NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen/Bcgen • 110586
| Product name | B-NDG mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 110586 |
| Strain name | NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | NOD scid |
| NCBI gene ID | 16186 |
| Aliases | Prkdc: DNA-PKcs, DNAPDcs, DNAPK, DNPK1, DOXNPH, HYRC1, XRCC7, dxnph, p460, scid, slip Il2rg: CD132, [g]c, gamma(c), gc, p64 |
| Application | Immune reconstitution, CDX, transplantation, drug evaluation |
on this page
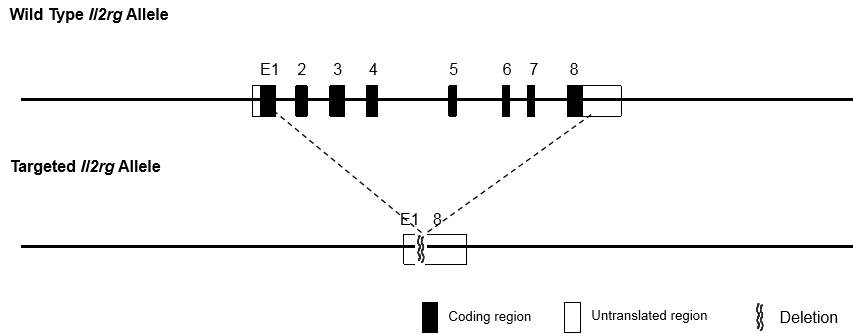
The immunodeficient B-NDG mice (NOD.CB17-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Bcgen/Bcgen) was independently designed and generated by Biocytogen. B-NDG mice were generated by deleting the Il2rg gene from NOD scid mice with severe immunodeficient phenotype. This mouse model lacks mature T cells, B cells and functional NK cells. It is internationally recognized as an immunodeficient mouse model well suited for human-derived tissue or cell engraftment.
B-NDG mice: Combined NOD scid-Il2rg null background features, severe immunodeficient phenotype, absence of mature T cells, B cells, and functional NK cells, decreased function of macrophages and dendritic cells. It is very suitable for the transplantation of human hematopoietic stem cells (CD34+ HSCs) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to obtain humanized mice with human immune system.
Beijing Biocytogen Co., Ltd. has applied for the B-NDG trademark registration for its use in different classes of goods/services (Class 5, Class 31, Class 42 and Class 44). Each letter in the name stands for: B-Biocytogen; N-NOD background; D-DNAPK (Prkdc) null; G-IL2rg knockout.
Detailed information of each class (until the date of application):
Class 5:medicines for human purposes; leeches for medical purposes; diagnostic biomarker reagents for medical purposes; preparations of microorganisms for medical or veterinary use; dietetic foods adapted for medical purposes;reagents for veterinary purposes;insecticides;wadding for medical purposes; stem cells for veterinary purposes
Class 31:live animals; poultry, live; fish, live; crustaceans, live; trees; grains [cereals]; plants; seeds for planting / plant seeds; hay; animal foodstuffs
Class 42: quality control; chemical research; biological research; clinical trials; material testing
Class 44:pharmacy advice; hospital services; artificial insemination services; diet and nutrition guidance; animal breeding; veterinary assistance; artificial insemination services (for animals); in vitro fertilization services/in vitro fertilization services (for animals); rental of sanitation facilities; in vitro fertilization services/in vitro fertilization services

1. Breeding facilities
2. Food
3. Water
4. Bedding
5. Breeding environments
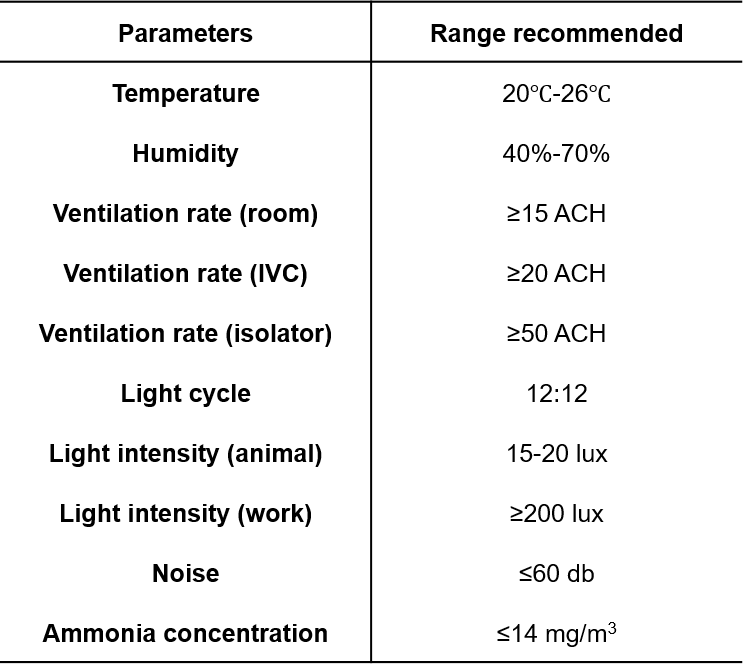
6. Transportation
7. Adaptive feeding
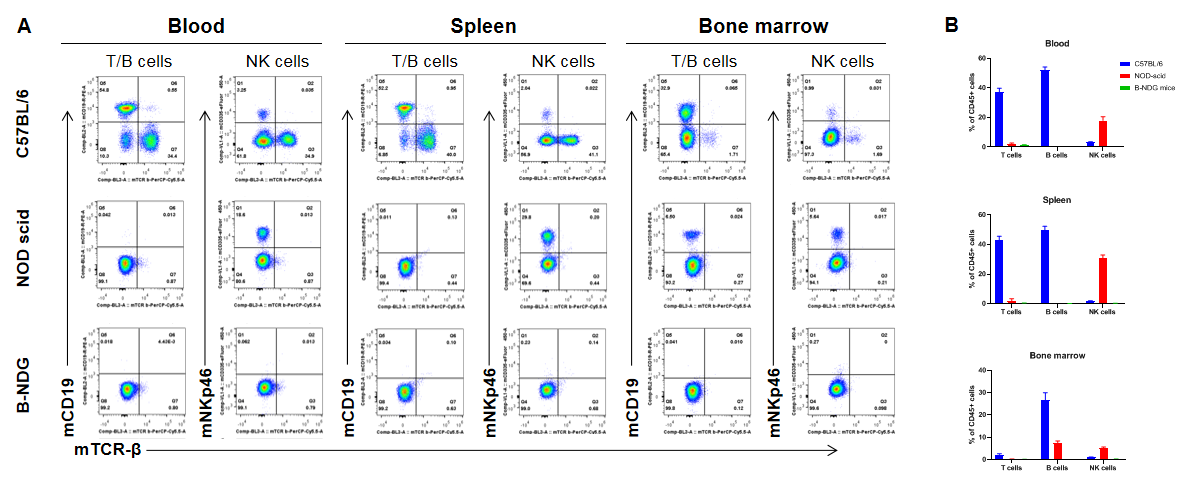
Complete loss of T, B and NK cells in B-NDG mice. Blood, spleen and bone marrow were collected from C57BL/6, NOD scid and B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=3). Leukocyte subpopulations were analyzed by flow cytometry analysis. A. Representative FACS plots. B. Statistical analysis of FACS. Results showed that T cells, B cells and NK cells were detectable in all tissues of C57BL/6 mice. Only NK cells were detectable in blood and spleen of NOD scid mice. But none of the three cells were detectable in any tissue of B-NDG mice.
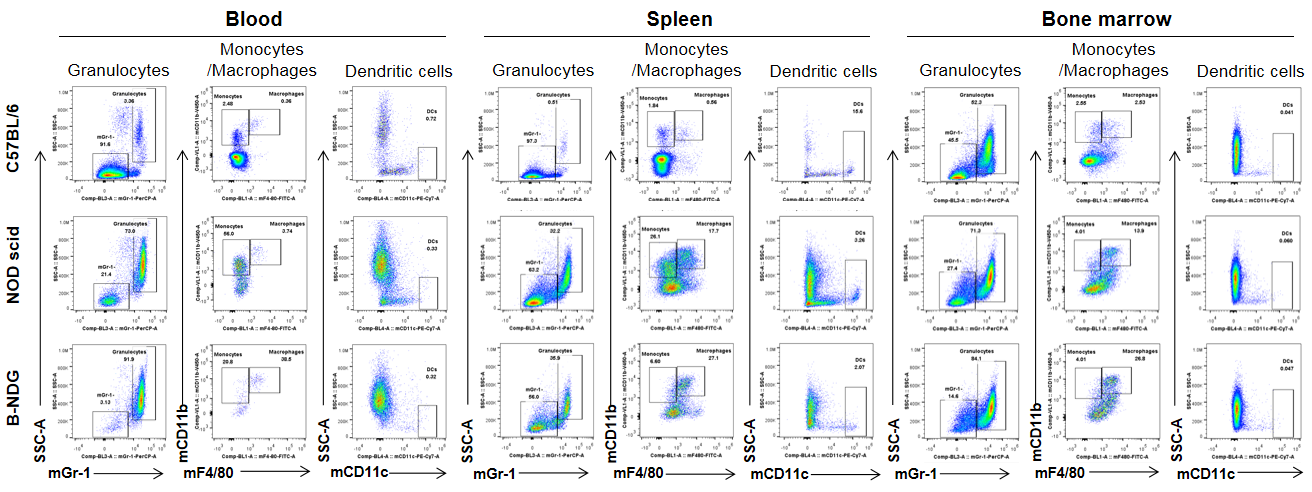
Analysis of myeloid cells in B-NDG mice. Blood, spleen and bone marrow were collected from C57BL/6, NOD scid and B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=3). Leukocyte subpopulations were analyzed by flow cytometry analysis. A. Representative FACS plots. B. Statistical analysis of FACS. Results showed that percentages of granulocytes and monocytes/macrophages of blood, spleen and bone marrow in B-NDG mice were relatively higher than that in wild-type C57BL/6 and NOD scid mice. But the percentages of DCs were lower in B-NDG mice than that in wild-type C57BL/6 and NOD scid mice.
