


C57BL/6-Tfrctm1(TFRC)Bcgen Mapttm1(MAPT)Bcgen/Bcgen • 113290

| Product name | B-hTFR1/hTAU mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 113290 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Tfrctm1(TFRC)Bcgen Mapttm1(MAPT)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| NCBI gene ID | 7037, 4137 (Human) |
| Aliases | CD71, IMD46, T9, TFR, TFR1, TR, TRFR, p90;TAU, MSTD, PPND, DDPAC, MAPTL, MTBT1, MTBT2, tau-40, FTDP-17, PPP1R103, Tau-PHF6 |
| Application | This product is used for pharmacodynamics evaluation of Alzheimer's disease (AD). |
on this page
Gene targeting strategy for B-hTFR1/hTAU mice.The exons 2~10 of mouse Mapt gene that encode the full-length protein were replaced by human MAPT exons 2~15 in B-hTFR1/hTAU mice. The 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are replaced by human counterparts. The chimeric MAPT expression is driven by endogenous mouse Mapt promoter, while mouse Mapt gene transcription and translation will be disrupted. The exons 4-19 of mouse Tfr1 gene that encode the extracellular region were replaced by human TFR1 exons 4-19 in B-hTFR1/hTAU mice.
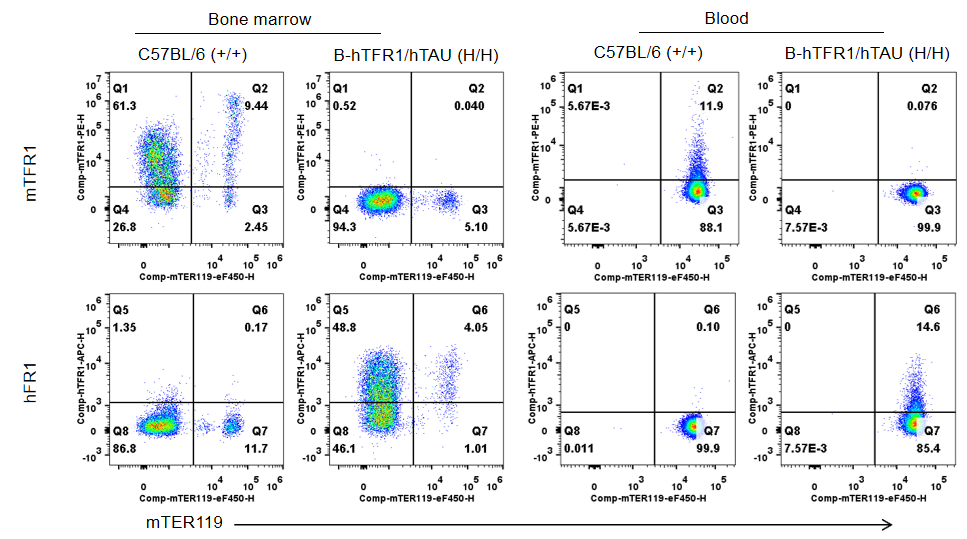
Strain specific TFR1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTFR1/hTAU by flow cytometry. Bone marrow and blood cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTFR1/hTAU mice (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-mouse TFR1 antibody (Biolegend, 113808) and anti-human TFR1 antibody (Biolegend, 334108). Mouse TFR1 was detectable in wild-type mice. Human TFR1 was exclusively detectable in homozygous hTFR1/hTAU mice but not in wild-type mice.
Strain specific TFR1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTFR1/hTAU by flow cytometry. Bone marrow and blood cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTFR1/hTAU mice (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-mouse TFR1 antibody (Biolegend, 113808) and anti-human TFR1 antibody (Biolegend, 334108). Mouse TFR1 was detectable in wild-type mice. Human TFR1 was exclusively detectable in homozygous hTFR1/hTAU mice but not in wild-type mice.
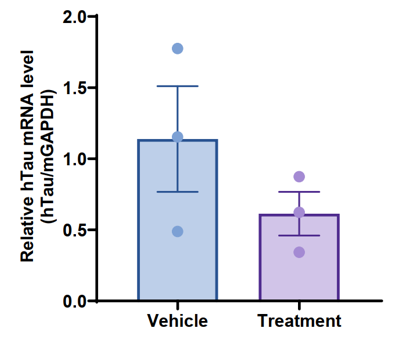
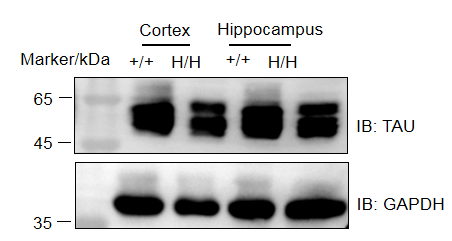
Note: This experiment was performed by the client using B-hTFR1/hTAU mice. All the other materials were provided by the client.