C57BL/6-Il27tm1(IL27)BcgenIl27ratm1(IL27RA)Bcgen/Bcgen • 121566
| Product name | B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 121566 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Il27tm1(IL27)BcgenIl27ratm1(IL27RA)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| Aliases | IL-27, IL-27AA, IL27p28, IL30, p28, IL27CRL1, IL-27RA, IL27R, TCCR, WSX1, zcytor1 |
Gene targeting strategy for B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice. The mouse Il27 gene was replaced by full coding region gene sequence of human IL27 in B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice. The extracellular gene sequences of mouse Il27ra gene were replaced with human IL27RA counterpart gene in B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice.
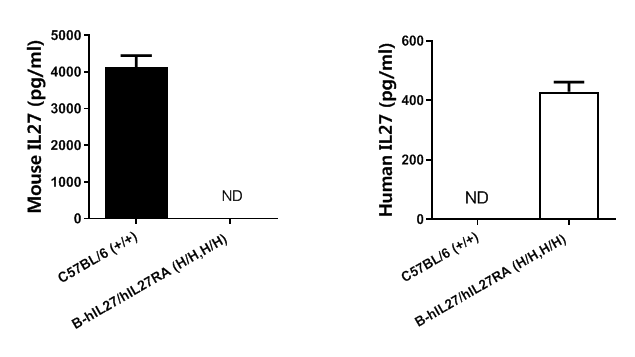
Strain specific IL27 expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice by ELISA. BMDC culture supernatant was collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (H/H,H/H) stimulated with LPS(1μg/ml), and analyzed by ELISA with species-specific IL27 ELISA kit. Mouse IL27 was exclusively detectable in wild-type mice. Human IL27 was detectable in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice but not in wild-type mice. ND: Not detected.
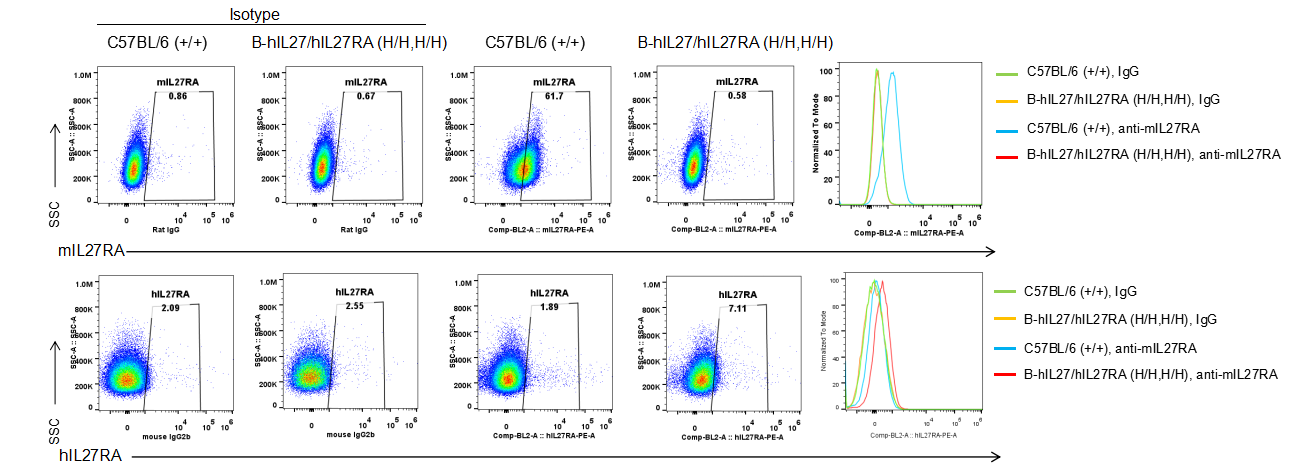
Strain specific IL27RA expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice by flow cytometry. CD4+ T cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (H/H,H/H) stimulated with anti-CD3ε and anti-CD28 in vitro for 48h, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL27RA antibody. Mouse IL27RA was exclusively detectable in the wild-type mice. Human IL27RA was detectable in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice but not in wild-type mice.
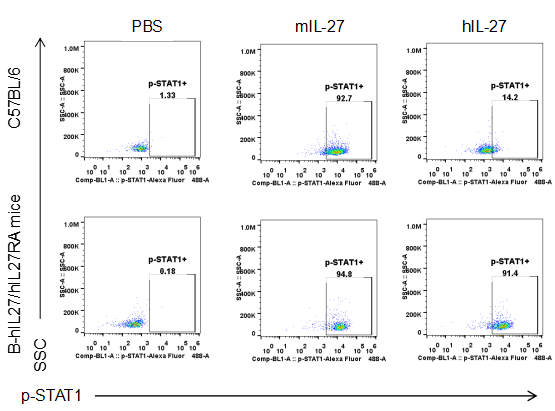
Intracellular pSTAT1 analysis in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice by flow cytometry. T cells were isolated from spleen of wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (H/H,H/H). CD4+ T cells were purified using magnetic beads then stimulated with mouse or human IL27 in vitro for 15 min, and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-p-STAT1 antibodies. Both mouse and human IL27 can induce STAT1, which means that IL27RA humanized do not affect the function of receptor.