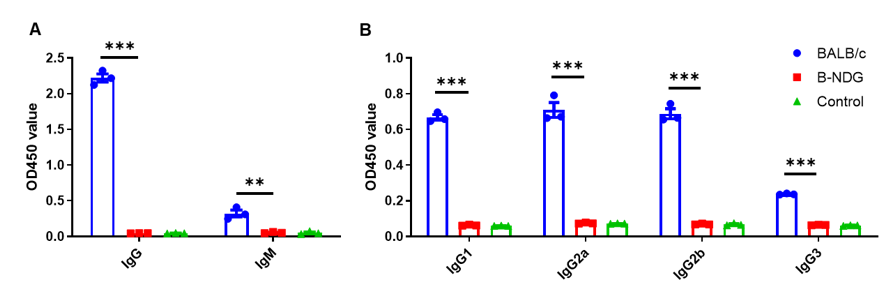
Complete loss of antibody production in B-NDG mice. Serum were collected from BALB/c mice and B-NDG mice. 1% BSA was added as control group. Mouse antibodies were detected with ELISA method. (A) Mouse IgG and IgM detection. (B) mouse IgG subclasses detection. Results showed that mouse IgG, IgM and IgG subclasses were detectable in serum of BALB/c mice, but not detectable in serum of B-NDG mice. These results demonstrate a complete loss of antibody production in B-NDG mice.
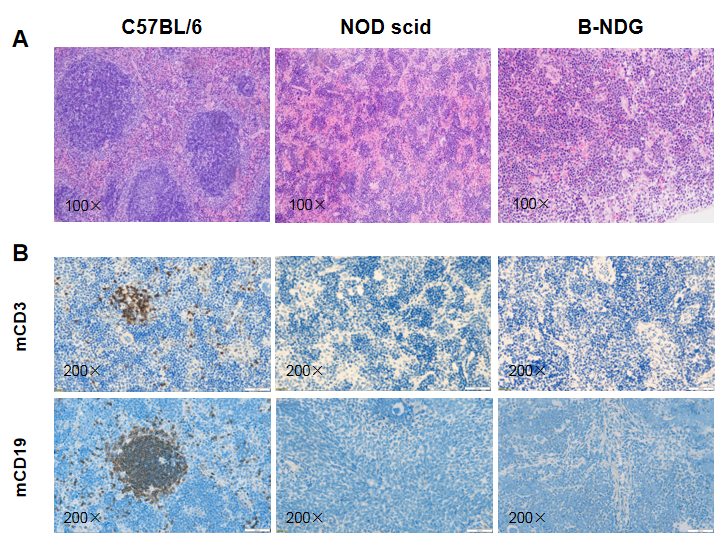
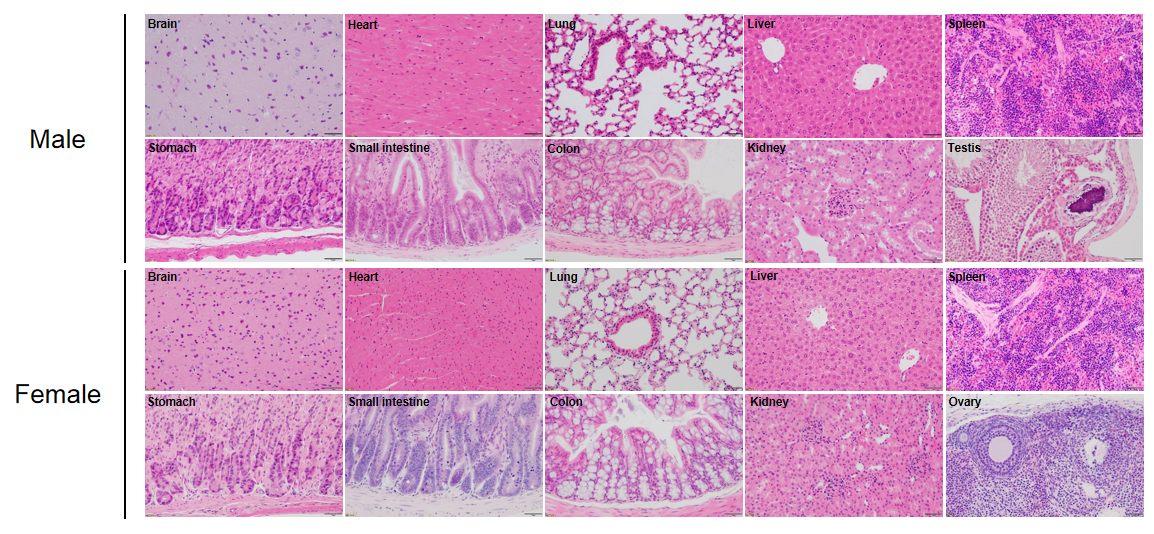
Histological analysis of mouse spleen. Spleen tissues of C57BL/6, NOD scid and B-NDG mice were respectively subjected to HE staining and immunohistochemical analysis (female, 9-week-old, n=3). (A) Splenic tissue HE staining. The results showed that the splenic structure of C57BL/6 mice was normal and the follicles were clear; The splenic structure of NOD scid mice showed white pulp hypoplasia; But B-NDG mice showed a complete disappearance of follicular structure. (B) Immunohistochemical analysis of T cells and B cells in spleen. Mouse T cells and B cells were respectively detected with anti-mouse CD3 antibody or anti-mouse CD19 antibody. The results showed that the number and distribution of mCD3+ T cells and mCD19+ B cells in the spleen tissue of C57BL/6 mice were normal (brown); But both T cells and B cells were not detectable in NOD scid mice and B-NDG mice, indicating that there were no T cells and B cells in spleen of NOD scid mice and B-NDG mice.
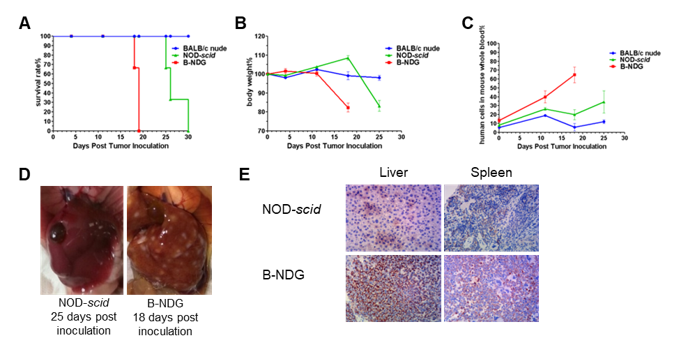
Raji lymphoma cell line can successfully establish hematologic and metastatic mouse tumor model in B-NDG mice. Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice, NOD scid mice and BALB/c nude mice. (A) Survival curves of the three strain of mice; (B) Body weight change; (C) The whole blood were collected from the orbital venous plexus of mice every week. Percent of human cells in the whole blood cells were assessed by qPCR; (D) B-NDG mice and NOD scid mice were euthanized and livers were respectively dissected at 18 or 25 days after cell inoculation. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis of human cells in mouse liver and spleen. Human lymphoma cells were detected with anti-human mitochondrial membrane protein antibody. These results showed that CDX mouse model with B-NDG mice had the lowest survival rate, fasted body weight loss compared to the CDX model with nude mice and NOD scid mice. The number of liver metastases in B-NDG mice was significantly higher than that of NOD scid mice. More human lymphoma cells were detected in liver and spleen of B-NDG mice compared to that in NOD scid mice. The results demonstrated that B-NDG mice was the best strain of mice to establish human-derived tumor models compared with nude mice and NOD scid mice.
