

Our innovative gene-editing technology increases gene-editing efficiency by 10 to 20 fold, making our custom model development process faster and more affordable for your research.
on this page
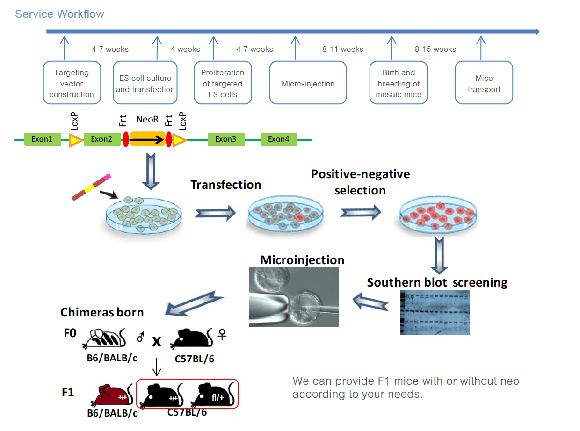
Embryonic stem cell or ESC-based gene targeting uses a stem cell's plasticity to engineer gene targeted mice. Mouse stem cells are first electroporated with a targeting vector. Following successful homologous recombination between the targeting vector and ESC cell DNA, targeted embryonic stem cells are then injected into a normal mouse blastocyst. When injected, the stem cells colonize the blastocyst, resulting in a chimera with cells of distinct genotypes. Blastocysts are then implanted into a host mouse that will carry and deliver it. Finally, chimeric (founder) mice are bred with strains of mice to produce animals that have germline transmission of the targeted gene.
Although traditional way to edit genomes but ESC/HR based gene editing offers following advantages:

In ESC-based gene knockout targeting, we use a positive selection marker to replace an exon of a targeted gene. The targeted gene is deleted globally, whereas in conditional knockout animals the gene is deleted only in selected cells, as determined by a tissue specific promoter. Conditional knockout mouse models are usually generated using Cre-LoxP or Flp-Frt recombination systems.
To generate a knockin mouse, a DNA fragment of interest is inserted at the desired location in the genome. This modality also allows for a variety of models to be created including point mutant, reporter (GFP), tagged (FLAG), Cre, and humanized mice.
Targeting via ES cells allows for complex targeting and for making insertions greater than 6 kb in the mouse genome.
Biocytogen's ES cells are 100% pure C57BL/6 background. This can save up to 2 years back cross time.
When projects are initiated, you will be assigned a project manager, and he or she will give you monthly updates on the status of your model. Even better, you can reach out the project manager any time.
During targeting vector construction, a positive selection marker (NEO resistance gene) and a DTA negative selection marker are introduced; at the same time, a restriction enzyme site is added to a specific position in the targeting vector. After electroporation of the targeting vector into the ES cells, G418 selection is used to screen for positive cells. We also perform Southern blot to ensure that there are no random insertions. In addition, we monitor karyotype changes in ES cell subjected to long-term in vitro culture by performing karyotype analysis. Using chrsomosome banding technology, the chromosomes are analyzed, compared, sequenced and numbered according to chromosome length, centromere position and arm ratio, ensuring that subsequent micro-injection is performed only after high-quality ES cells are obtained.
The most important factor in gene targeting is the strain of the mouse embryonic stem cell; it is easier to target ES cells in some strains compared to others. The number reported in literature is 0.5-3%, but it is easier to target at some loci, such as the Rosa26 locus, with significantly higher efficiency. Gene targeting efficiency is relatively high, if recombination is performed with embryonic stem cells from C57BL/6.