


C57BL/6-Igf1rtm1(IGF1R)Bcgen/Bcgen • 111274
| Product name | B-hIGF1R mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 111274 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Igf1rtm1(IGF1R)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| Aliases | IGF1R (IGFR; CD221; IGFIR; JTK13) |
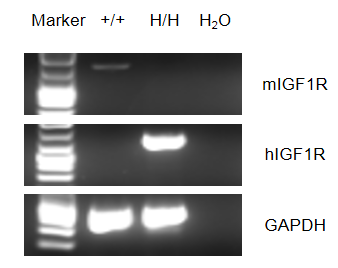
This receptor binds insulin-like growth factor with a high affinity. It has tyrosine kinase activity. The insulin-like growth factor I receptor plays a critical role in transformation events. Cleavage of the precursor generates alpha and beta subunits. It is highly overexpressed in most malignant tissues where it functions as an anti-apoptotic agent by enhancing cell survival. A chimeric CDS that encodes mouse Igf1r signal peptide and human extracellular domain, human IGF1R transmembrane and mouse cytoplasmic domain is inserted right after mouse Igf1r exon 2 to replace the exon 2 of mouse Igf1r gene. The chimeric IGF1R protein expression will be driven by endogenous mouse Igf1r promoter, while mouse Igf1r gene transcription and translation will be disrupted. Human IGF1R mRNA was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIGF1R mice but not wild-type mice, and mouse Igf1r mRNA was detectable in wild-type mice. Mouse IGF1R was detectable in wild-type mice, human IGF1R was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIGF1R mice but not in wild-type mice. Figitumumab can bind well to B-hIGF1R mice at 10 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL, 1 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, and 100 μg/mL, and the antibody binding reaches saturation at 1 μg/mL. The human IGF1 can activate the phosphorylation of IGF1R and AKT, and this phosphorylation can be inhibited by the positive drug Figitumumab. Application: This product is used for pharmacodynamics and safety evaluation of antibody drugs for cancers.
Gene targeting strategy for B-hIGF1R mice. A chimeric CDS that encodes mouse Igf1r signal peptide and human extracellular domain, human IGF1R transmembrane and mouse cytoplasmic domain is inserted right after mouse Igf1r exon 2 to replace the exon 2 of mouse Igf1r gene. The chimeric IGF1R protein expression will be driven by endogenous mouse Igf1r promoter, while mouse Igf1r gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
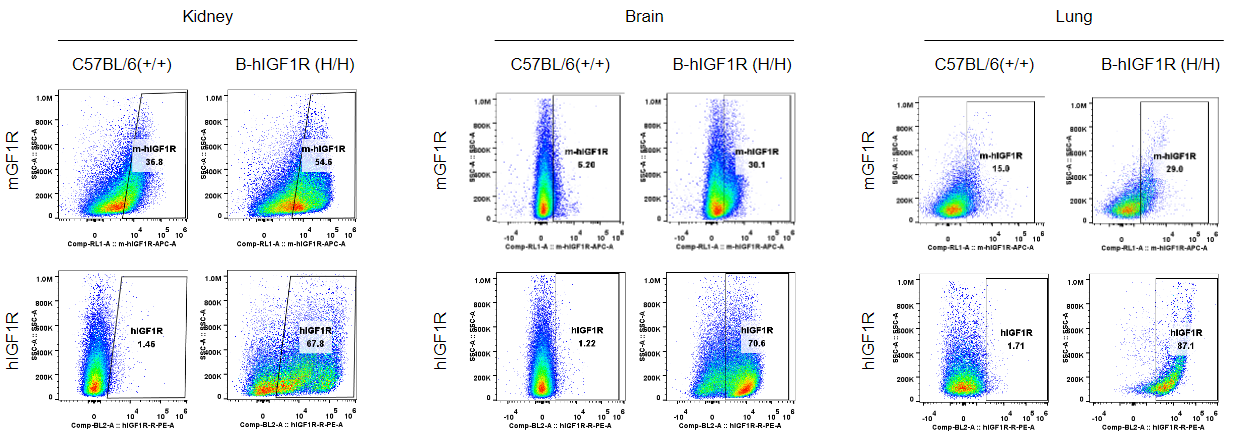
Strain specific IGF1R expression analysis in homozygous B-hIGF1R mice by flow cytometry. Kidney, brain and lung were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice, and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-mouse IGF1R antibody (abcam, ab225298) and anti-human IGF1R antibody (Biolegend, 351805) by flow cytometry. Mouse IGF1R was detectable in wild-type mice and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice, as the antibody is crossly reactive with IGF1R in human and mice. Human IGF1R was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIGF1R but not in wild-type mice.