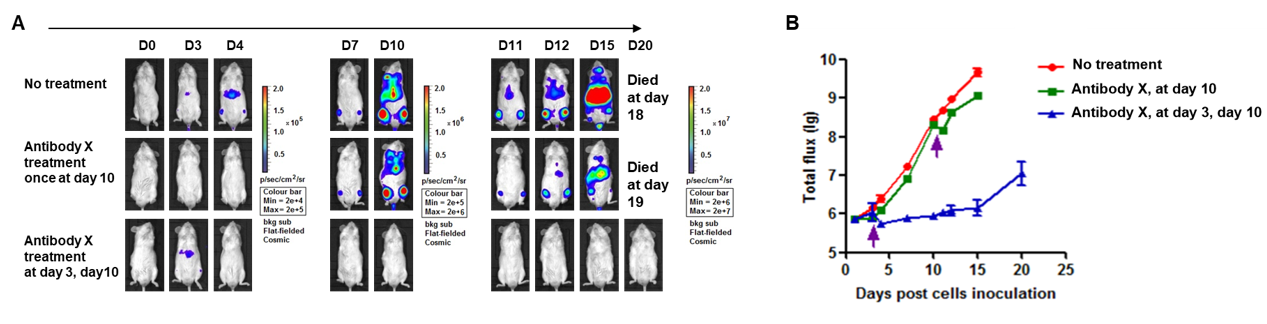
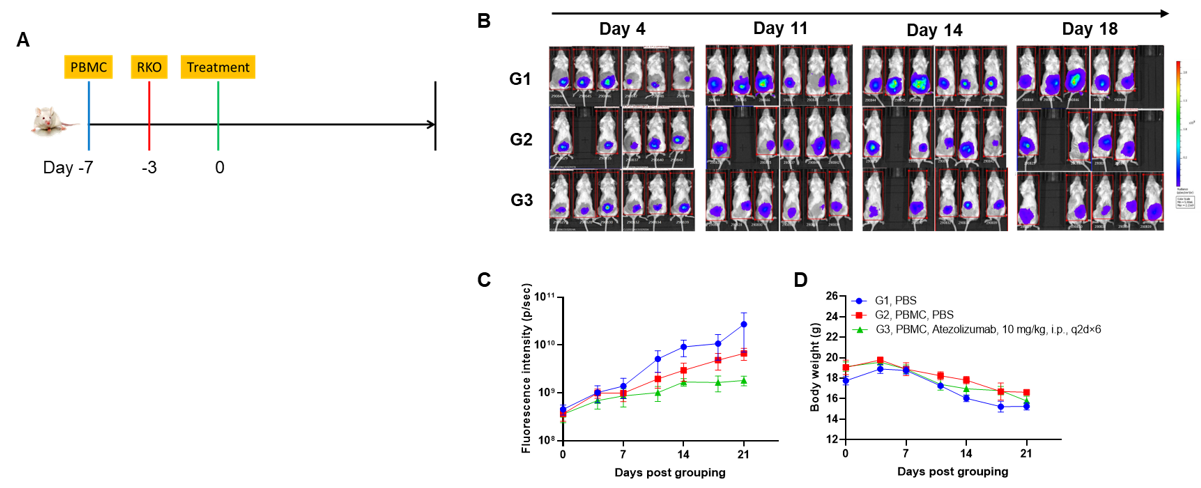
A Raji lymphoma mouse model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of antibody X was verified. B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice and divided into 3 groups: no dosing group, day 10 dosing group, day 3 and day 10 dosing group. Both dosing groups were given the same dose of antibody X and tumor growth was observed with imaging at different time points. (A) Imaging of mice to observe tumor growth; (B) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells. The results showed that early antibody therapy (started 3 days after Raji cell transplantation and re-administered 10 days later) was significantly more effective than late antibody therapy (started 10 days after Raji cell transplantation). B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of anti-human antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
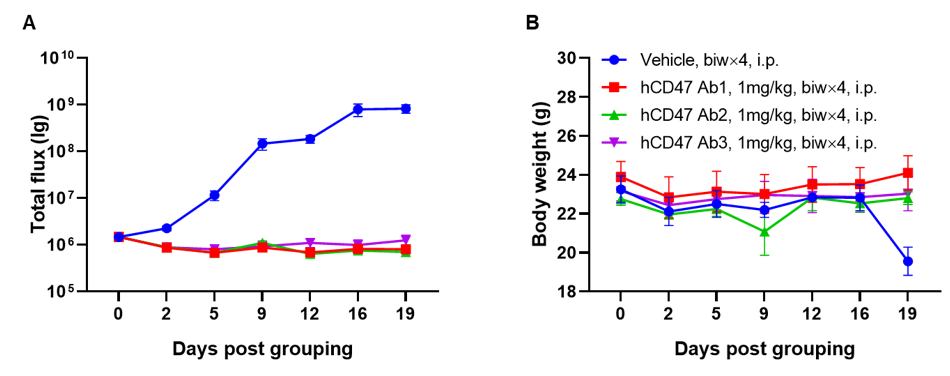
A Raji lymphoma mouse model was established using B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human CD47 antibodies were verified. B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5×105) were injected via tail vein of B-NDG mice. Small animal imager was used to observe tumor growth. When the fluorescence intensity of the tumor reaches about 1×106 p/sec, the animals were divided into one control group and three treatment group (n=6). (A) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells; (B) Body weight. The results showed that all three anti-human CD47 antibodies could significantly inhibit tumor growth. B-NDG mice is a powerful model for efficacy verification of anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
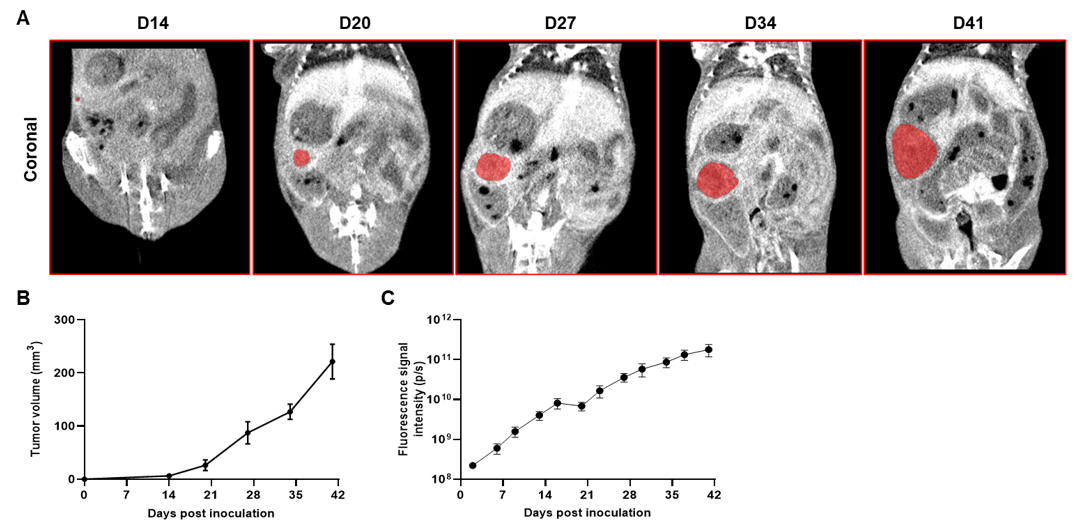
Imaging of orthotopic model for pancreatic cancer by Micro-CT. B-luc MIA Paca-2 cells were orthotopically inoculated into B-NDG mice (n=5). (A) Micro-CT images of orthotopic model in B-NDG mice were scanned from day 14 after inoculation. The images showed the coronal plane of the abdomen, with red areas representing the actual tumor. (B) Tumor growth curve was recorded by contrast-enhanced CT. (C) Dynamic changes of total fluorescence signal in the tumor site after inoculation. The results showed that human pancreatic cancer cell line (B-luc MIA Paca-2 cells) could successfully form tumors in situ pancreas of B-NDG mice.
