

on this page
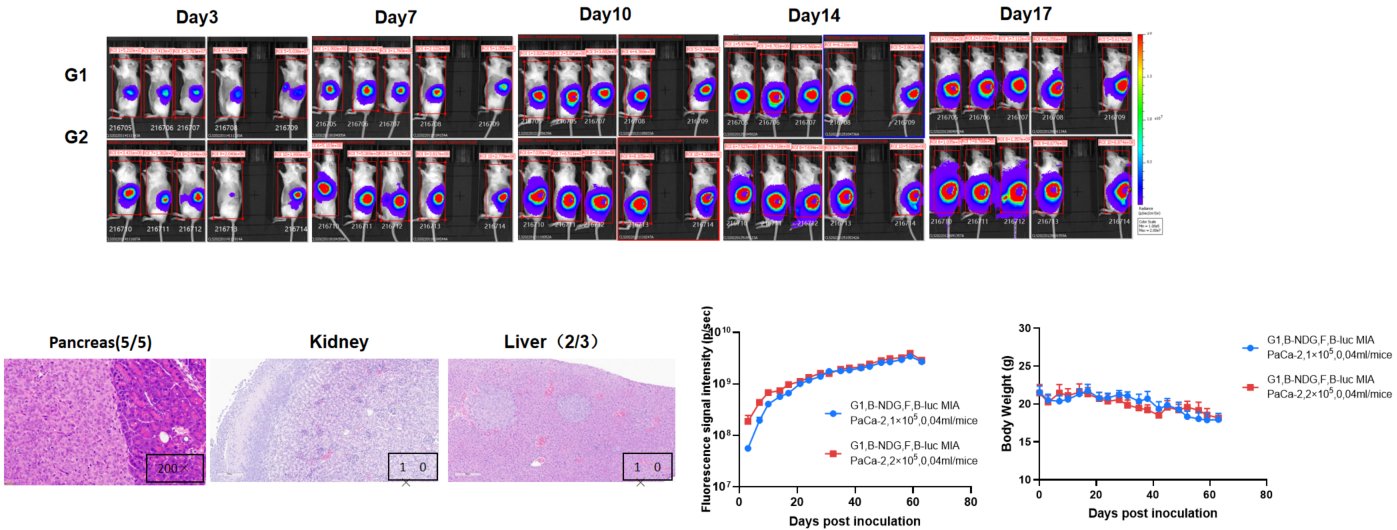
Establishment of orthotopic pancreatic cancer model.
The B-NDG mice (F, n=5) were inoculated with B-luc MIA PaCa-2 cell suspension (1×105, 2×105), which were mixed with Matrigel (1:1), and the body weight and tumor fluorescence signal of the mice were recorded weekly. The results showed that the fluorescence signal gradually increased, and the body weight of mice gradually decreased slightly in the later stage. This indicates that the cell line was successfully constructed as an orthotopic tumor model. H&E staining showed that tumors metastasized in the kidney and liver.
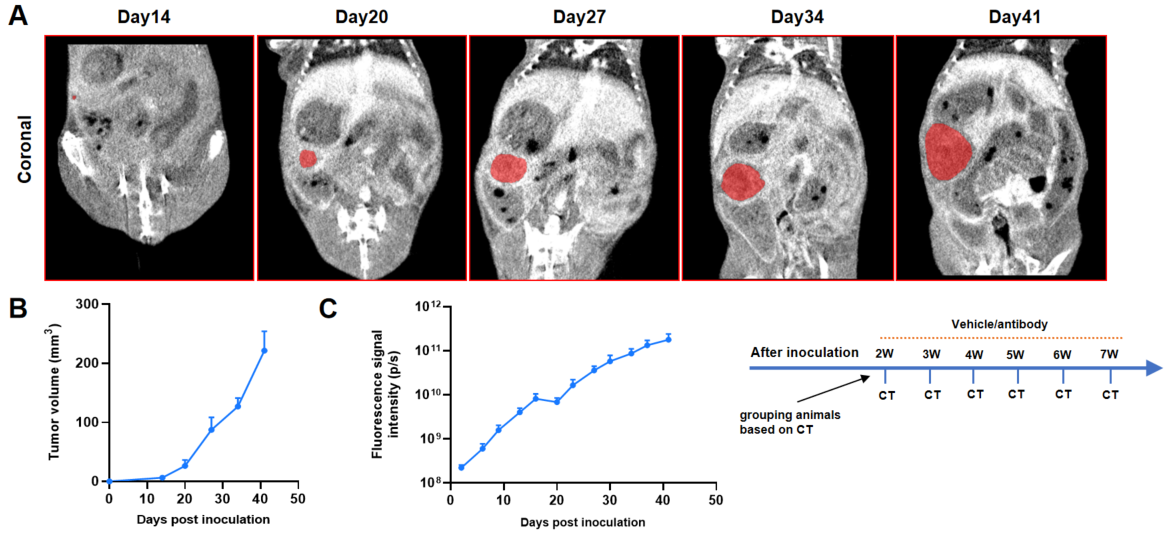
Orthotopic pancreatic cancer models imaging by Micro-CT.
