


C57BL/6-Apoetm1Bcgen/Bcgen • 110168
| Product name | B-Apoe KO mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 110168 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Apoetm1Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| Aliases | AD2, APO-E, ApoE4, LDLCQ5, LPG |
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is primarily produced by the liver and macrophages in the peripheral tissues, or by astrocytes and microglia in the central nervous system. ApoE transports lipoproteins, fat-soluble vitamins and cholesterol into the lymph systems, and then into the blood, preventing the accumulation of cholesterol-rich particles in the plasma. The function of ApoE protein has been widely studied in cardiovascular disease, lipid metabolism, and Alzheimer’s diseases.
H&E staining and blood biochemical results in the mouse model of atherosclerosis after 12 weeks of WD diet feeding. (A) The H&E staining results indicate a significant increase in AS plaques in the aortic sinus. (B-C) Immunohistochemistry shows the migration of smooth muscle cells and the infiltration of inflammatory cells. (D) ALT, AST, TC, TG, HDL-C and LDL-C levels in serum. After 12 weeks of Western diet induction, the serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in B-Apoe KO mice were significantly higher than those in mice on a normal diet.
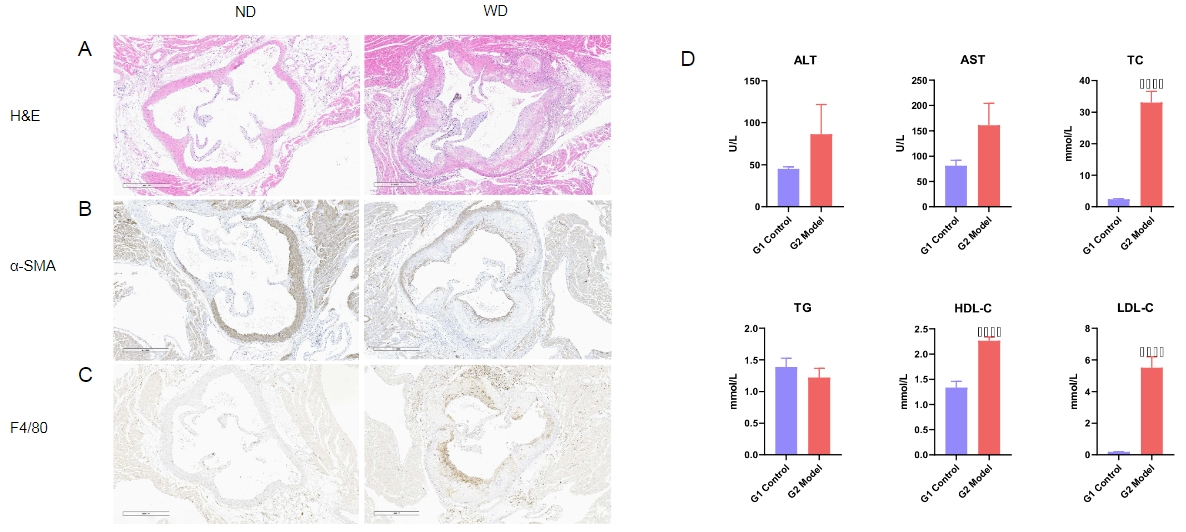
H&E staining and blood biochemical results in the mouse model of atherosclerosis after 20 weeks of WD diet feeding. (A) The H&E staining results indicate a significant increase in AS plaques in the aortic sinus. (B-C) Immunohistochemistry shows the migration of smooth muscle cells and the infiltration of inflammatory cells. (D) ALT, AST, TC, TG, HDL-C and LDL-C levels in serum. After 20 weeks of Western diet induction, the serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in B-Apoe KO mice were significantly higher than those in mice on a normal diet.