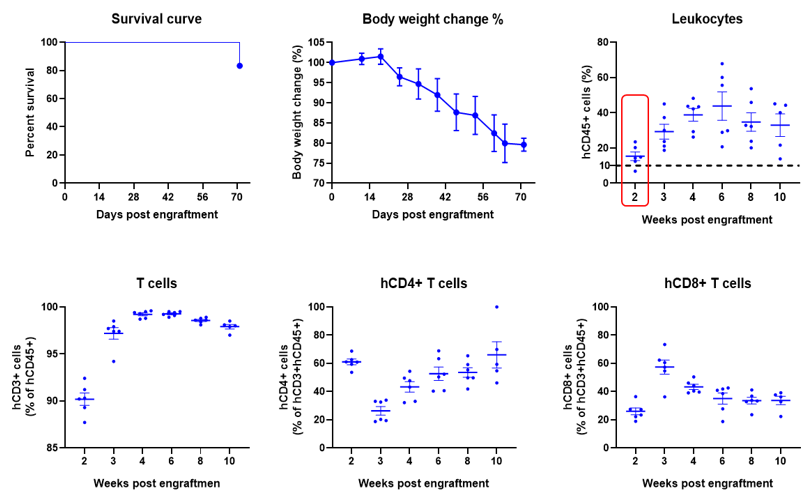
Engraftment of human PBMCs in B-NDG mice enhances reconstitution of human T cells. Human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenous engrafted into B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=6). Body weight of each mouse was recorded every week. Death data were collected every day. The peripheral blood was taken at different time points to analyze the reconstitution levels of human immune cells. B-NDG mice showed a high percentage of human CD45+ cells and T cells. B-NDG mice exhibit shortened survival and reduced body weight likely due to GvHD caused by a high Percentages of human T cell reconstitution. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
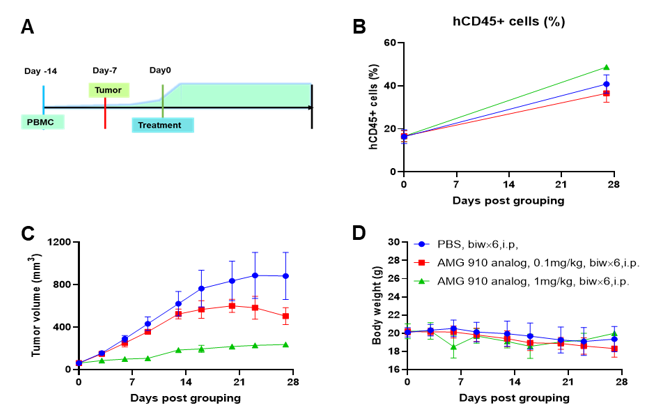
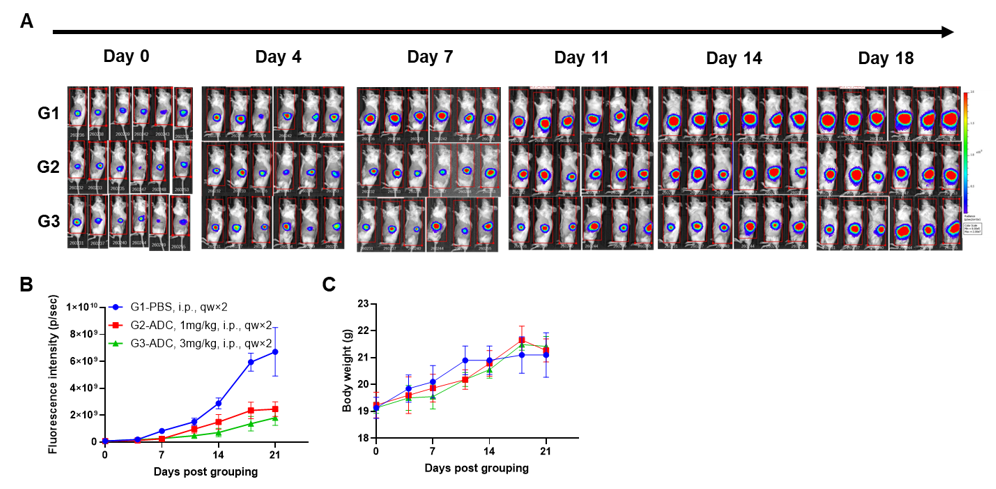
A NUGC4 human gastric cancer model was established using human PBMCs engrafted B-NDG mice and the efficacy of anti-human CD3/CLDN18.2 bispecific antibody was verified. Human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG mice (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Human gastric cancer cell line NUGC4 (5E6) were inoculated subcutaneously 7days after PBMCs engraftment. AMG 910 (in house) was injected intraperitoneally 7 days after tumor inoculation. The animals were grouped into control and treatment when the tumor volume reached to 50-80 mm3 and the percentage of human blood hCD45+ cells ≥ 10%, at which time they were treated with drugs. (A) Schematic diagram of tumor model and drug delivery strategy; (B) Percentages of human CD45+ cells taken from peripheral blood on the day of administration (Day 0) and at the end point (Day 27); (C) Tumor volume; (D) Body weight. Results showed that the percentages of reconstituted human CD45+ cells continued to increase during administration. The anti-human CD3/CLDN18.2 bispecific antibody showed significant dose-dependent tumor suppression. B-NDG mice engrafted with human PBMCs can be used to establish tumor models and verify the efficacy of bispecific antibodies in vivo. Values are expressed as averages ±SEM.
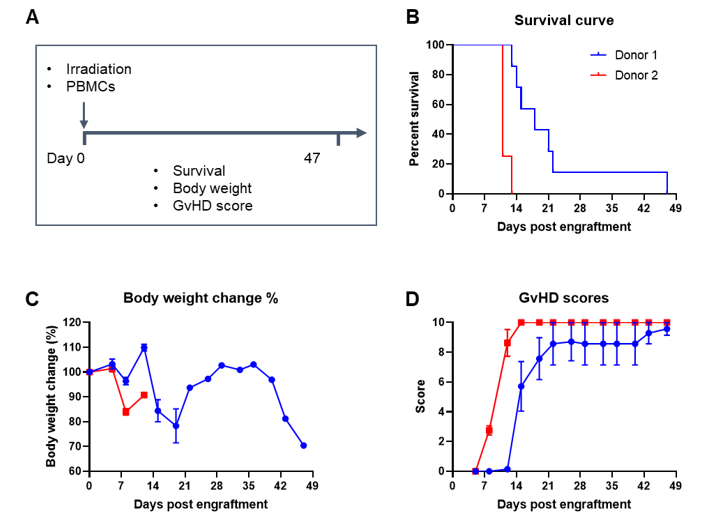
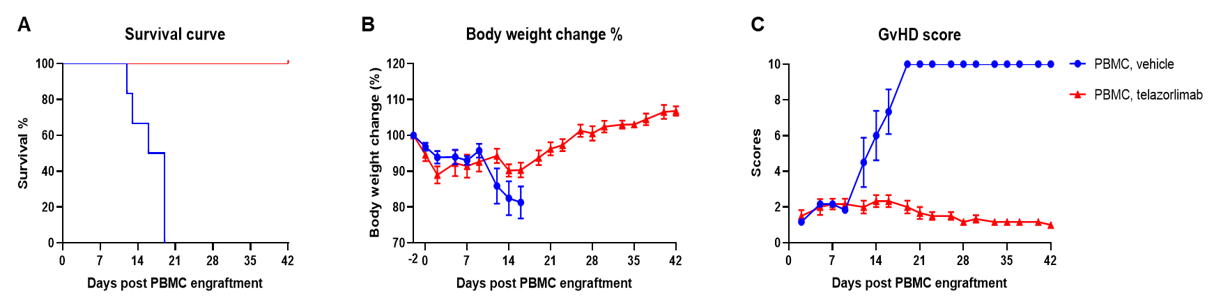
Engraftment of human PBMCs in B-NDG mice successfully constructed a graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) model. Human PBMCs (1E7) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG mice 4 hrs after 1.0 Gy irradiation (female, 8-week-old, n=7/8). Mice were weighed twice a week and the health status of mice were recorded every day. Each mouse was scored according to the GvHD scoring standard. (A) Schematic diagram of the model-building strategy; (B) Survival curve; (C) Changes of body weight; (D) GvHD score. The results showed that the survival rate and the body weight of B-NDG mice were significantly reduced after irradiated and PBMC engraftment. GvHD scores were significant increased. But the GvHD symptoms vary between different donor sources of PBMCs. Therefor, B-NDG mice can be used to establish GvHD mouse model. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
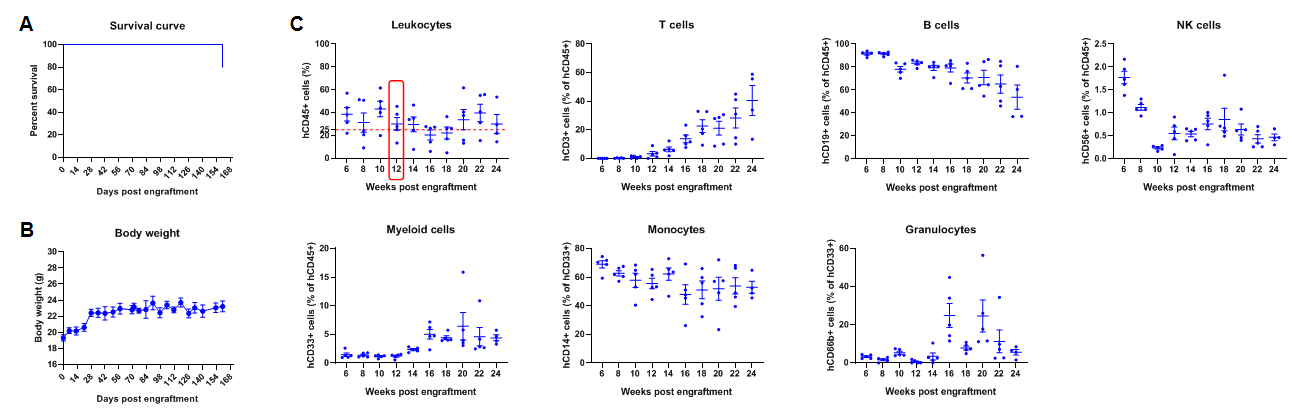
Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in adult B-NDG mice successfully reconstituted human T and B cells, a small number of NK and myeloid cells. Human CD34+ HSCs (1E5) were engrafted via the tail veins of B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=5) within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 1.0 Gy of X-ray. The reconstitution level of human immune cells in peripheral blood was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Survival curve of human CD34+ HSCs engrafted mice; (B) Body weight; (C) Percentages of reconstituted human immune cells. The results showed that no mice died before 22 weeks of human CD34+ HSCs engraftment. Only one mouse died after 160 days of reconstitution. All the mice continued to gain body weight. The percentage of human CD45+ cells exceeded 25% at 6 weeks of reconstitution and can still be maintained at about 25% after 24 weeks of reconstitution. The percentage of human T cells begins to increase persistently at 10 weeks of reconstitution. The percentage of human B cells reached more than 90% at 6 weeks of reconstitution and continued to decline after 8 weeks. A small percentage of human NK cells, total myeloid cells, monocytes and granulocytes can also be detected throughout the reconstitution process.
