


NOD.CB17-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1BcgenIl15tm1(IL15)Bcgen/Bcgen • 112478
| Product name | huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 112478 |
| Strain name | NOD.CB17-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1BcgenIl15tm1(IL15)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | B-NDG |
| Aliases | IL-15 |
| Application | Promote differentiation of human NK cells |
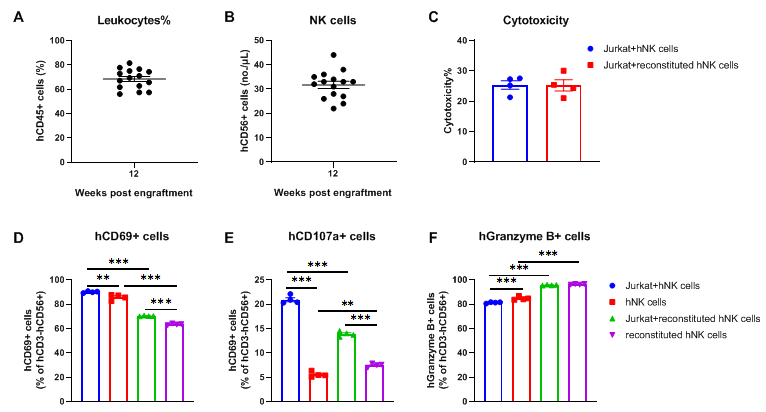
NK cells isolated from the spleen of huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice possess tumor-killing activity against Jurkat cells. NK cells were isolated from the spleen of huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice 14 weeks after hCD34+ HSCs engraftment (n=4). The isolated NK cells were cultured with human T lymphoblastoid cell line Jurkat cells and the cytotoxicity were measured with LDH assay. Human NK cells isolated from PBMCs were used as positive control. (A) The proportion of reconstituted human CD45+ cells ranged from 56% to 81%. (B) The number of reconstituted human NK cells ranged from 22 to 44 per microliter of blood. (C) There was no significant difference in cytotoxicity of reconstituted human NK cells compared to human PBMC-purified NK cells. (D-F) Activity markers of NK cells were detected with flow cytometry. Different proportions of NK cells expressing hCD69, hCD107a and hGranzyme B could be detected in reconstituted NK cells. After incubation with Jurkat cells, the proportion of NK cells expressing hCD69 and hCD107a increased. There was no significant change in the proportion of NK cells expressing hGranzyme B. Compared with PBMC-purified NK cells, the proportion of NK cells expressing hCD69 and hCD107a in reconstituted NK cells was lower. But the proportion of cells expressing hGranzyme B was higher. The results indicated that the reconstituted human NK cells in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice possess similar cytotoxicity compared to human NK cells purified from PBMCs.
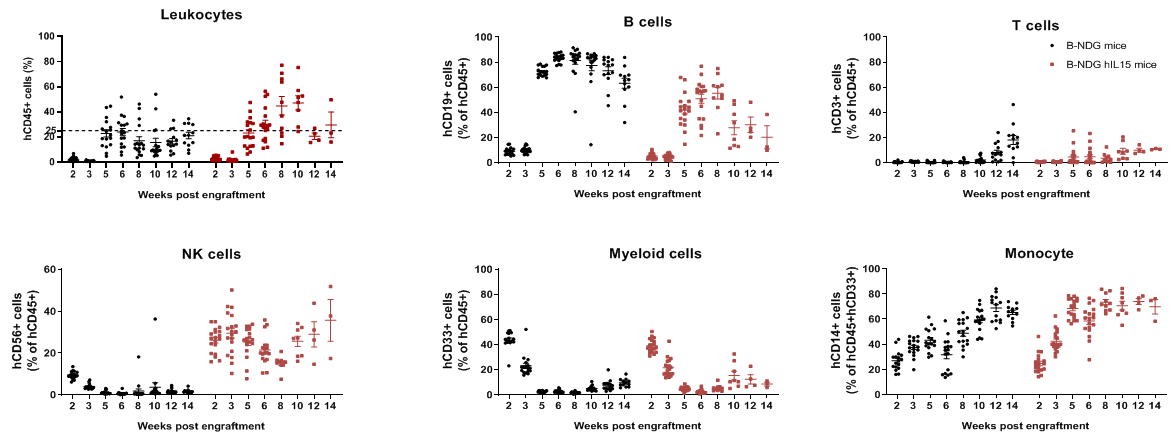
Human immune cell phenotyping in B-NDG hIL15 engrafted with human HSCs. Human CD34+ cells (0.15 M) were intravenously injected into homozygote B-NDG hIL15 (female, 6-week-old, n=19) and B-NDG mice (female, 6-week-old, n=17). All mice were treated with 1.6 Gy irradiation. Representative flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood lymphocyte from mice after engraftment with human CD34+ cells. B-NDG hIL15 showed a higher percentage of human NK cells compared with B-NDG. Our results suggest that human NK, T, and B cells in reconstituted B-NDG IL15 mice were successfully propagated.