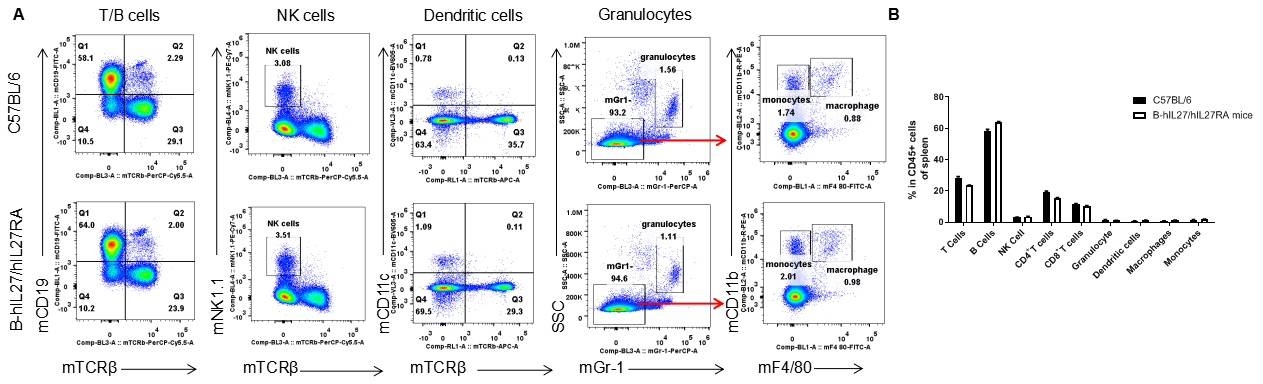
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes were performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, granulocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that IL27 and IL27RA humanized do not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
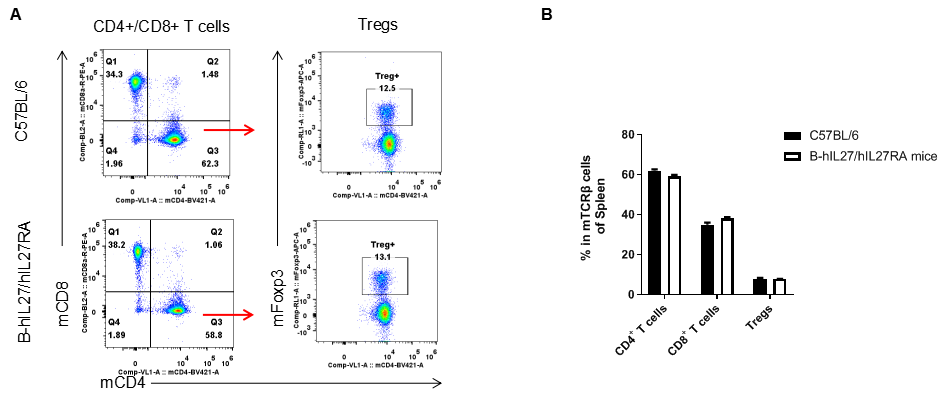
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in spleen. The lymphocytes were isolated from spleen in C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (n=3, 6-week-old). The proportion of T cells subpopulation was tested by flow cytometry. There were no differences between C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice, demonstrating that humanized of IL27 and IL27RA does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
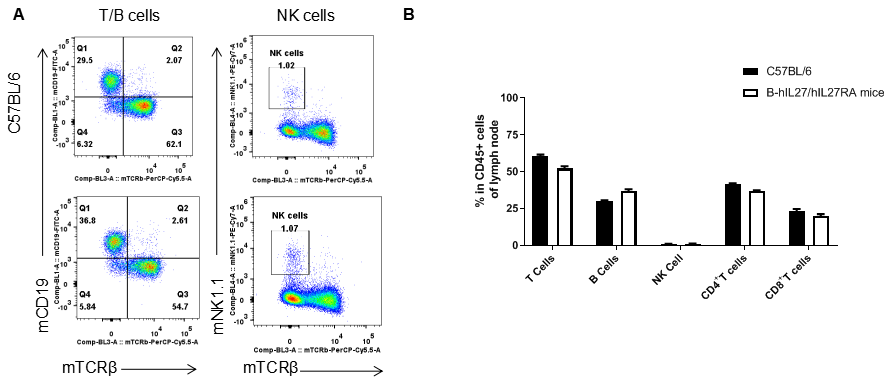
Analysis of lymph node leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Lymph node were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the lymph node were performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells and NK cells in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that IL27 and IL27RA humanized do not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in lymph node. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
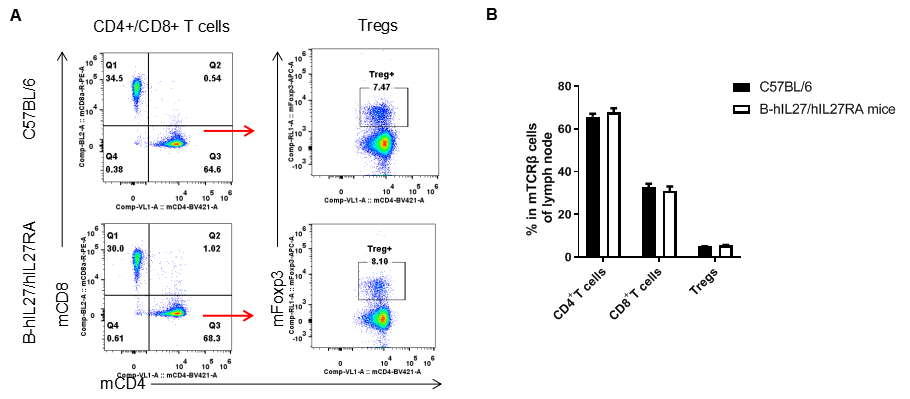