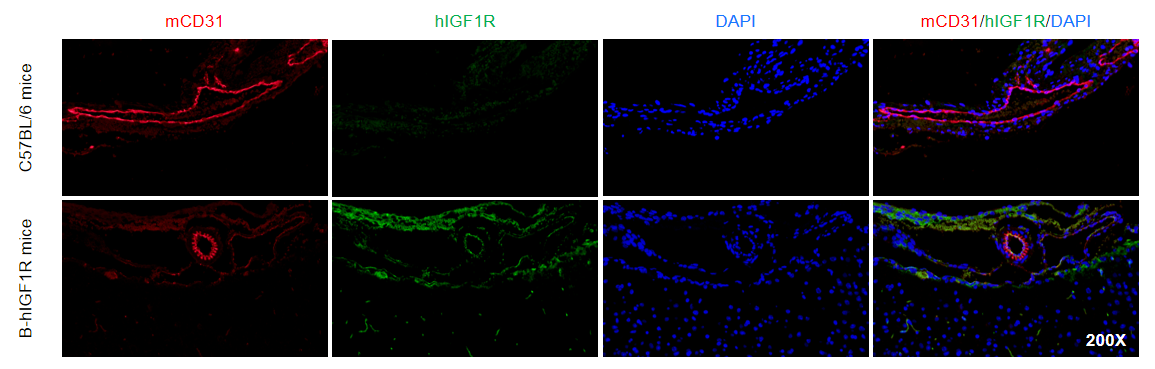
Immunofluorescence analysis of isolated brain microvessels from the wild-type mice and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice. Brain microvessels were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice, and analyzed by immunofluorescence with anti-mCD31(abcam, ab182981) and anti-hIGF1R antibody(abcam, ab263903). Human IGF1R was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIGF1R but not in wild-type mice.
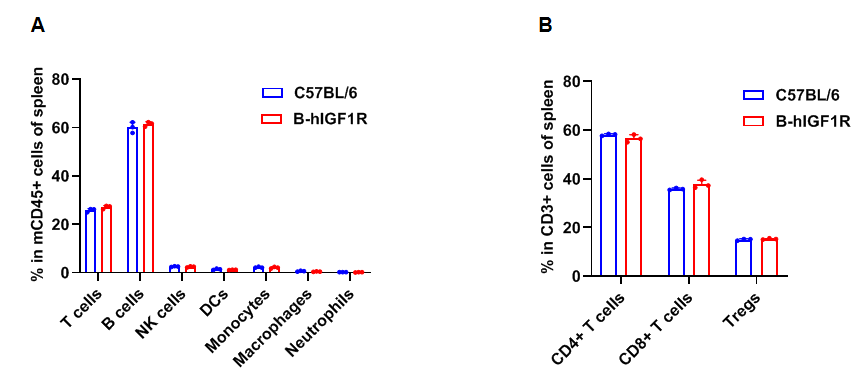
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (female, 8-week-old, n=3). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Frequencies of T cells, B cells, NK cells, DCs, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and Tregs in B-hIGF1R mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that humanization of IGF1R does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in spleen. The frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in lymph nodes and blood of B-hIGF1R mice were also comparable to wild-type C57BL/6 mice (Data not shown). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