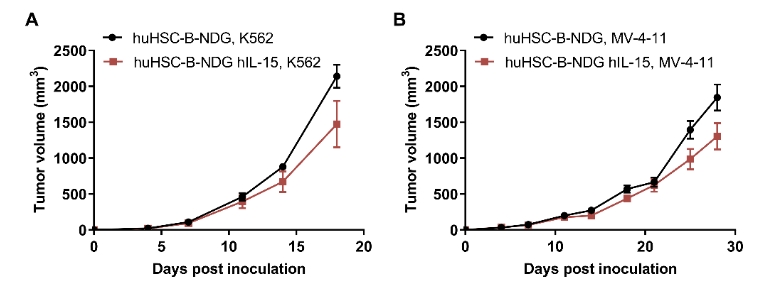
CDX model were well established on human immune system engraftment mice. Human CD34+ cells (0.15M) were intravenous implanted into homozygote B-NDG hIL15 (female, 7 week-old, n=30) and B-NDG mice (female, 7 week-old, n=30). All mice were treated with 1.6gry-irradiation. Mice were grouped as hCD45% ≥ 10%. K562 cells (1E6), MV-4-11 (1E7), Panc-1 (5E6) were subcutaneously implanted into B-NDG hIL15 and B-NDG mice respectively. (A-C) The mean ± SEM of tumor sizes. K562 and MV-4-11 were successfully tumorigenic on a mouse model of human HSC immune system reconstitution, and tumor growth was delayed in B-NDG hIL15 mice compared to B-NDG mice.
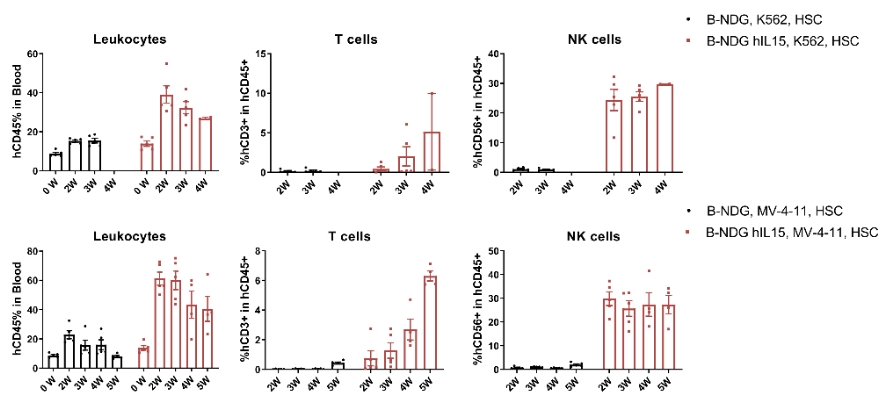
CDX model were well established on human immune system engraftment mice. Human CD34+ cells (0.15M) were intravenous implanted into homozygote B-NDG hIL15 (female, 7 week-old, n=30) and B-NDG mice (female, 7 week-old, n=30). All mice were treated with 1.6gry-irradiation. Mice were grouped as hCD45% ≥ 10%. K562 cells (1E6), MV-4-11 (1E7) were subcutaneously implanted into B-NDG hIL15 and B-NDG mice respectively. During the establishment of CDX model using K562 cells and MV-4-11, the proportion of immune cells in the blood of mice were measured. The results showed that during the establishment of tumor models, the proportion of leukocytes, T cells and NK cells in the blood of B-NDG hIL15 mice was higher than B-NDG mice.
