ASD Mouse Model Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent difficulties in social interaction and communication, alongside restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. Symptoms typically emerge in early childhood and exhibit considerable variability in severity and manifestation across individuals. Although the precise etiology of ASD remains unknown, it is widely accepted that both genetic predispositions and environmental influences contribute to its development. Given the heterogeneity of the disorder, individuals with ASD may require varying levels of support, ranging from minimal assistance to lifelong care.
Summary of ASD models in Biocytogen
| Model type |
Model names |
Modeling reagent |
Core Index |
Optional tests |
| Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) |
B-Fmr1 KO mice |
- |
Three-chamber social test
Marble burying test |
Open field test
Inflammation analysis |
| B-Mecp2 KO mice |
- |
Three-chamber social test
Marble burying test |
Open field test
Inflammation analysis |
Results
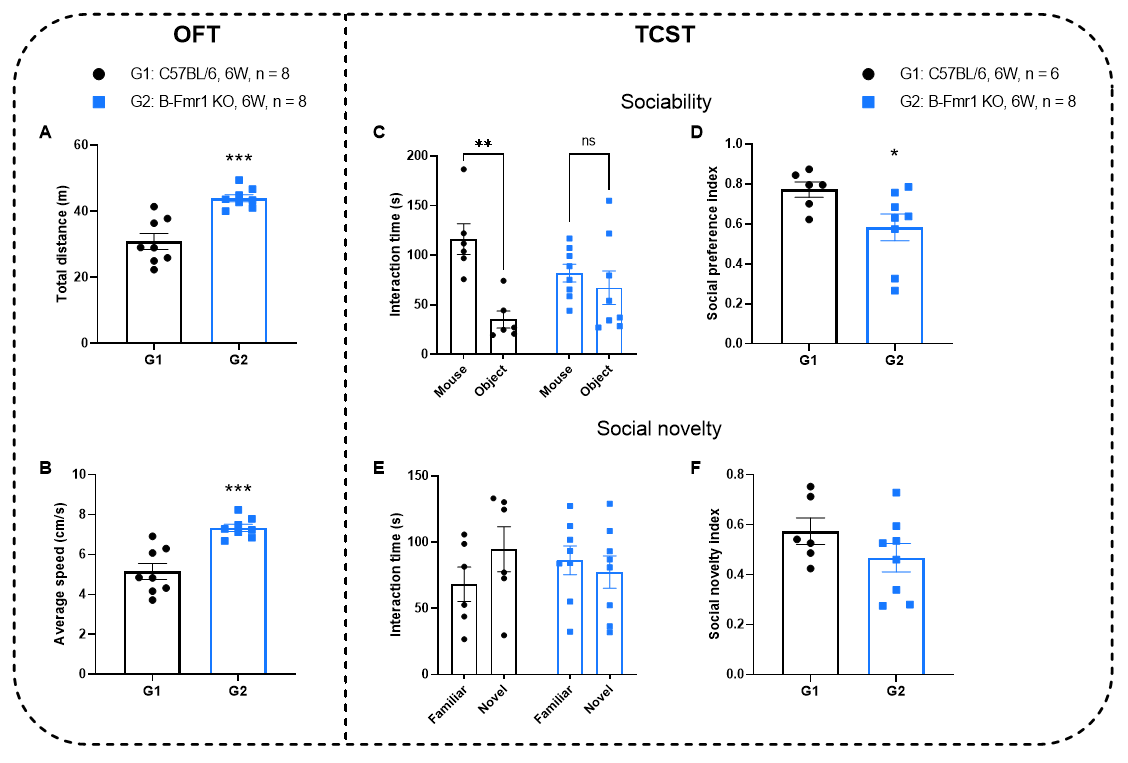
Behavioral assessment in B-Fmr1 KO mice
Behavioral assessment in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc and B-Fmr1 KO mice. A-B, Open Field Test (OFT): Total distance (A): B-Fmr1 KO mice (G2) traveled significantly farther than C57BL/6 (G1) , indicating hyperlocomotion. Average speed (B): KO mice showed higher speed (***p < 0.001), confirming increased activity. C-F: Three-Chamber Social Test (TCST): Sociability (C, D): KO mice exhibited reduced interaction time with mice vs. objects (lower preference index), though not statistically significant. Social novelty (E, F): Diminished interest in novel vs. familiar mice (lower novelty index), with marginal significance.. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.