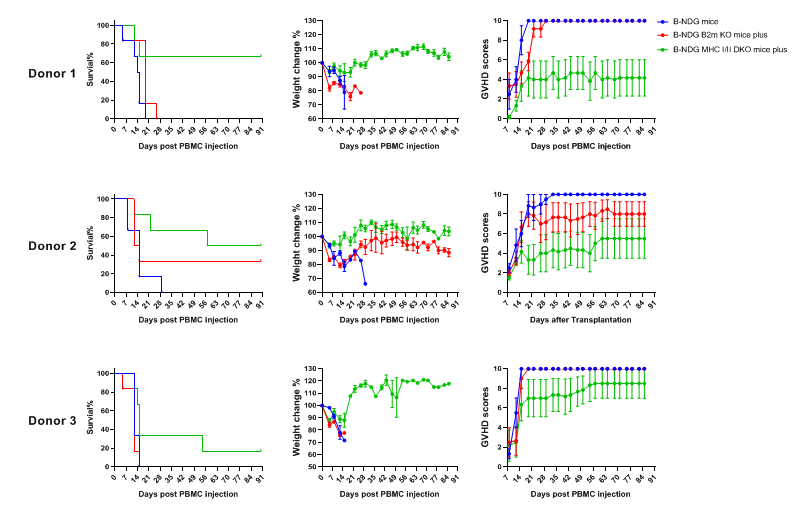
Comparison of the severity of GvHD induced with human PBMC engraftment in B-NDG mice, B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus. Five weeks old of female B-NDG mice, B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus were respectively engrafted intravenously with human PBMCs (5 × 106) from three healthy donors (Donor 1-3) on day 0 (n=5). A. Survival rates of the mice were analyzed with Kaplan Meier survival curves. B. Body weight changes. C. Clinical signs of GvHD were scored twice a week. Results showed that MHC I/II double knocked-out in B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus can significantly extend the life span and reduced the GvHD induced with human PBMC engraftment when compared that in B-NDG mice or in B-NDG B2m KO mice plus. Therefore B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus are more suitable mouse model for human PBMC engraftment into the immunodeficient mice. Values were expressed as mean ± SEM.
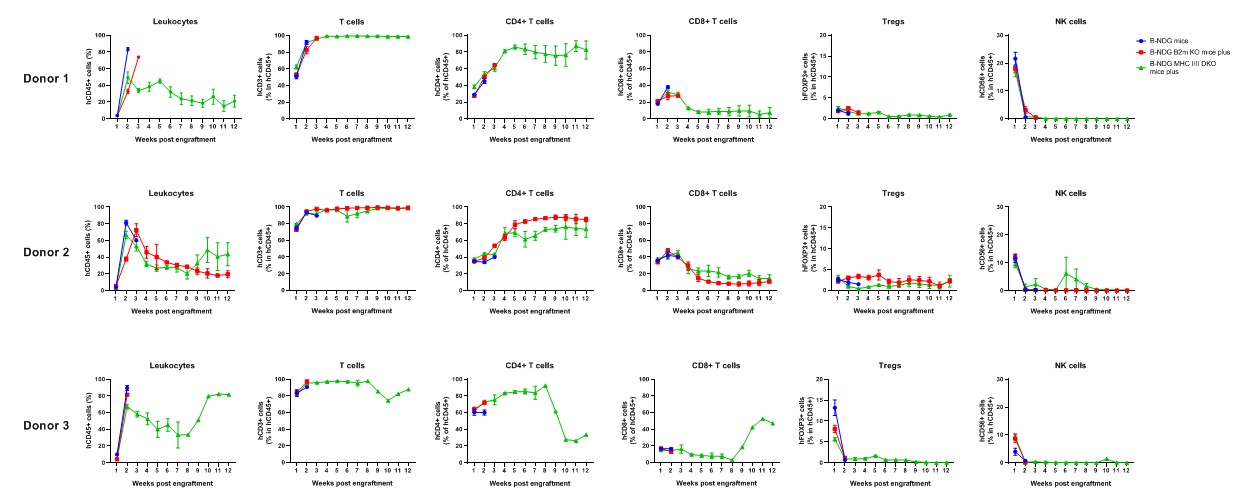
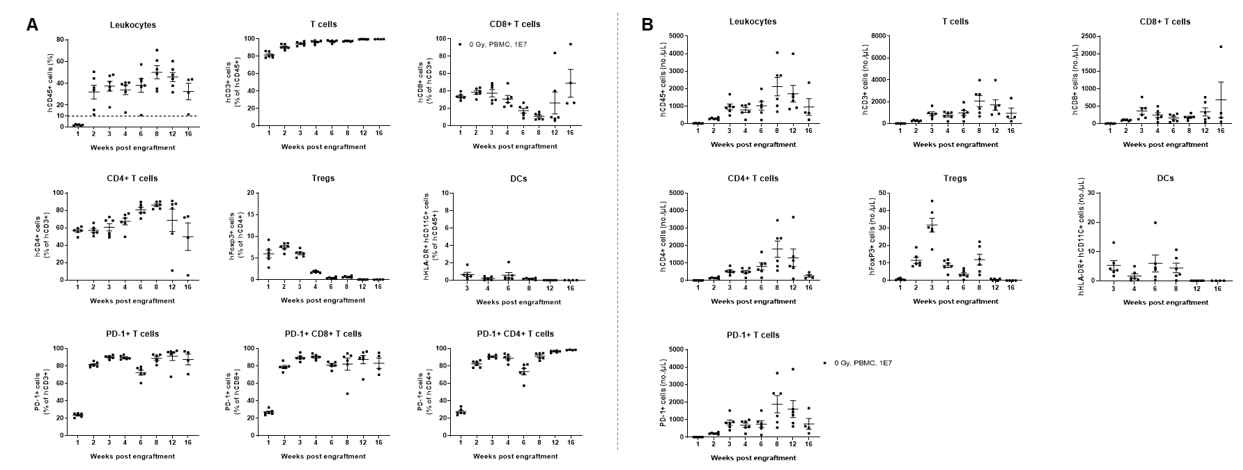
Comparison of the peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulations in B-NDG mice, B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus after human PBMC engraftment. Five weeks old of female B-NDG mice, B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus