

on this page
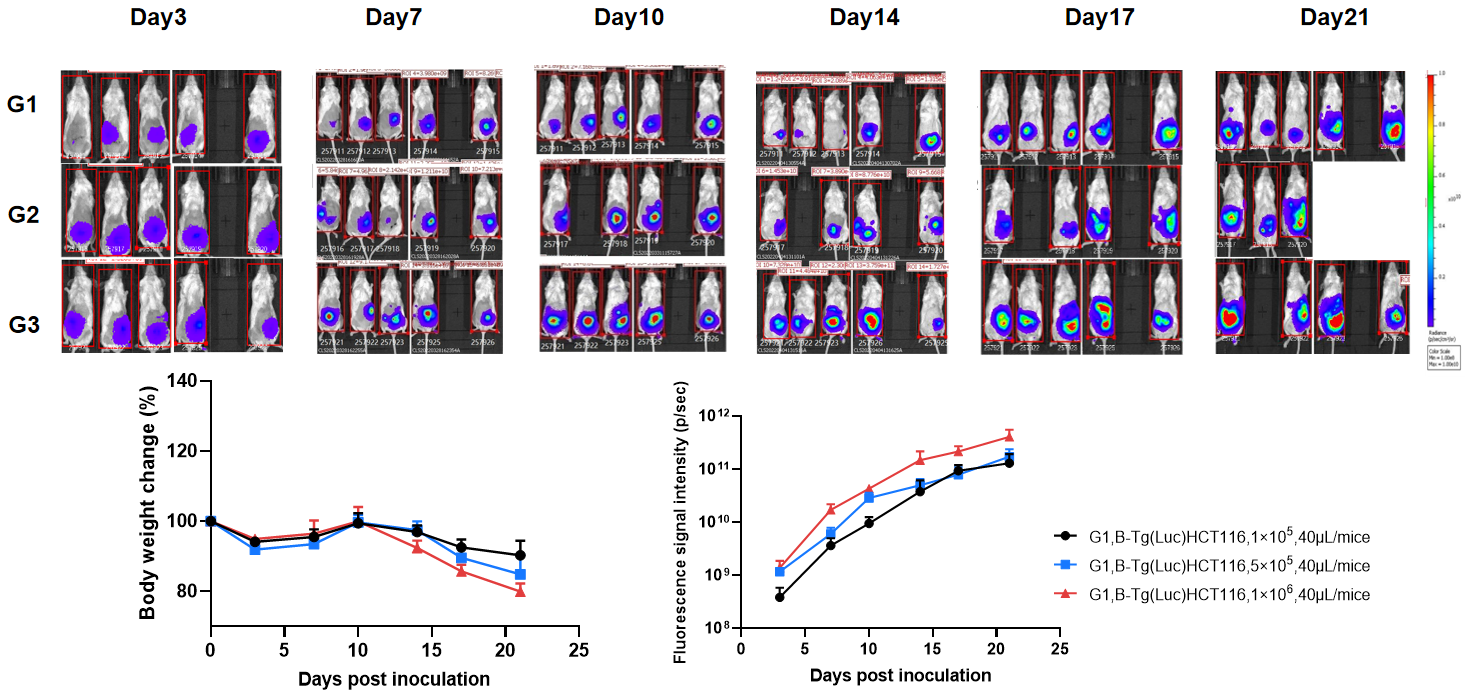
Establishment of orthotopic colorectal cancer model.
The B-NDG mice were inoculated with a volume of 40 μL of B-Tg(Luc) HCT 116 cell suspension (1×105, 5×105, 1×106), and the body weight and tumor fluorescence signal of the mice were recorded weekly. The results showed that the fluorescence signal gradually increased and body weight of mice had modest weight loss over time. This indicated that the cell line was successfully constructed as an orthotopic tumor model.