A: Micro-CT images of B-Luc MIA PaCa-2 orthotopic model in B-NDG mice were scanned from day 14 after inoculation. The image shows the coronal planes of the mice abdomen, with red region representing the actual tumor. B: Tumor growth curves were recorded by contrast-enhanced CT. C: Dynamic changes of fluorescence signal in the tumor site after inoculation.
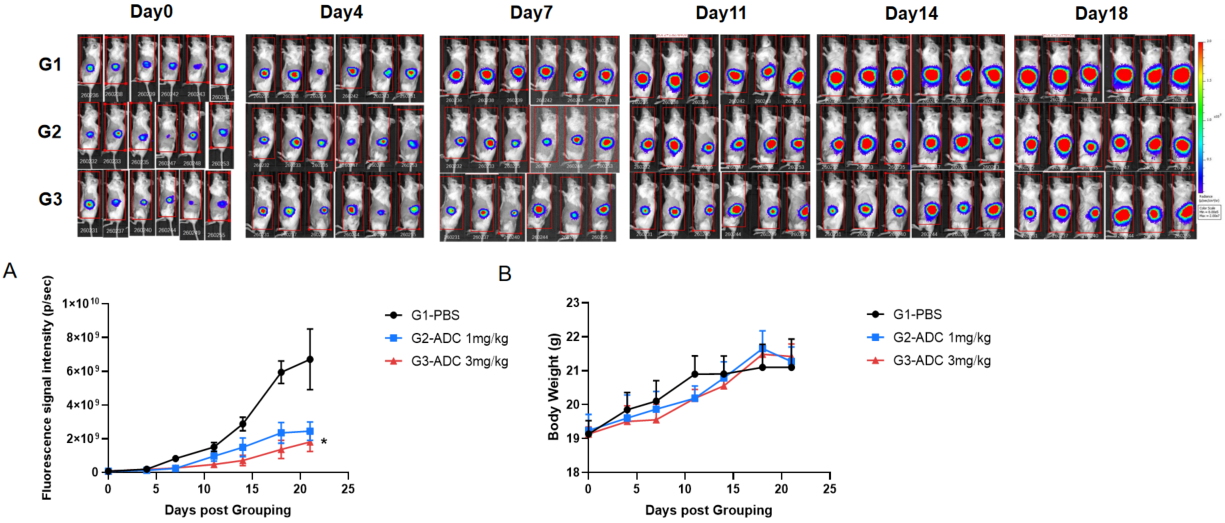
Antitumor activity of Antibody-drug Conjugate in B-luc MIA PaCa-2 Pancreatic orthotopic model. The ADC significantly inhibited B-luc MIA PaCa-2 tumor growth in B-NDG mice. B-luc MIA PaCa-2 cells (1×105)suspension mixed in Matrigel solution (1:1) was orthotopically implanted into B-NDG mice (female, 7 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when Imaging signal value reached approximately 7E7 p/sec, at which time they were treated with the ADC drug with different doses and schedules indicated in panel (A) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel B, this ADC drug was efficacious but mild, demonstrating that B-luc MIA PaCa-2 Pancreatic orthotopic model could provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of ADC drug. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05.