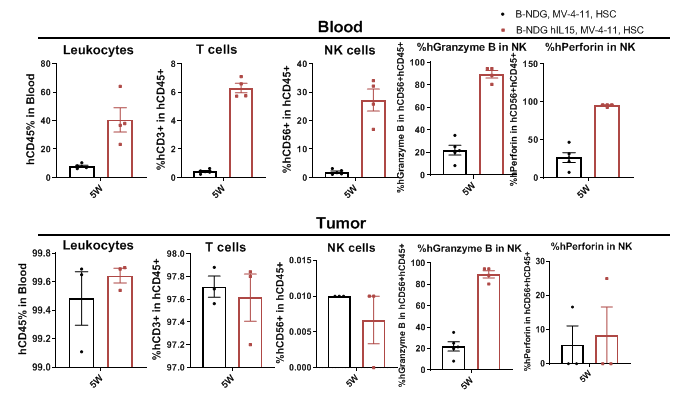
CDX model were well established on human immune system engraftment mice. Human CD34+ cells (0.15M) were intravenously implanted into homozygote B-NDG hIL15 and B-NDG mice. All mice were treated with 1.6 Gy-irradiation. Mice were grouped as hCD45% ≥ 10%. MV-4-11 (1E7) were subcutaneously implanted into B-NDG hIL15 and B-NDG mice respectively. The proportion and function of NK cells in mouse blood and tumor tissues were measured at the end of the experiment. The results showed that B-NDG hIL15 show a higher percentage of human NK cells compared with B-NDG, and NK cell express functional proteins.
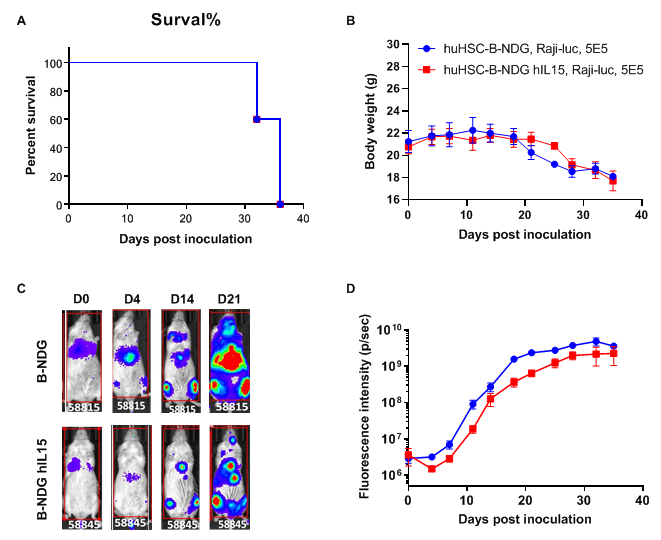
Raji lymphoma CDX model was well established in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. Human CD34+ HSCs (0.15 M) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG mice and B-NDG hIL15 mice within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 1.6 Gy of X-ray. Mice were grouped when the proportion of hCD45+ cells in blood was more than 10%, at which time B-luciferase-GFP Raji cells (5E5) were intraveneously inoculated into B-NDG mice and B-NDG hIL15 mice respectively. (A) Survival curve; (B) Changes of body weight; (C) Imaging of mice to observe tumor growth; (D) Fluorescence intensity curve of tumor cells. The results showed that B-luciferase-GFP Raji cells were successfully tumorigenic in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. The tumor growth in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice was slightly slower than that in huHSC-B-NDG mice.