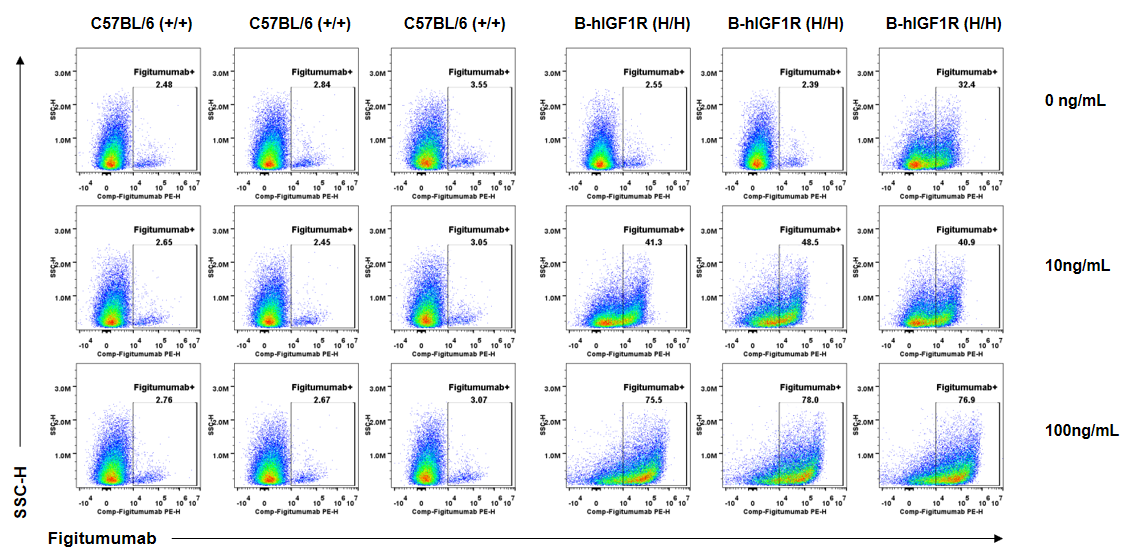
Anti-human IGF1R antibody Figitumumab binding assessment in B-hIGF1R mice. Kidney single cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (H/H) (n=3, 6-old-week, female) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Anti-hIGF1R antibody Figitumumab (MCE, HY-P99197) can bind kidney single cells from B-hIGF1R mice at the concentration of 10ng/mL and 100ng/mL, but not in wild-type mice. And the increase of positive cells in total live cells was accompanied by the increase of Figitumumab concentration.
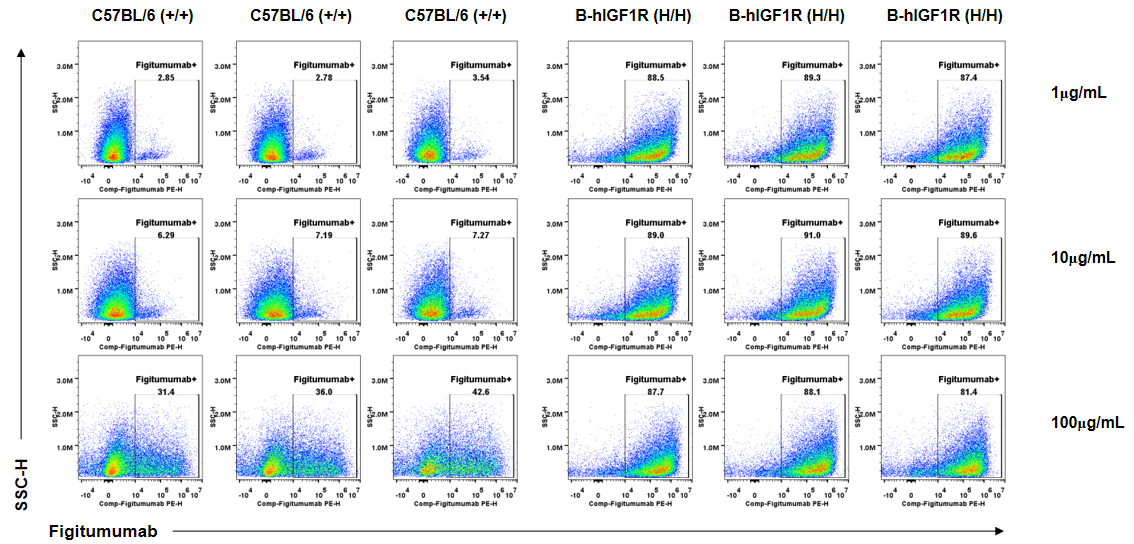
Anti-human IGF1R antibody Figitumumab binding assessment in B-hIGF1R mice. Kidney single cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (H/H) (n=3, 6-old-week, female) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Anti-hIGF1R antibody Figitumumab (MCE, HY-P99197) can bind kidney single cells from B-hIGF1R mice at the concentration of 1μg/mL, 10μg/mL and 100μg/mL. Anti-hIGF1R antibody Figitumumab could also bind wild-type mice at the concentration of 10μg/mL and 100μg/mL.