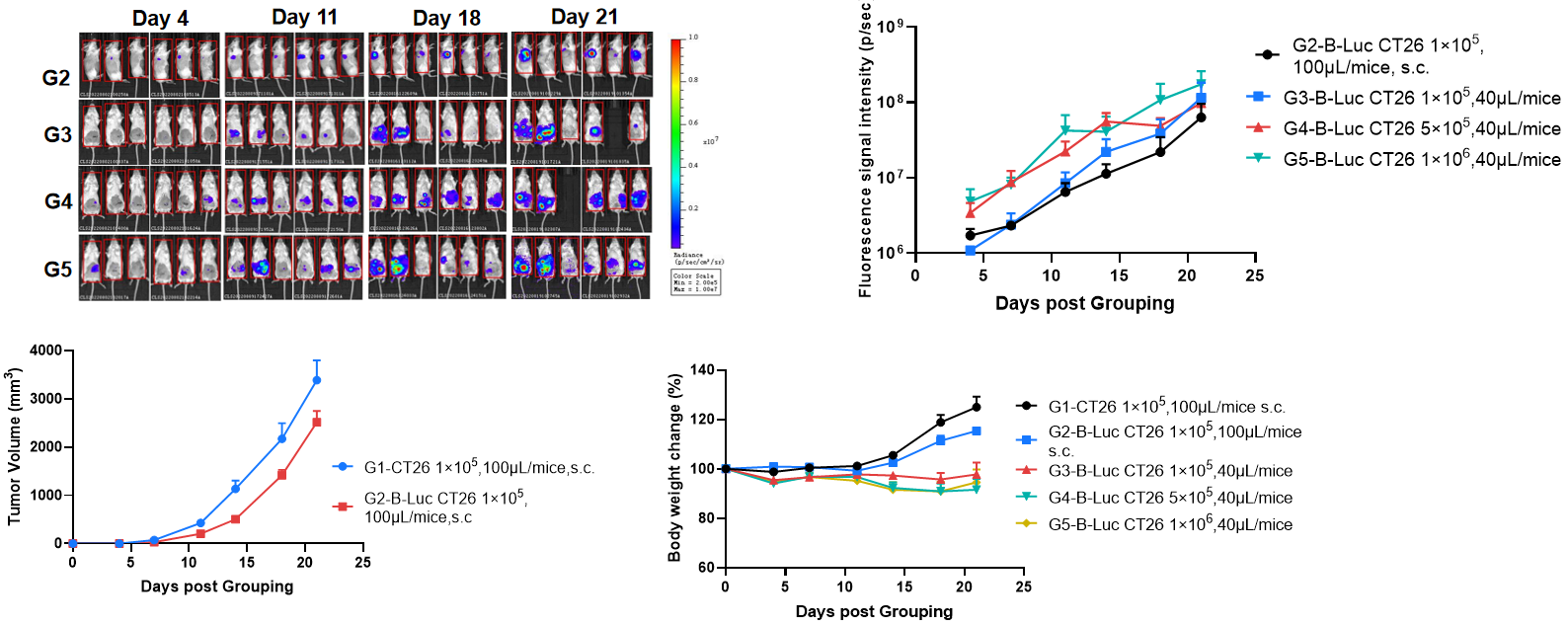
Establishment of orthotopic colorectal cancer model.
The B-NDG mice (F, n=6) were inoculated with B-Luc CT26.WT cell suspension. Subcutaneous tumor formation of B-Luc CT26.WT is slower than that of wild-type cells. and the body weight and tumor fluorescence signal of the mice were recorded weekly. The results showed that the fluorescence signal gradually increased and body weight of mice had modest weight loss over time. This indicated that the cell line was successfully constructed as an orthotopic tumor model.
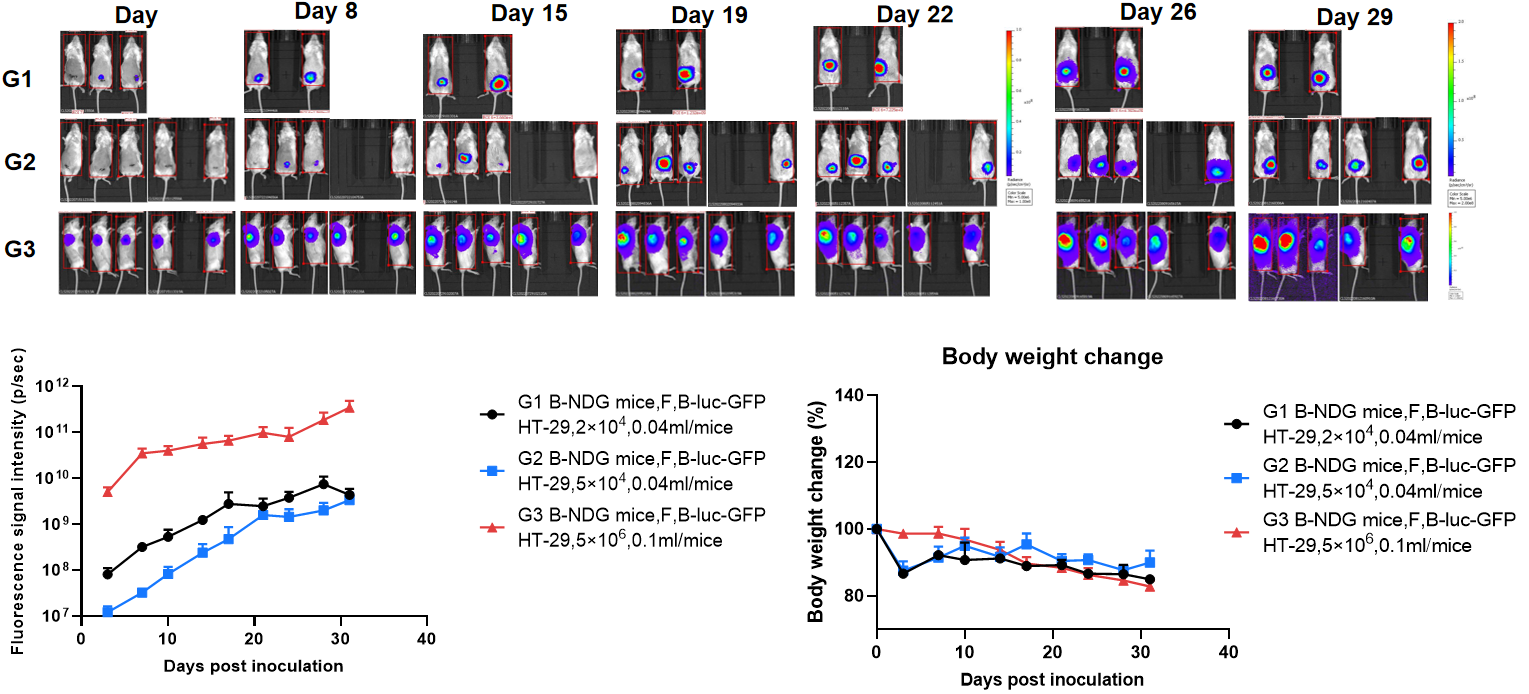
