


C57BL/6-F11tm1(F11)Bcgen/Bcgen • 112749
| Product name | B-hFXI mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 112749 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-F11tm1(F11)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| Aliases | FXI; PTA |
Gene targeting strategy for B-hFXI mice. The exons 1~15 of the mouse Fxi gene that encode full-length molecule (ATG to STOP codon), including 3’UTR were replaced by human counterparts in B-hFXI mice. The human FXI expression is driven by the human FXI promoter and 5’UTR, while mouse Fxi gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
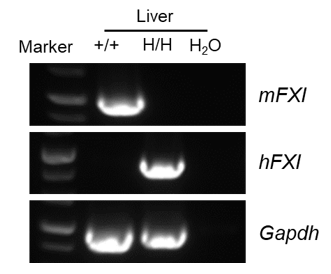
Strain specific analysis of FXI mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hFXI mice by RT-PCR. Liver RNA were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hFXI mice (H/H), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse or human FXI primers. Mouse FXI mRNA were detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human FXI mRNA was only detectable in homozygous B-hFXI mice.
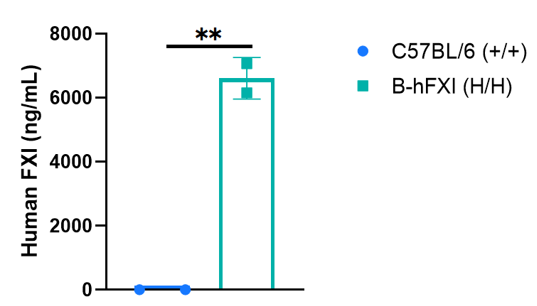
Strain specific FXI expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous humanized B-hFXI mice by ELISA. Serum was collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hFXI mice (H/H) (n=2). Protein expression level of FXI was analyzed by ELISA. Human FXI was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hFXI mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001.
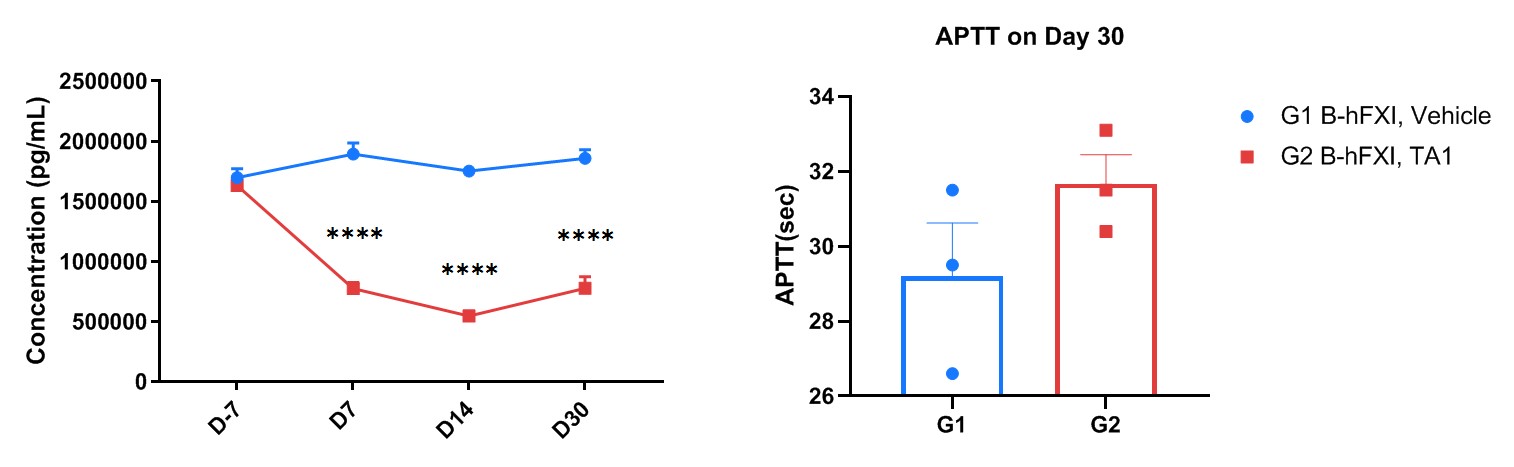
The inhibitory efficiency of the FXI-targeted nucleic acid drugs in homozygous B-hFXI mice. B-hFXI mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (8-week-old, female). The human FXI-targeted nucleic acid drug (from a client) and saline were administered to the mice individually. The mice were sacrificed on day 30. (A) The changes in FXI protein expression levels in serum on days -7, 7, 14, and 30 after administration, compared to the levels before administration. The human FXI levels in the treatment group were reduced compared to the control group (G1). (B) Activated Partial Thromboplastin Clotting Time (aPTT) assay on Day 30. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Analyzed by 2 way-ANOVA, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.