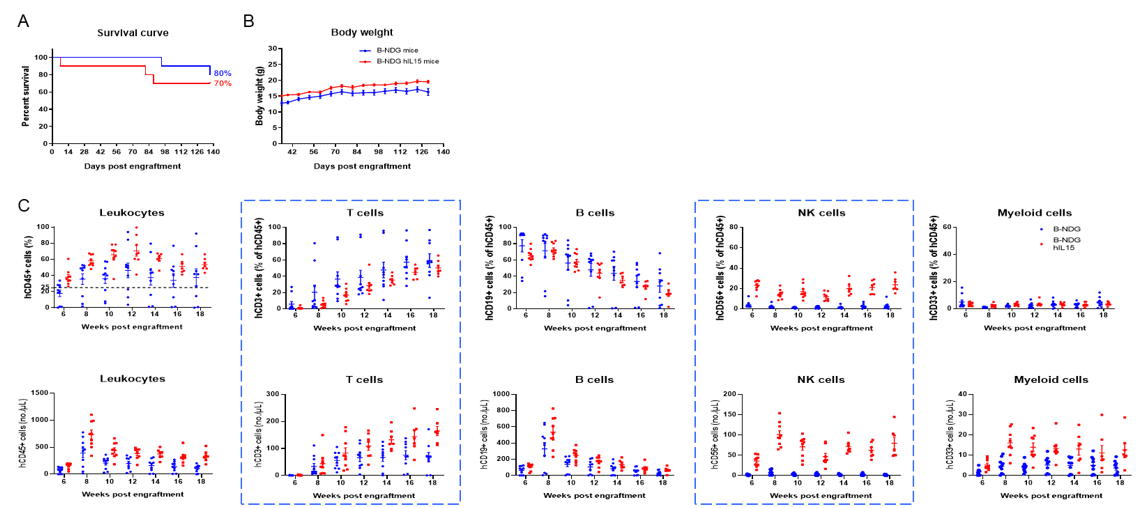
Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in neonatal B-NDG hIL15 mice successfully reconstituted human T, B and NK cells, a small number of myeloid cells. Human CD34+ HSCs (3E4) were engrafted via the facial vein of B-NDG hIL15 mice and B-NDG mice (female, 24-48 hour-old, n=10) within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 0.9 or 1.0 Gy of X-ray. The reconstitution level of human immune cells in peripheral blood was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Survival curve of human CD34+ HSCs engrafted mice; (B) Body weight; (C) Percentages and number of reconstituted human immune cells. The results showed that the survival rate of huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice reached to 70% at 20 weeks after HSCs engraftment. But the lived mice continued to gain body weight. The percentages of human CD45+ cells and NK cells in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice were much higher than that in huHSC-B-NDG mice. But the number of all cell types including human CD45+ cells, T cells, B cells, NK cells and myeloid cells in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice were much more than that in huHSC-B-NDG mice.
