


C57BL/6-Cldn3tm1(CLDN3)Bcgen Cldn4tm1(CLDN4)Bcgen/Bcgen • 111299
| Product name | B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 111299 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Cldn3tm1(CLDN3)Bcgen Cldn4tm1(CLDN4)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| Aliases | C7orf1, CPE-R2, CPETR2, HRVP1, RVP1;CPE-R, CPER, CPETR, CPETR1, WBSCR8, hCPE-R |
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice.
Mouse Cldn3 and Cldn4 gene were replaced by human CLDN3 and CLDN4 gene in B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice.
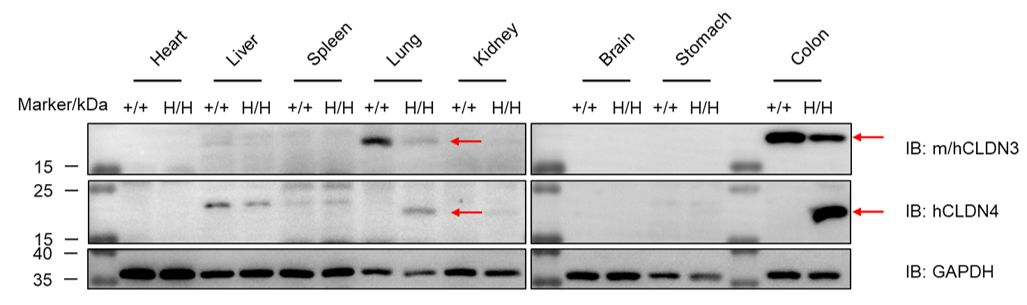
Western blot analysis of CLDN3 and CLDN4 protein expression in homozygous B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice. Various tissue lysates were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice (H/H, H/H), and then analyzed by western blot with cross-reactive anti-CLDN3 antibody or species-specific anti-CLDN4 antibody. 40 μg total proteins were loaded for western blotting analysis. CLDN3 and CLDN4 were detected in lung and colon.
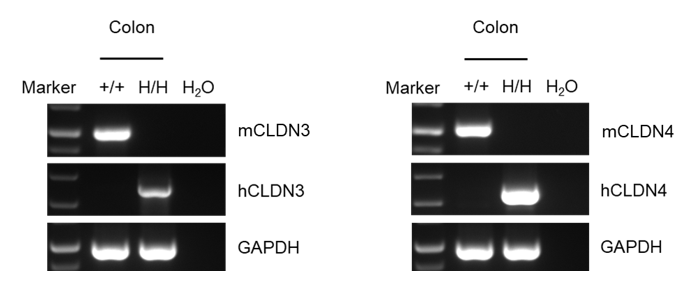
Strain specific analysis of CLDN3 and CLDN4 mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice by RT-PCR. Colon RNA was isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice (H/H, H/H), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse or human CLDN3 or CLDN4 primers. Mouse Cldn3 and Cldn4 mRNA were detectable only in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human CLDN3 and CLDN4 mRNA were detectable only in homozygous B-hCLDN3/hCLDN4 mice but not in wild-type mice.