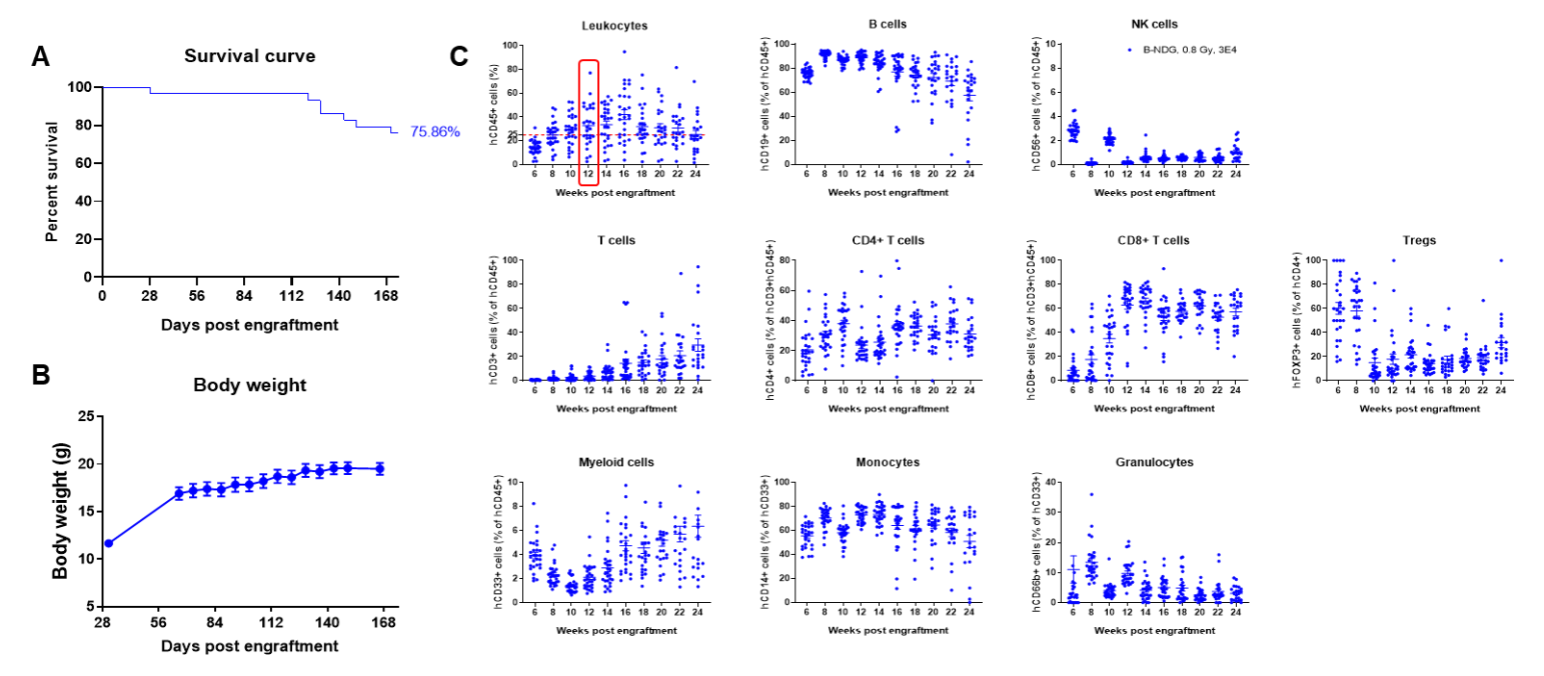
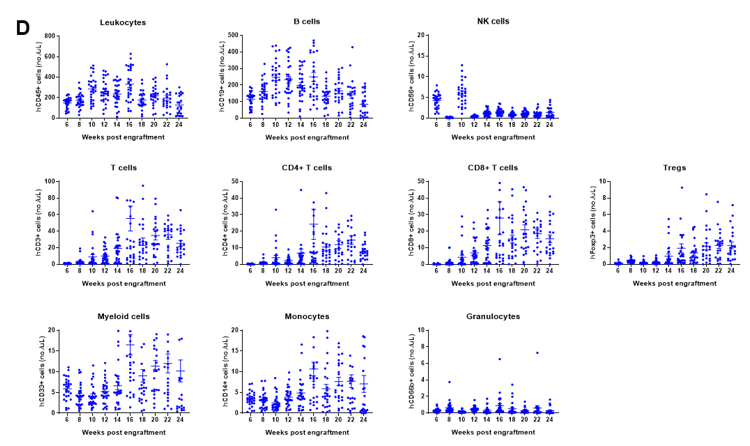
Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in neonatal B-NDG mice successfully reconstituted human T and B cells, a small number of NK and myeloid cells. Human CD34+ HSCs (1.5E5) were engrafted via the facial vein of B-NDG mice (male and female, 24-8 hour-old, n=28) within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 0.8 Gy of X-ray. The reconstitution level of human immune cells in peripheral blood was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Survival curve of human CD34+ HSCs engrafted mice; (B) Body weight; (C) Percentages of reconstituted human immune cells; (D) Number of human immune cells. The results showed that the mice began to die from 17 weeks of reconstitution. But the lived mice continued to gain body weight. The percentage of human CD45+ cells exceeded 25% from 8 weeks of reconstitution. But there are obvious individual differences. The percentage of human T cells began to increase continuously at 10 weeks of reconstitution. Human CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and Tregs could be detected at a relatively high level. The percentage of human B cells reached more than 70% at 6 weeks of reconstitution and continued to decline slowly after reaching the highest value at 8 weeks. A small percentage of human NK cells, total myeloid cells, monocytes and granulocytes can also be detected throughout the reconstitution process.
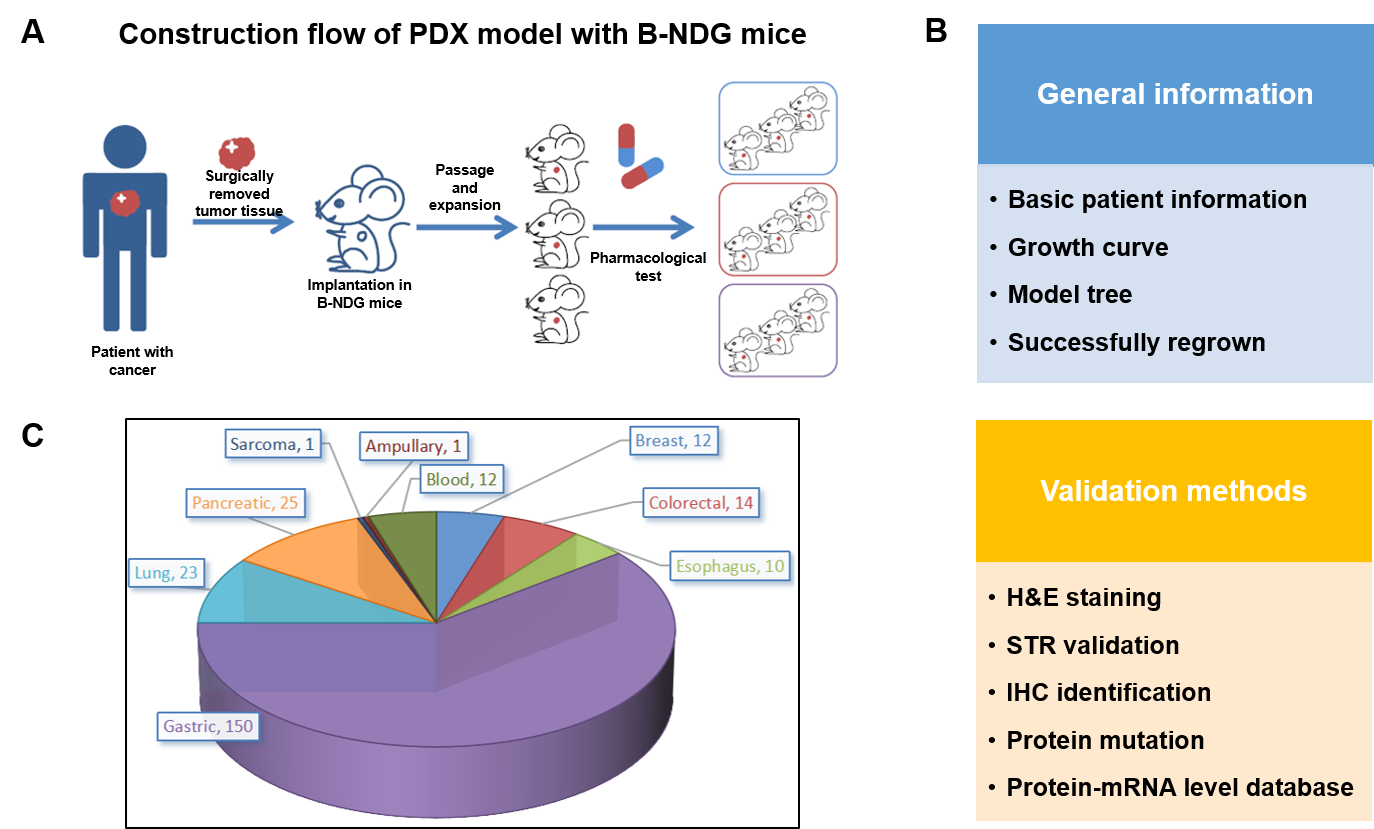
PDX (Patient-derived xenograft) models were successfully established in B-NDG mice. (A) General construction flow of the PDX model; (B) General information of tumor to be collected and the validation methods for the PDX model. (C) 248 PDX models derived from 9 types of tumors have been successfully established with B-NDG mice in Biocytogen by now.