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in lymph node. The lymphocytes were isolated from lymph node in C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (n=3, 6-week-old). The proportion of T cells subpopulation was tested by flow cytometry. There were no differences between C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice, demonstrating that humanized of IL27 and IL27RA does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
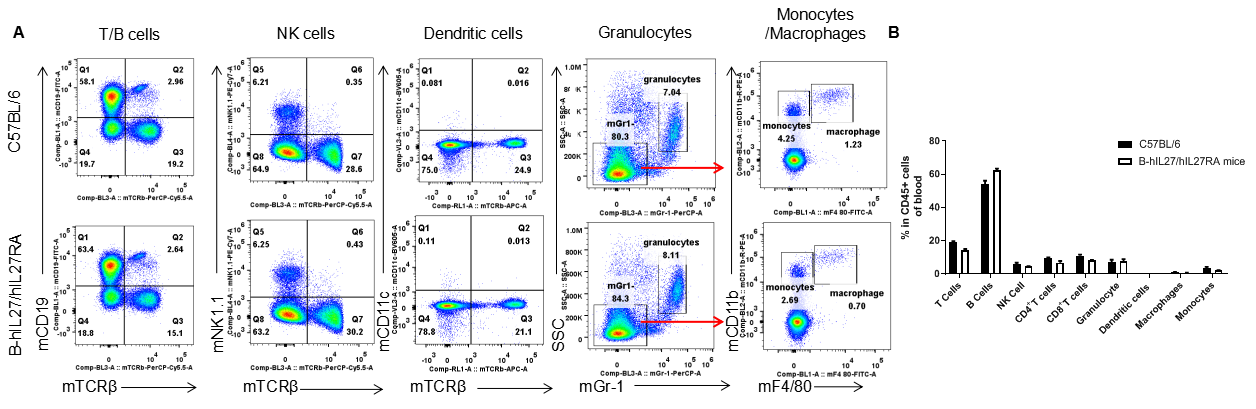
Analysis of blood leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Blood cells were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the blood cells were performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, granulocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that IL27 and IL27RA humanized do not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
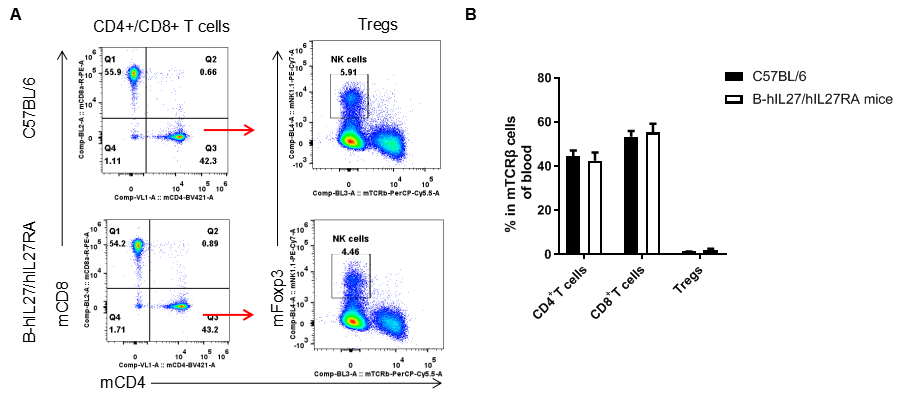
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in blood. The lymphocytes were isolated from blood in C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice (n=3, 6-week-old). The proportion of T cells subpopulation was tested by flow cytometry. There were no differences between C57BL/6 and B-hIL27/hIL27RA mice, demonstrating that humanized of IL27 and IL27RA does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.