Establishment of orthotopic colorectal cancer model.
The colon of B-NDG mice were inoculated with B-luc-GFP HT-29 cell suspension, and the body weight and tumor fluorescence signal of the mice were recorded weekly. The results showed that the fluorescence signal gradually increased and body weight of mice had modest weight loss over time. This indicates that the cell line was successfully constructed as an orthotopic tumor model. This indicates that the cell line was successfully constructed as an orthotopic tumor model.
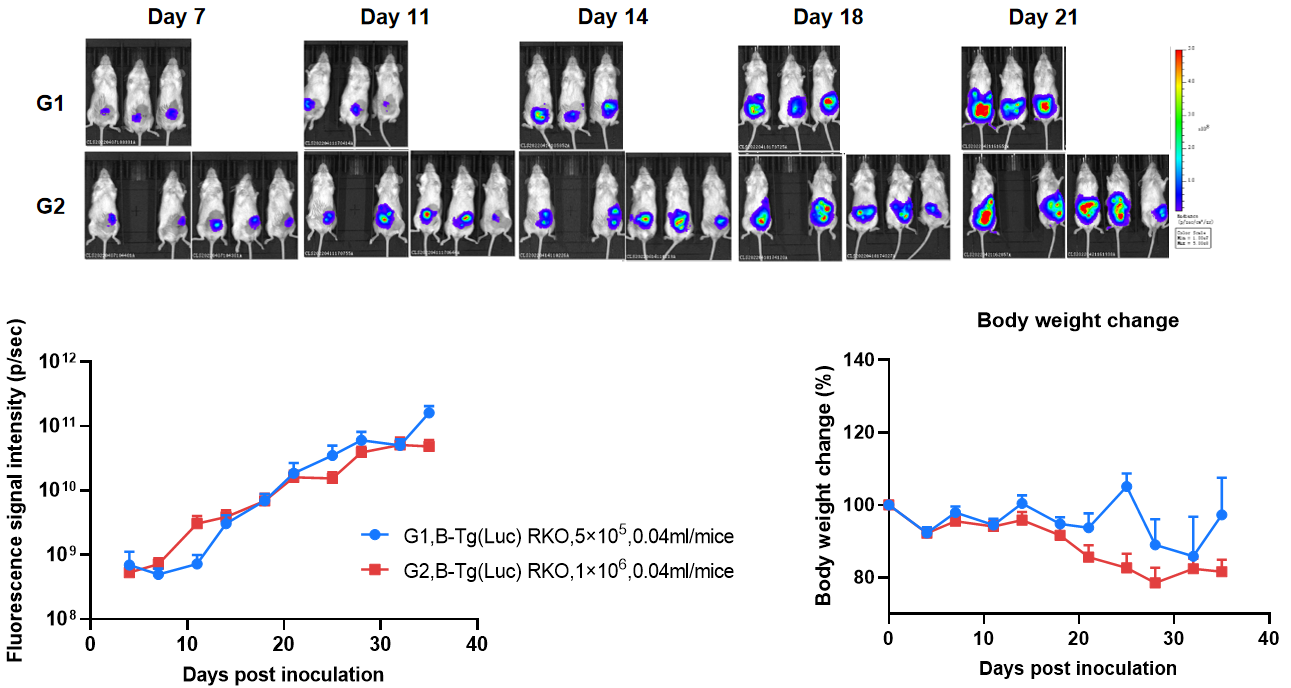
Establishment of orthotopic colorectal cancer model.