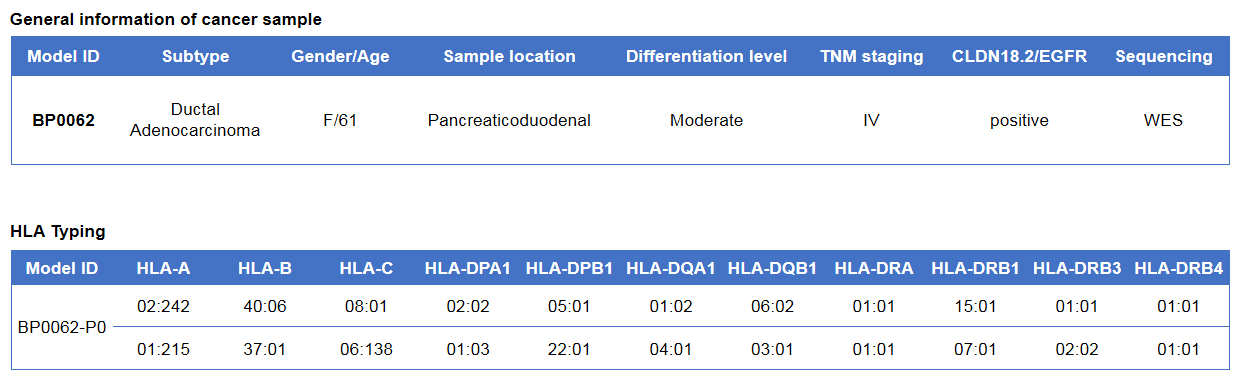
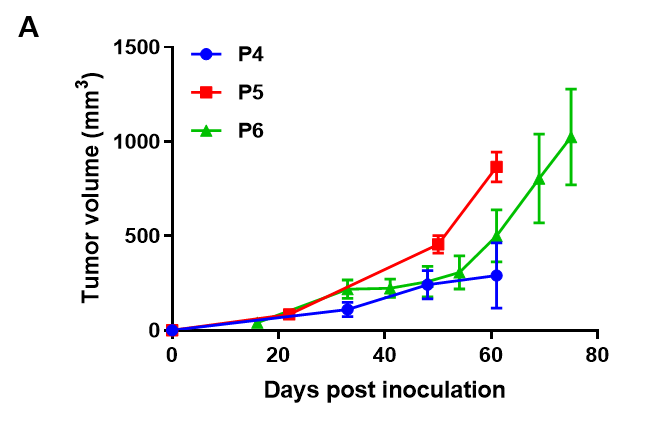
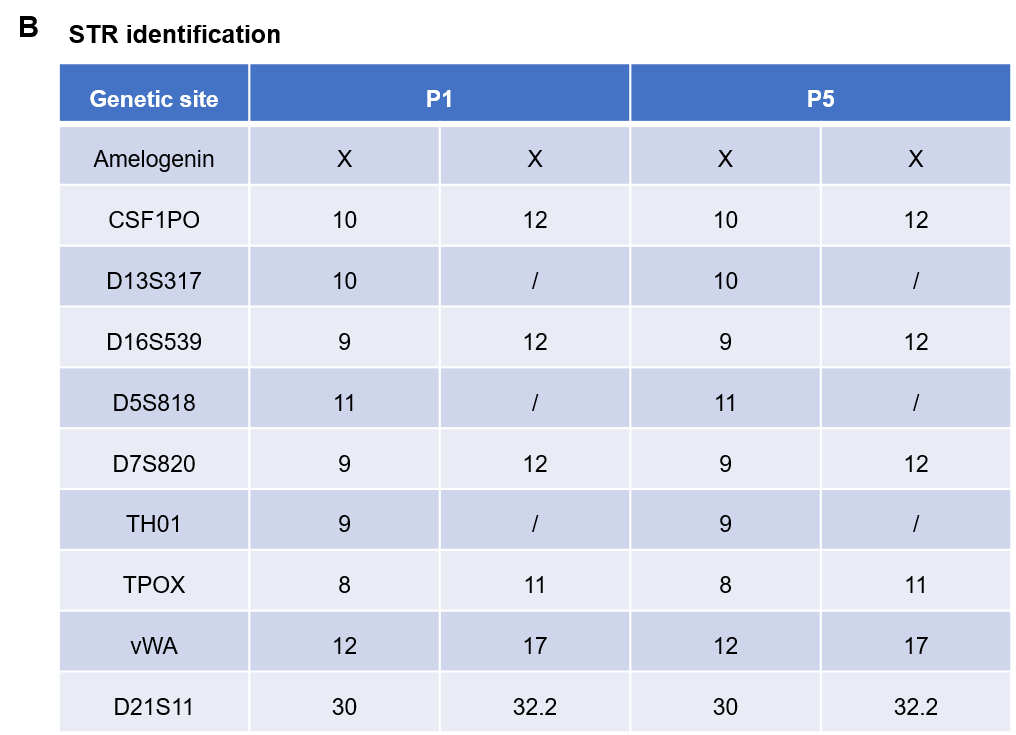
Pancreatic cancer BP0062 can successfully establish PDX model. Primary tumor sample was obtained from patient undergoing surgery for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumor pieces were subcutaneously inoculated into B-NDG mice. (A) Growth curve of passage 4, 5, 6 of the PDX tumor; (B) STR identification results of passage 1 and passage 5. Results showed that PDX model was successfully established in B-NDG mice implanted with pancreatic cancer BP0062. The STR of 5th generation of tumor cells is 100% matched to that of 1st generation, indicating that there was no change in the genetic background of the 5th generation of tumor tissue. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
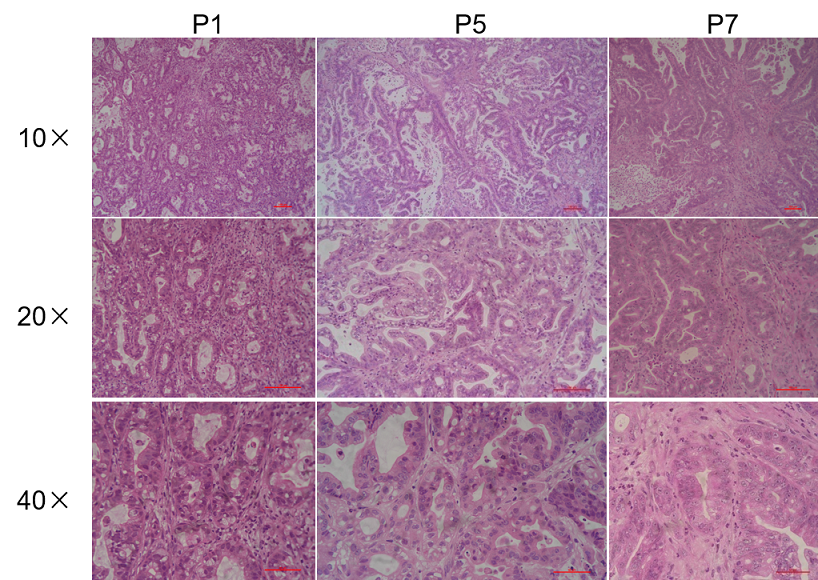
Histopathological analysis of BP0062 PDX tumor in B-NDG mice. Tumor tissue was collected from PDX model established with Pancreatic cancer BP0062 and analyzed with H&E staining. Results showed that patient-derived xenografts were found to well recapitulate the structures in original patient sample and maintain similar heterogeneity in different generations.
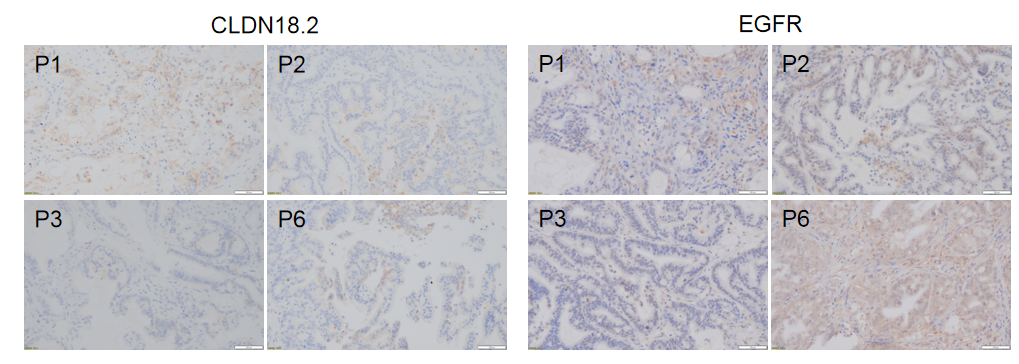
Immunohistochemical analysis of CLDN18.2 and EGFR in different generation of BP0062 PDX tumor tissue. Human CLDN18.2 and EGFR were respectively detected with anti-human CLDN18.2 antibody or anti-human EGFR antibody. The results showed that the number and distribution of CLDN18.2+ cells or EGFR+ cells in different generation of PDX tumor were obviously different (brown), indicating that the heterogeneity was maintained in different generation of PDX models.
