


C57BL/6-Tektm1(TEK)Bcgen Tie1tm1(TIE1)Bcgen/Bcgen • 112513
| Product name | B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 112513 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Tektm1(TEK)Bcgen Tie1tm1(TIE1)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| NCBI gene ID | 7010, 7075 |
| Aliases | CD202B, GLC3E, TIE-2, TIE2, VMCM, VMCM1; JTK14, LMPHM11, TIE |
TEK
TEK2b, also known as Tie-2 or TEK, is a 145 kD type I transmembrane protein. It is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family of proteins and is expressed by endothelial cells and their progenitors, quiescent hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), and a subpopulation of monocytes. Angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) is an activator of TEK2b to promote, maintain, and stabilize mature vessels and to maintain HSCs in the quiescent state. Ang-2 is another ligand of TEK2b, which is involved in postnatal angiogenesis and in antagonizing the effects of Ang-1. Tie-2 also binds to Ang-4.
TIE1
Gene targeting strategy for B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice.
Exons 2~14 of the mouse Tek gene that encode the full-length protein were replaced by human TEK exons 2~14 in B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice.
Exons 2~14 of the mouse Tie1 gene that encode the full-length protein were replaced by human TIE1 exons 2~14 in B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice.
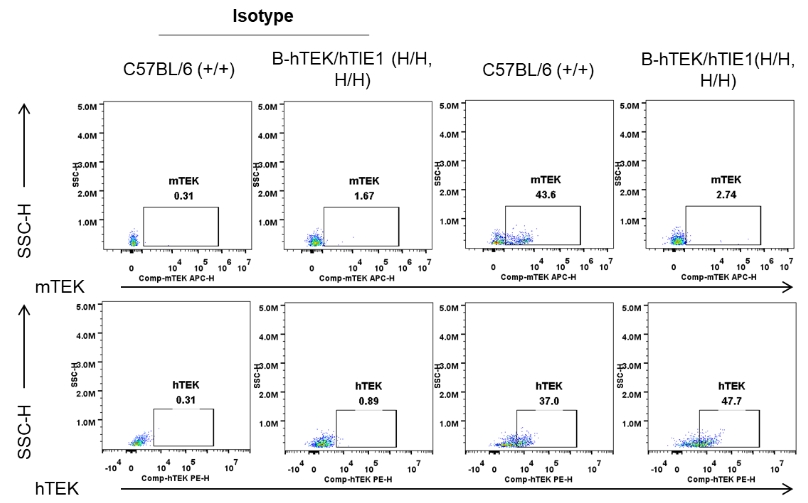
Strain specific TEK expression analysis in homozygous B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice by flow cytometry. Lung were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice (H/H, H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-TEK antibody. mTEK was detectable in wild-type, hTEK was detectable in wild-type and homozygous B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice, as the antibody is cross-recognize both human and mouse TEK.
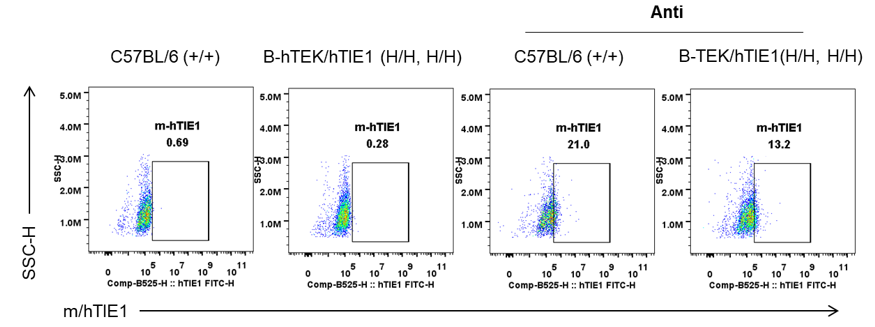
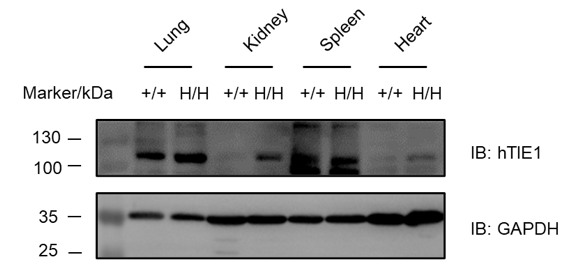
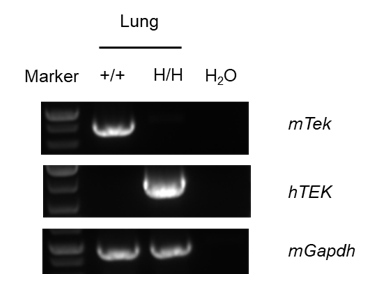
Strain specific analysis of TEK mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice by RT-PCR. Lung RNA were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice (H/H), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse or human TEK primers. Mouse Tek mRNA was detectable only in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human TEK mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice but not in wild-type mice.
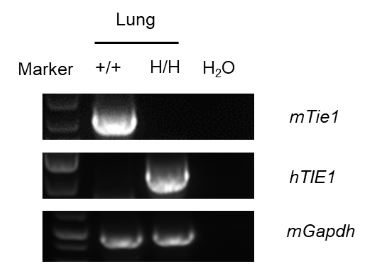
Strain specific analysis of TIE1 mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice by RT-PCR. Lung RNA were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice (H/H), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse or human TIE1 primers. Mouse Tie1 mRNA was detectable only in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human TIE1 mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hTEK/hTIE1 mice but not in wild-type mice.