were respectively engrafted intravenously with human PBMCs (5 × 106) from three healthy donors (Donor 1-3) on day 0 (n=5). Blood was collected weekly after engraftment of human PBMC for flow cytometric analysis. The reconstitution levels of all the leukocytes analyzed were similar among the three mice.
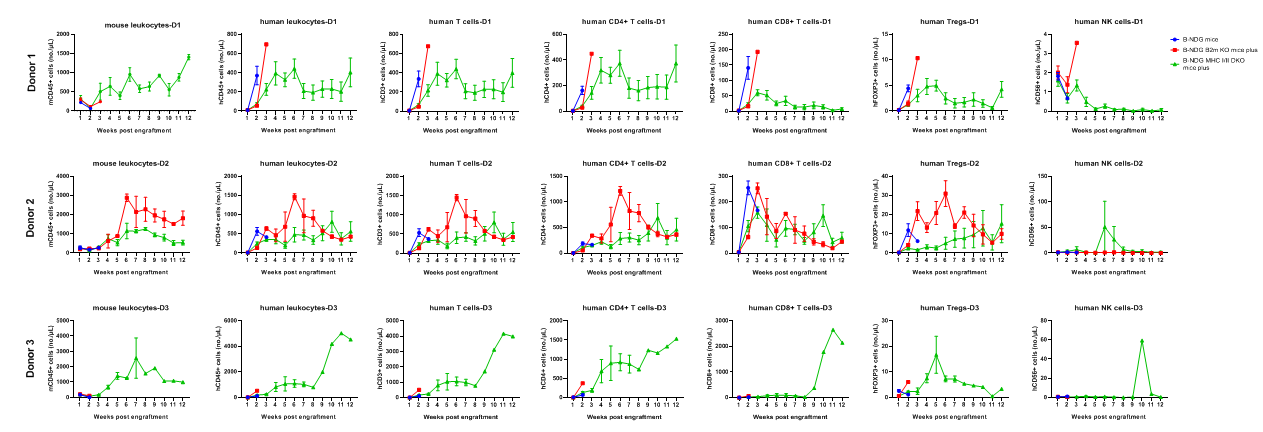
Comparison of reconstitution levels of human PBMCs among B-NDG mice, B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus. Five-week-old female B-NDG mice, B-NDG B2m KO mice plus and B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus were irradiated with 1.0 Gy and then engrafted intravenously with human PBMCs (5×106) from three healthy donors (Donor 1-3) on day 0 (n=6). Peripheral blood was taken weekly to analyze the reconstitution level of human immune cells. The experiment was ended 90 days after reconstitution. The results showed that regardless of which donor derived PBMCs were implanted, various types of human T cells could be reconstituted in B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus. However, the numbers of all reconstituted cells in B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus were lower than those in B-NDG mice and B-NDG B2m KO plus mice. Donor 3 has the most severe GvHD, and its human T cells and CD4 + T cells reconstitute the largest number.