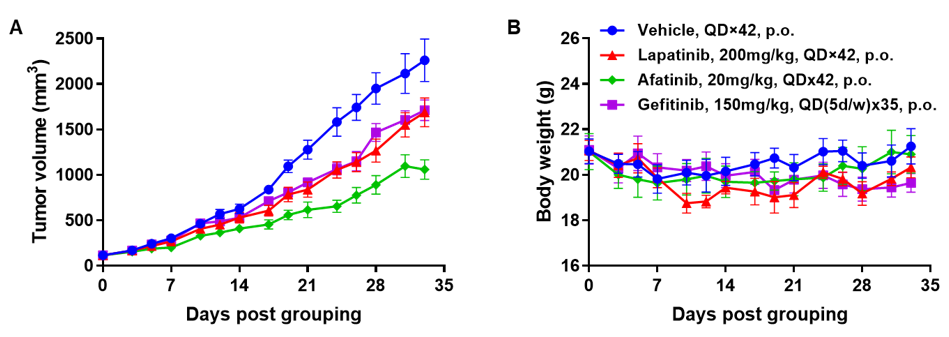
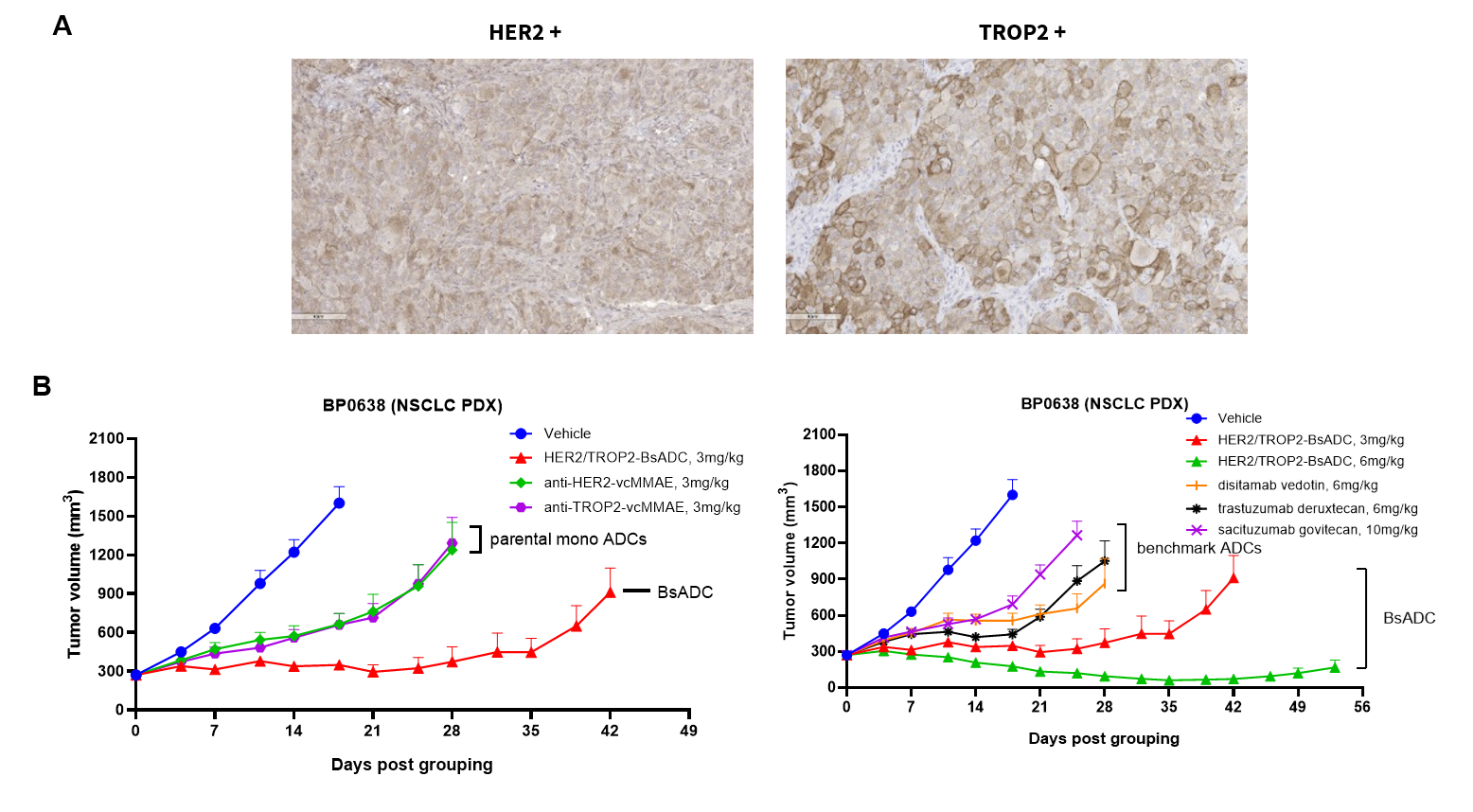
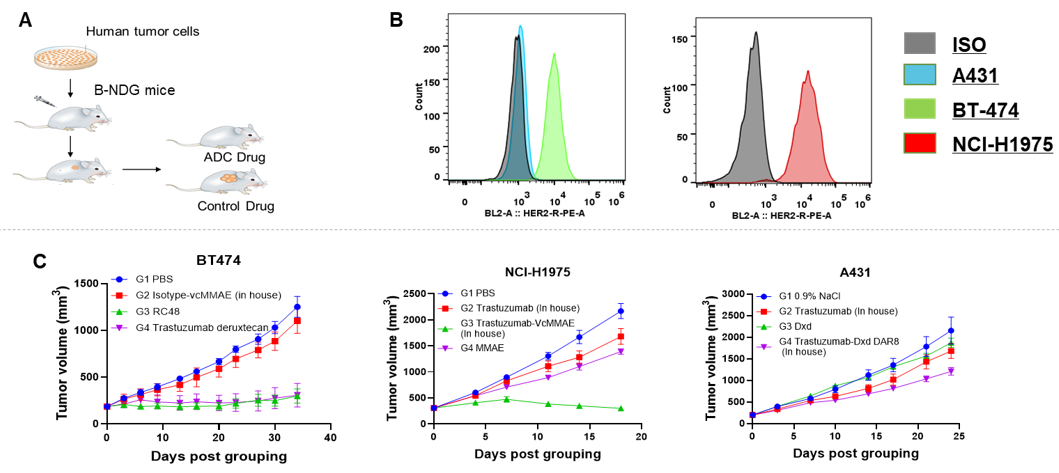
Antitumor activity of HER2-targeting and TROP2-targeting ADC drugs in NSCLC PDX model. (A) Expression analysis of HER2 and TROP2 in NSCLC (Non small Cell Lung Cancer) PDX (BP0638) tumor tissue by immunohistochemistry. The results showed both HER2 and TROP were low expression in this PDX model. (B) Efficacy verification of ADC drugs. PDX tumor pieces of BP0638 were subcutaneously implanted into B-NDG mice (n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 250-300 mm3, at which time they were treated with (HER2/TROP2-BsADC), two parental mono ADCs of the BsADC and other three commercial-derived ADC drugs (sacituzumab govitecan, disitamab vedotin, trastuzumab deruxtecan). The results showed that HER2/TROP2-BsADC had a stronger and longer inhibitory effect on tumor growth than ADCs. This inhibition was dose-dependent. Therefore, NSCLC PDX model of BP0638 provides a powerful preclinical NSCLC model for efficacy evaluation of various types of ADC drugs. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
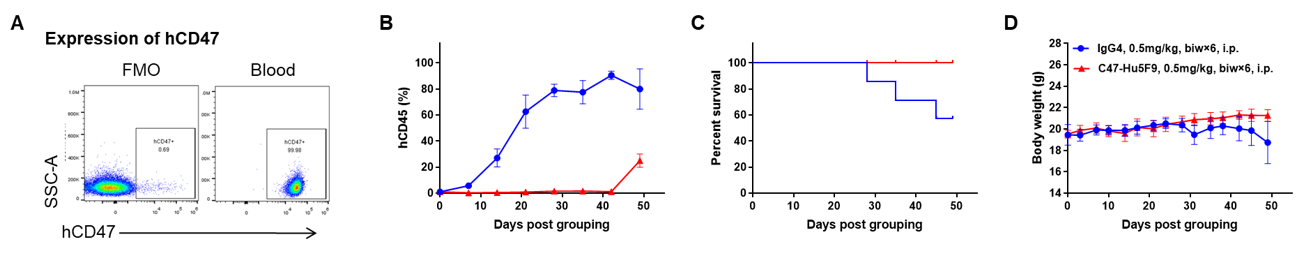
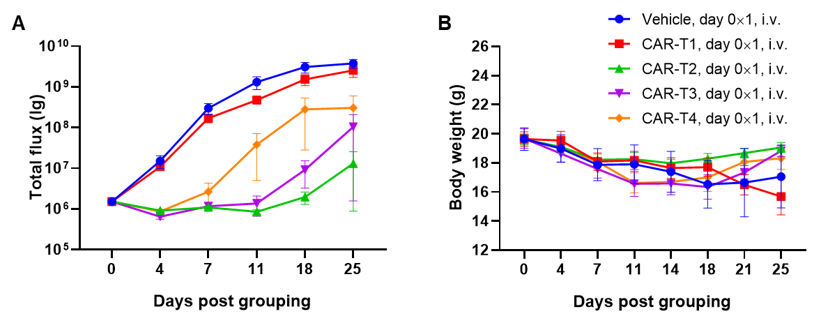