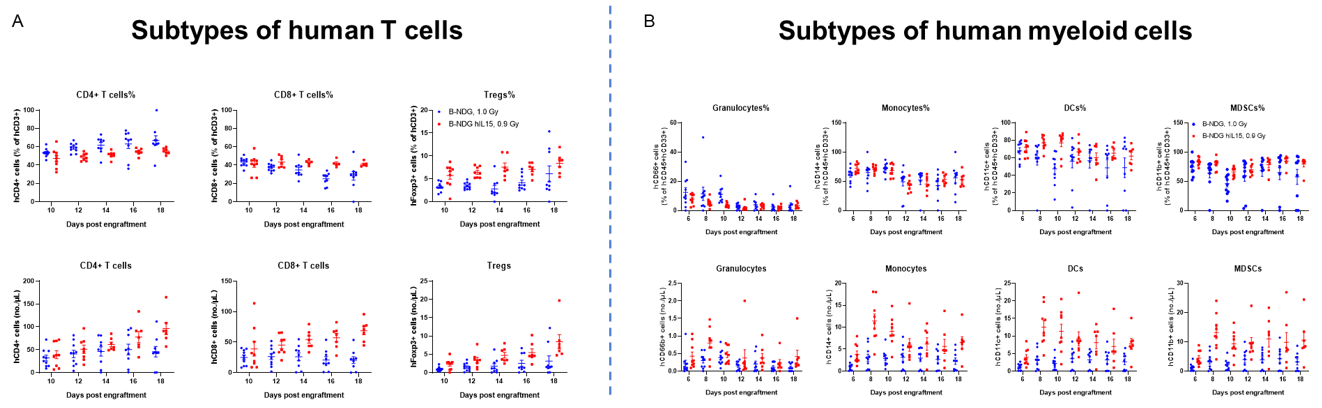
Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in neonatal B-NDG hIL15 mice successfully reconstituted human T, B and NK cells, a small number of myeloid cells. Human CD34+ HSCs (3E4) were engrafted via the facial vein of B-NDG hIL15 mice and B-NDG mice (female, 24-48 hour-old, n=10) within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 0.9 or 1.0 Gy of X-ray. The reconstitution level of human immune cells in peripheral blood was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Percentages and number of reconstituted human T cells. (B) Percentages and number of reconstituted human myeloid cells. The results showed that the percentages of human CD8+ T cells, Tregs, monocytes, DCs and MDSCs in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice were higher than that in huHSC-B-NDG mice. But the number of all cell types including human CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, Tregs, granulocytes, monocytes, DCs and MDSCs in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice were much more than that in huHSC-B-NDG mice.
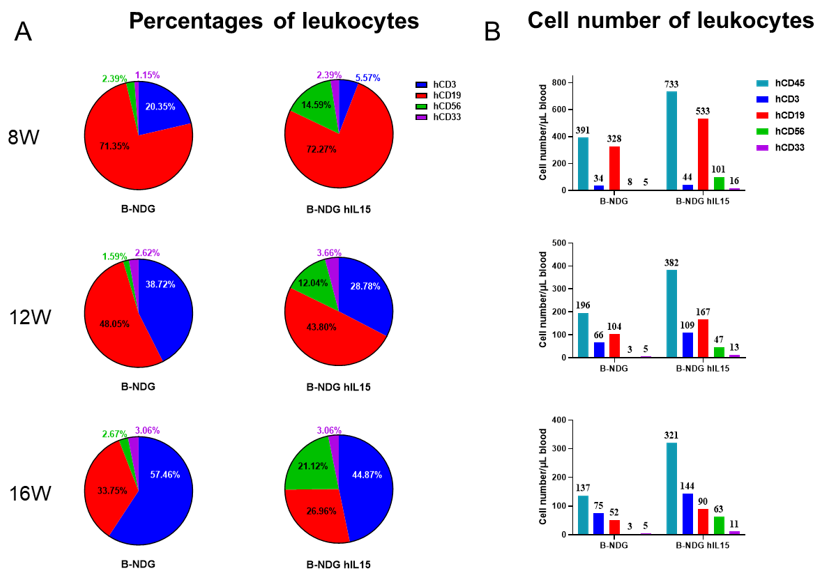
Engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in neonatal B-NDG hIL15 mice successfully reconstituted human T, B and NK cells, a small number of myeloid cells. Human CD34+ HSCs (3E4) were engrafted via the facial vein of B-NDG hIL15 mice and B-NDG mice (female, 24-48 hour-old, n=10) within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 0.9 or 1.0 Gy of X-ray. The reconstitution level of human immune cells in peripheral blood was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A, B) Statistical analysis of the percentages and number of reconstituted human immune cells. The results showed that reconstitution level of human NK cells in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice was much higher than that in huHSC-B-NDG mice. Meanwhile, the reconstitution levels of human T, B and myeloid cells were also increased in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice compared to that in huHSC-B-NDG mice.