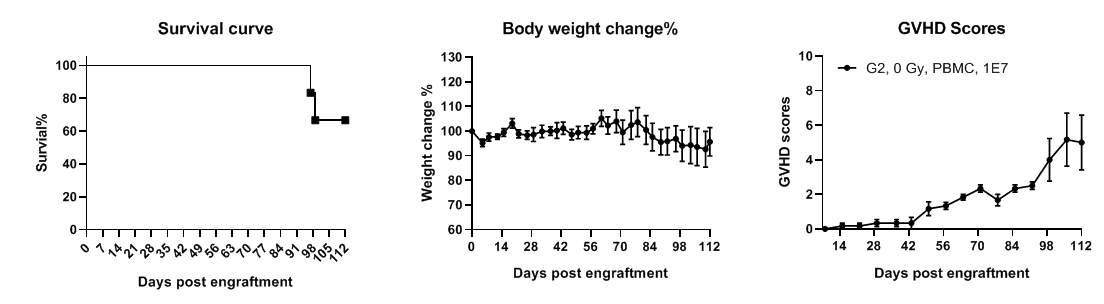
B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus has a long life span and reduced severity of GvHD when engrafted with human PBMCs. B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus were engrafted intravenously with human PBMCs (1×107) on day 0 (n=6). Survival rates of the mice were analyzed with Kaplan Meier survival curves. Body weight was measured twice a week. Clinical signs of GvHD were scored once a week. Euthanasia was implemented when the body weight decreased more than 20%. Meanwhile, the GvHD score of the mouse was recorded as 10. Results showed that all the mice can live up to 96 days. During this period, apart from weight loss, there were no other obvious symptoms of GvHD. Values were expressed as mean ± SEM.
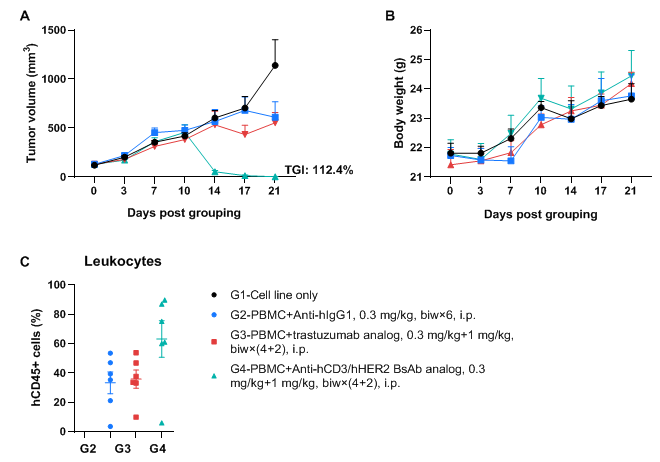
A NCI-N87 human gastric cancer model was established using human PBMCs engrafted B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus and the efficacy of anti-hCD3/hHER2 bispecific antibody was verified. Human gastric cancer cell line NCI-N87 (1×107) were subcutaneously inoculated in B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus. Human PBMCs (1×107) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG MHC I/II DKO mice plus (female, 6-9-week-old, n=6) 3 days after cell line inoculation. Anti-hCD3/hHER2 BsAb analog (in-house) and Anti-hHER2 antibody trastuzumab analog (in-house) were injected intraperitoneally 3 days after tumor inoculation. The animals were grouped into control and treatment when the tumor volume reached to 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with drugs. (A) Tumor volume; (B) Body weight. (C) Frequency of human CD45+ cells taken from peripheral blood at the end point. Results showed that anti-hCD3/hHER2 bispecific antibody significantly inhibited tumor growth with dose-dependent. Values are expressed as averages ±SEM.