Antitumor activity of anti-human CD47 antibody in AML PDX model BP2010 established with B-NDG mice. (A) Human CD47 was highly expressed on the surface of tumor cells of BP2010; (B) The proportion of hCD45+ cells in the anti-human CD47 antibody treatment group was significantly reduced. PDX tumor cells of BP2010 were injected into B-NDG mice via tail vein (female, n=7). Mice were grouped when hCD45+ cells of PB reached approximately 1%, at which time they were treated with anti-human CD47 antibody Hu5F9 (in house) and schedules indicated in panel; (C) The survival rate of mice in the treatment group was significantly improved; (D) Body weight changes during treatment. The results indicated that AML PDX model of BP2010 provides a powerful preclinical AML model for efficacy evaluation of anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
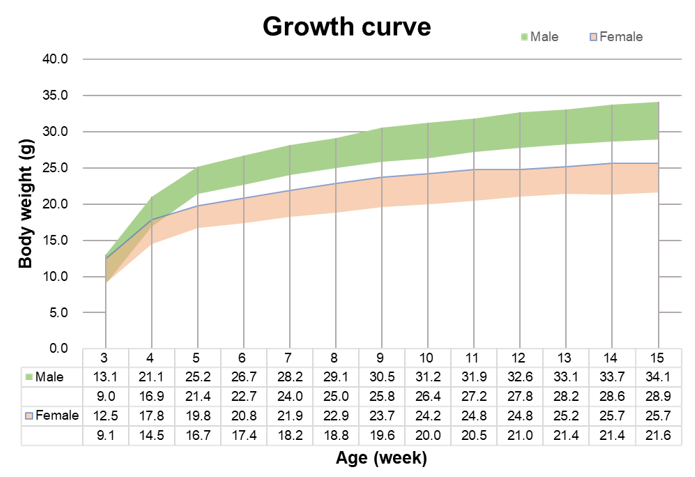
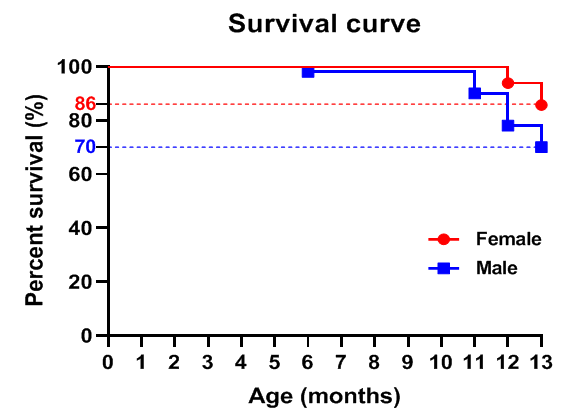
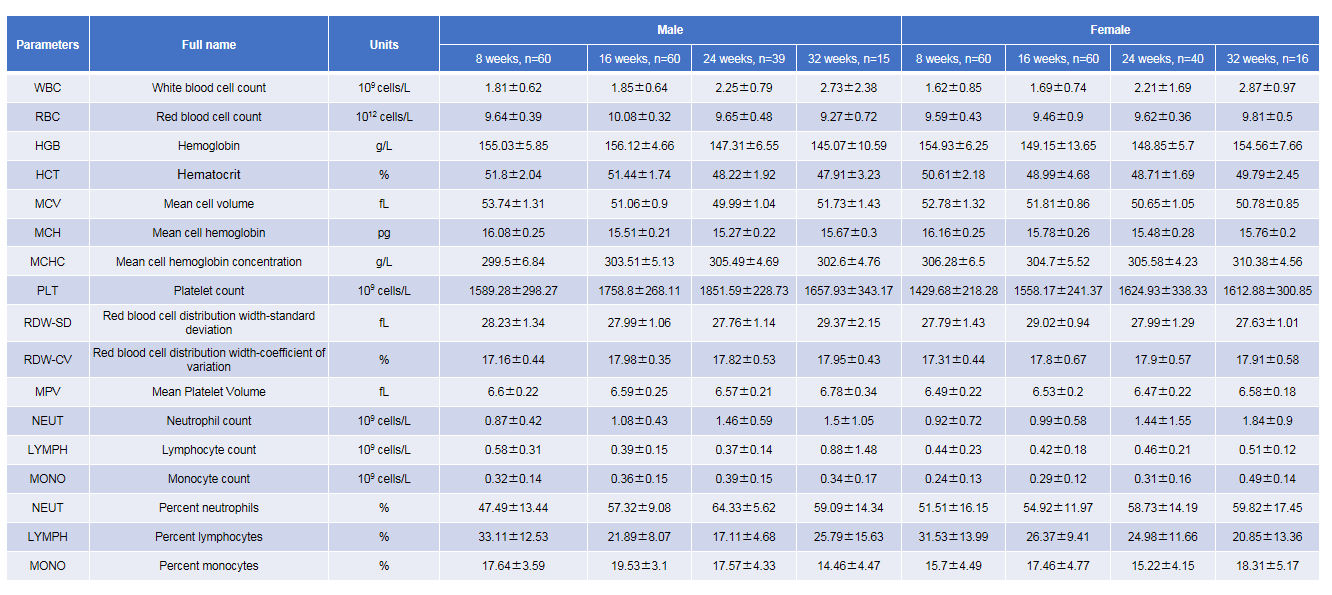
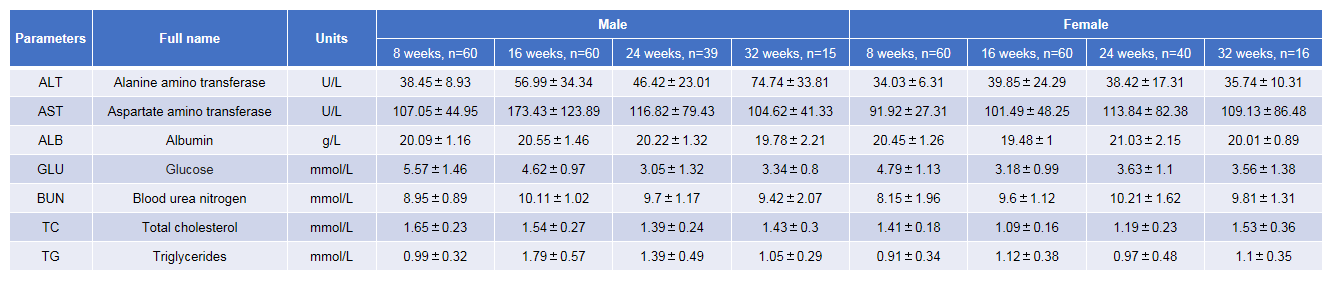
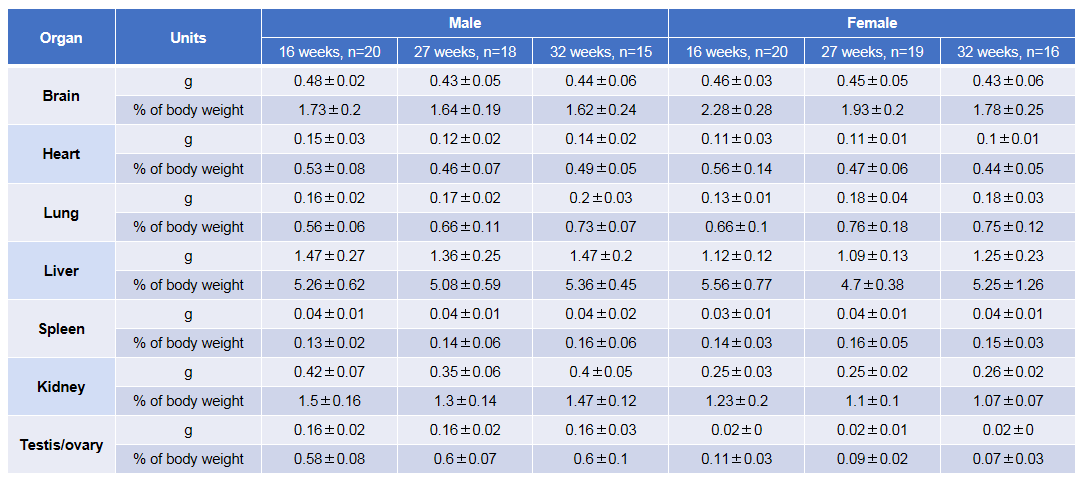
Growth curve of B-NDG mice.Three weeks old of newborn pups were obtained at weaning (50 males and 50 females, respectively). Body weight was measured on the same day of every week and lasted for 12 weeks. The lowest and highest values of mouse body weight in the table were calculated from the mean ± SD. The growth curve conforms to the normal distribution and the probability of random error falling within ± SD is 68%.