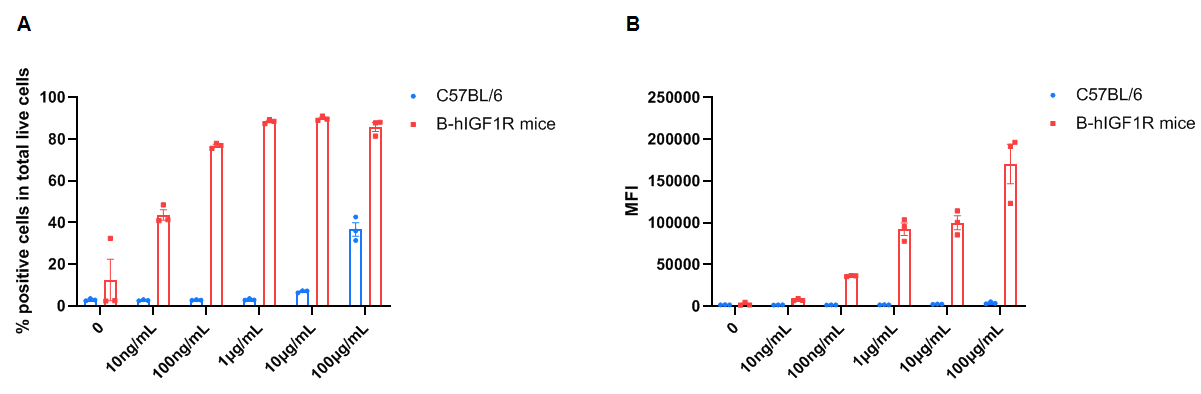
Frequency of Figitumumab positive cells in total live cells and Median Fluorescence Intensity in kidney. Kidney single cells were isolated from female wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the kidney single cells was performed to assess the frequency of Figitumumab positive cells in total live cells. B. Median Fluorescence Intensity of Figitumumab+ signal in total live cells. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
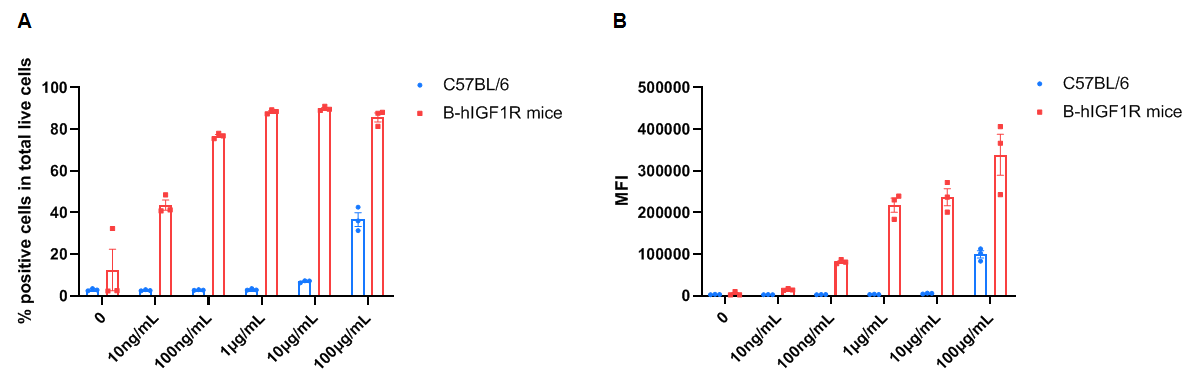
Frequency of Figitumumab positive cells in total live cells and Median Fluorescence Intensity in kidney. Kidney single cells were isolated from female wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the kidney single cells was performed to assess the frequency of Figitumumab positive cells in total live cells. B. Mean Fluorescence Intensity of Figitumumab+ signal in total live cells. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