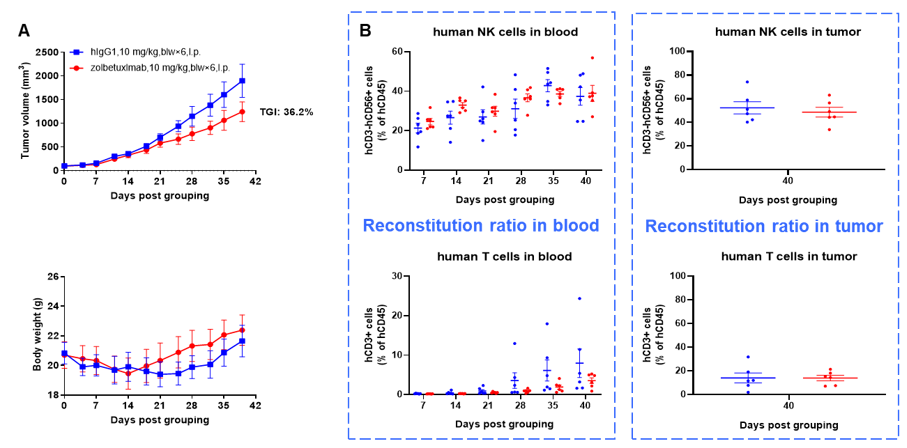
Antitumor activity of anti-human CLDN18.2 antibody in lung cancer cell line A549 CDX model established with huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. Human CD34+ HSCs (0.15 M) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG hIL15 mice within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 1.6 Gy of X-ray. B-hCLDN18.2 A549 cells (1E7) were subcutaneously inoculated into B-NDG hIL15 mice when the proportion of hCD45+ cells in blood was more than 25%. Mice were grouped when the tumor volume reached 80-100 mm3 at which time they were treated with anti-human CLDN18.2 antibody (zolbetuximab, in-house) with dose and schedule indicated in panel (female, 6-week-old, n=6). Peripheral blood was collected weekly to analyze the reconstitution levels of human NK cells and T cells. Tumor tissues were taken at the end of the experiment to detect the level of infiltrating human NK cells and T cells. The results showed that zolbetuximab could effectively inhibit tumor growth in huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. High levels of human NK cells could be detected in both peripheral blood and tumor tissues. Human T cells could also be detected in peripheral blood and tumor tissues.
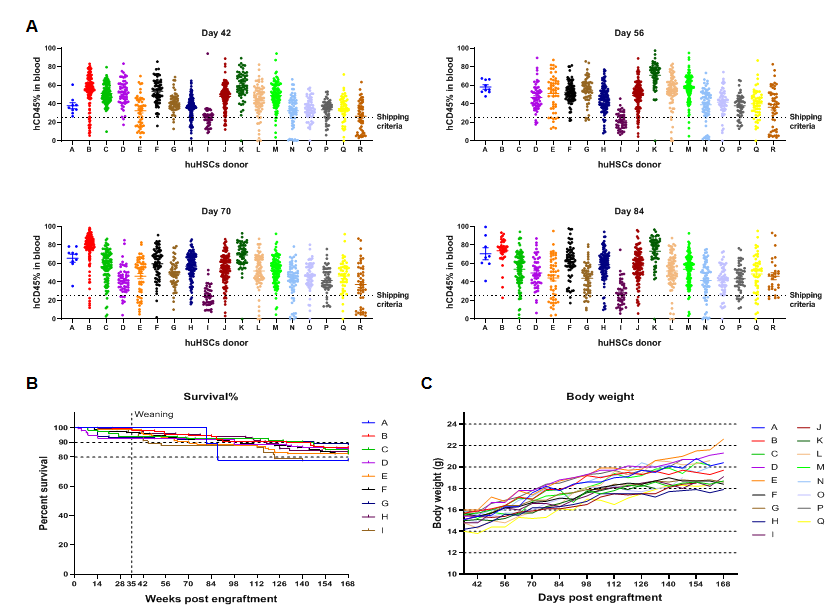
The reconstitution data of human CD34+ HSCs from different donors. (A) The engraftment of human CD34+ HSCs in newborn B-NDG hIL15 mice can stably reconstitute human immune cells. The success rate of reconstitution varies with different donors. (B) After 24 weeks of reconstitution, the survival rate of mice is between 80% and 90%. (C) The weight of the mice continues to increase after reconstitution.