The colon of B-NDG mice were inoculated with B-Tg(Luc) RKO cell suspension (5×105, 1×106), and the body weight and tumor fluorescence signal of the mice were recorded weekly. The results showed that the fluorescence signal gradually increased and body weight of mice had modest weight loss over time. This indicates that the cell line was successfully constructed as an orthotopic tumor model. H&E staining showed that tumors metastasized in the liver, small intestine and pancreas.
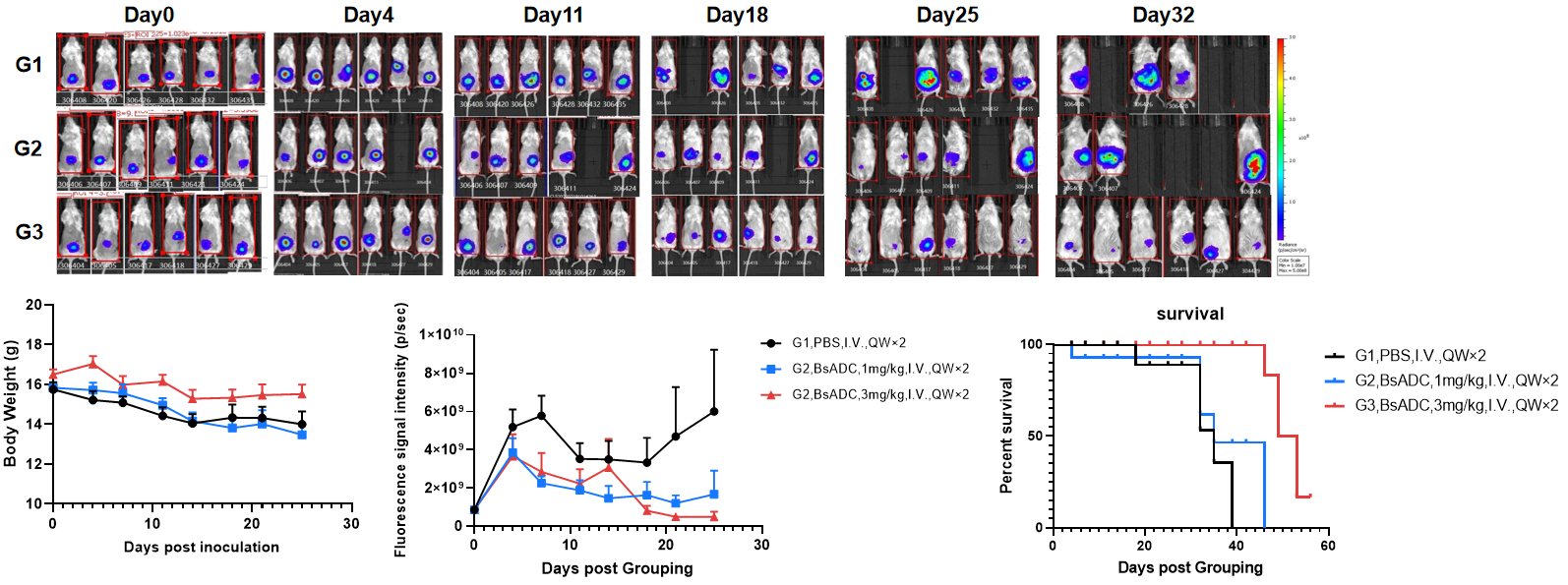
Evaluation of the efficacy of orthotopic colorectal cancer model.
The mice were randomly divided into PBS and BsADC groups after tumor inoculation based on imaging values. The body weight and tumor fluorescence signal of the mice were recorded weekly. BsADC significantly inhibited the growth of B-Tg(Luc) RKO orthotopic colorectal cancer, and the survival of the mice was significantly longer, demonstrating that this model can be well used for preclinical evaluation.