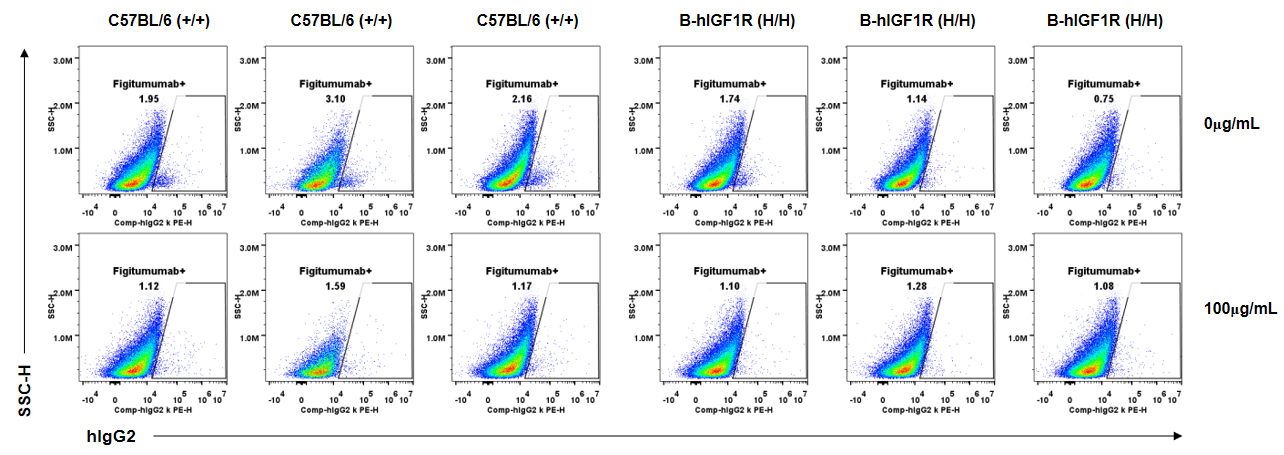
Anti-human IGF1R antibody Figitumumab binding assessment in B-hIGF1R mice. Kidney single cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (H/H) (n=3, 6-old-week, female) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Human IgG2 kappa isotype control can not bind kidney single cells from B-hIGF1R mice or wild-type mice at the concentration of 100μg/mL.
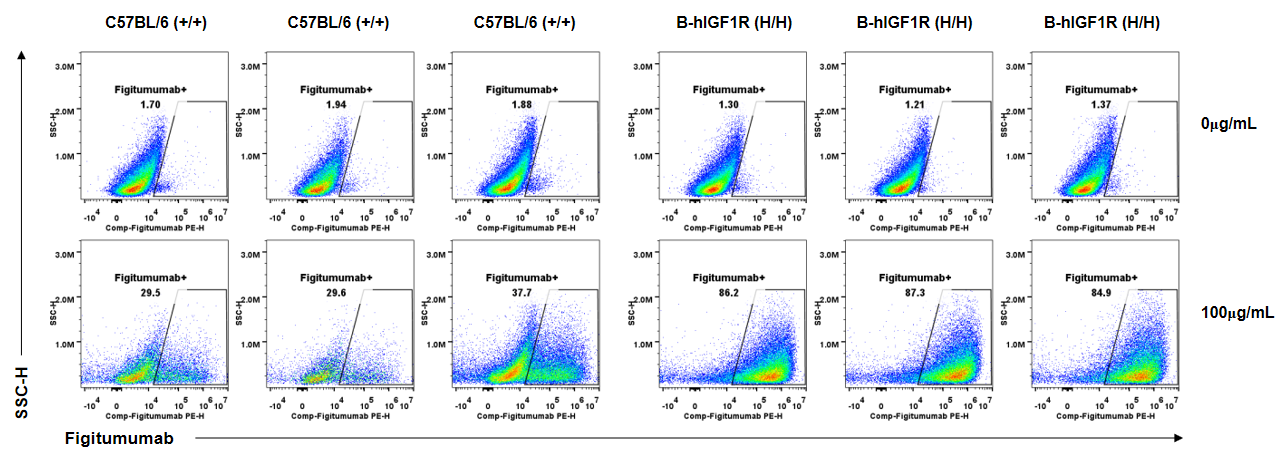
Anti-human IGF1R antibody Figitumumab binding assessment in B-hIGF1R mice. Kidney single cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (H/H) (n=3, 6-old-week, female) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Anti-hIGF1R antibody Figitumumab (MCE, HY-P99197) can bind kidney single cells from B-hIGF1R mice at the concentration of 100μg/mL. Anti-hIGF1R antibody Figitumumab could also bind wild-type mice at the concentration of 100μg/mL.