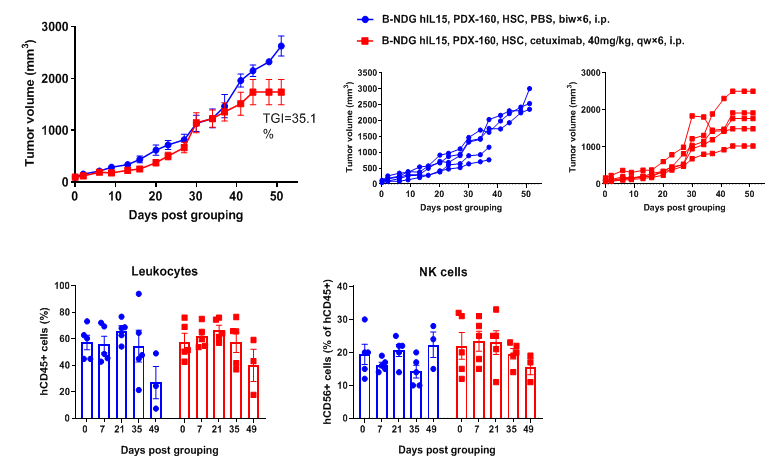
Antitumor activity of anti-human EGFR antibody in pancreatic cancer PDX model established with huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. Human CD34+ HSCs (0.15 M) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG hIL15 mice within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 1.6 Gy of X-ray. Pancreatic cancer PDX (BP0160-R4P7) were inoculated into B-NDG hIL15 mice. Mice were grouped when the tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human EGFR antibody (cetuximab, in-house) with dose and schedule indicated in panel. The proportion of leukocytes and NK cells in blood were measured once every other week. The results showed that cetuximab could effectively inhibit tumor growth in pancreatic cancer PDX model established with huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. High levels of human NK cells could be detected in peripheral blood.
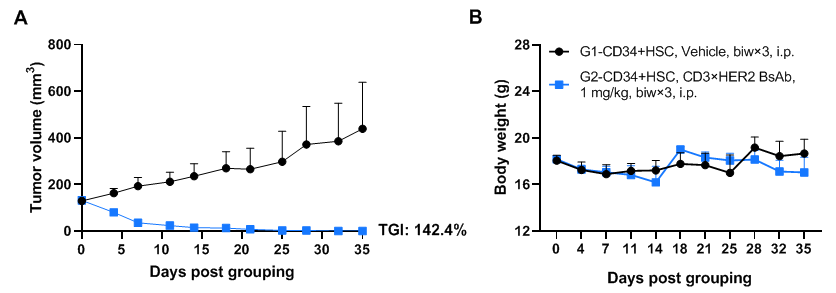
Antitumor activity of anti-human CD3×HER2 BsAb (in-house) in pancreatic cancer PDX model established with huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. Human CD34+ HSCs (3×104) were intravenously engrafted into B-NDG hIL15 mice within 4-12 hours after being irradiated with 0.9 Gy of X-ray. Pancreatic cancer PDX (BP0209) were inoculated into B-NDG hIL15 mice. Mice were grouped when the tumor volume reached approximately 100-150 mm3, at which time they were treated intraperitoneally with anti-human CD3×HER2 BsAb (in-house) with dose and schedule indicated in panel. The results showed that anti-human CD3×HER2 BsAb could effectively inhibit tumor growth in pancreatic cancer PDX model established with huHSC-B-NDG hIL15 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.The overage of this tumor model is 20%.