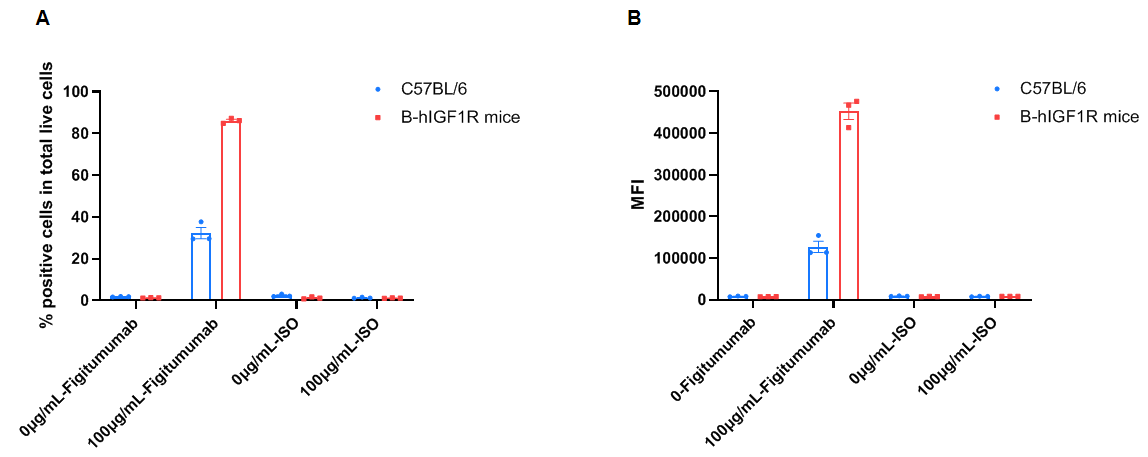
Frequency of Figitumumab positive cells in total live cells and Median Fluorescence Intensity in kidney. Kidney single cells were isolated from female wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hIGF1R mice (n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the kidney single cells was performed to assess the frequency of Figitumumab positive cells in total live cells. B. Mean Fluorescence Intensity for Figitumumab+ signal in total live cells. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
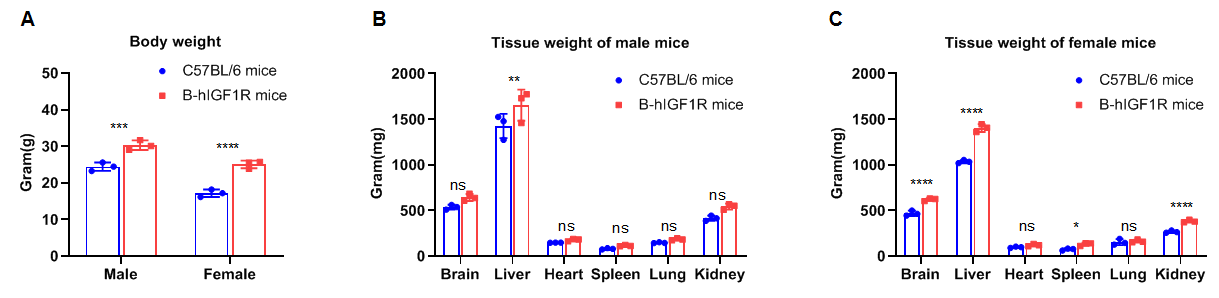
Comparison of body weights and tissues weights between WT and B-hIGF1R mice. The body weights of humanized mice were heavier than those of WT control mice regardless of gender(A). The weight of tissues such as the brain, spleen and kidney in female B-hIGF1R mice were heavier than those of WT female mice(C) while there is no difference in those three tissues’ weight between the male WT and B-hIGF1R mice(B). There is no difference in the weight of heart and lung between the male WT and B-hIGF1R mice regardless of gender. The weights of liver in B-hIGF1R mice were heavier than those of WT mice regardless of gender.