mRNA expression analysis
mRNA expression analysis
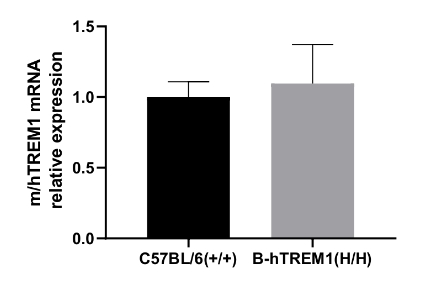
Strain specific analysis of TREM1 gene expression in wild type C57BL/6 (+/+) mice and homozygous B-hTREM1(H/H) mice by RT-qPCR. The mRNA expression of hTREM1 in B-hTREM1(H/H) was similar to mTrem1 in the C57BL/6 (+/+), demonstrating that introduction of hTREM1 in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the expression level of TREM1 mRNA.
 Protein expression analysis
Protein expression analysis
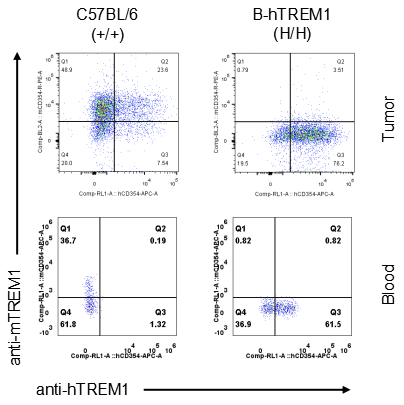
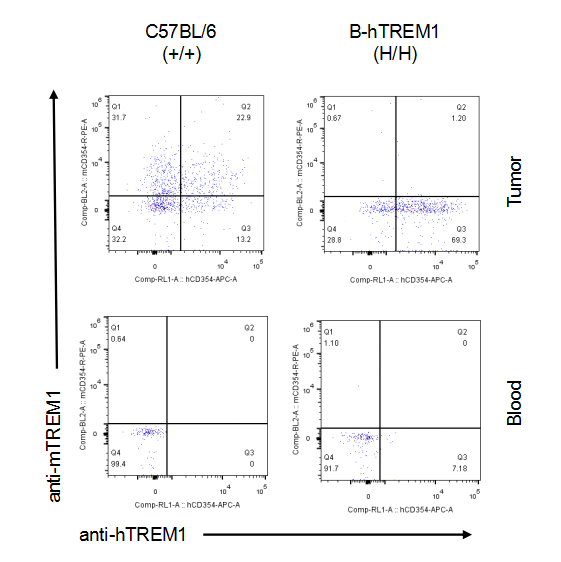
Strain specific TREM1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice by flow cytometry.MC38 cells were inoculated into wild-type C57BL/6(+/+) and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice(H/H). Blood and tumor were harvested when tumor volume reached approximately 500 mm3, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TREM1 antibody. Mouse TREM1 was exclusively detectable in blood and tumor macrophage of wild-type mice. Human TREM1 was exclusively detectable in blood and tumor macrophage of homozygous B-hTREM1 mice.* It is not clear what population of cells was stained with specific anti-hTREM1 in tumors of C57BL/6 (Q2).
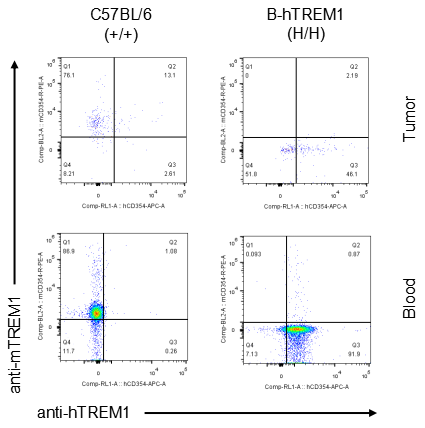
Strain specific TREM1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice by flow cytometry.MC38 cells were inoculated into wild-type C57BL/6(+/+) and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice(H/H). Blood and tumor were harvested when tumor volume reached approximately 500 mm3, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TREM1 antibody. Mouse and human TREM1 were not detectable in blood monocyte of wild-type mice and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice. Human TREM1 was exclusively detectable in tumor M-MDSC of homozygous B-hTREM1 mice.* It is not clear what population of cells was stained with specific anti-hTREM1 in tumors of C57BL/6 (Q2).
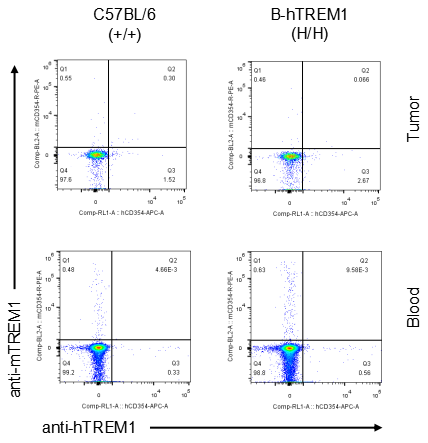
Strain specific TREM1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice by flow cytometry.MC38 cells were inoculated into wild-type C57BL/6(+/+) and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice(H/H). Blood and tumor were harvested when tumor volume reached approximately 500 mm3, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TREM1 antibody. Mouse TREM1 was exclusively detectable in blood and tumor neutrophil(G-MDSC) of wild-type mice. Human TREM1 was exclusively detectable in blood and tumor neutrophil(G-MDSC) of homozygous B-hTREM1 mice.
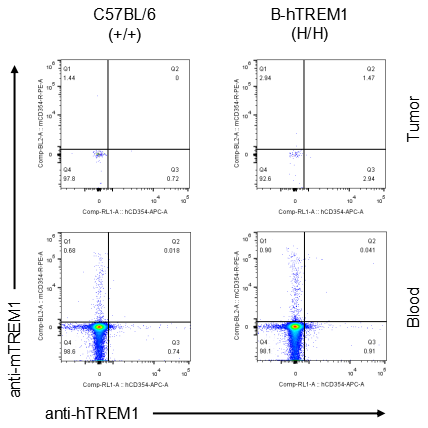
Strain specific TREM1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice by flow cytometry.MC38 cells were inoculated into wild-type C57BL/6(+/+) and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice(H/H). Blood and tumor were harvested when tumor volume reached approximately 500 mm3, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TREM1 antibody. Mouse and human TREM1 were not detectable in blood and tumor T cells of wild-type mice and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice.
Strain specific TREM1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice by flow cytometry.MC38 cells were inoculated into wild-type C57BL/6(+/+) and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice(H/H). Blood and tumor were harvested when tumor volume reached approximately 500 mm3, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TREM1 antibody. Mouse and human TREM1 were not detectable in blood and tumor B cells of wild-type mice and homozygous B-hTREM1 mice.
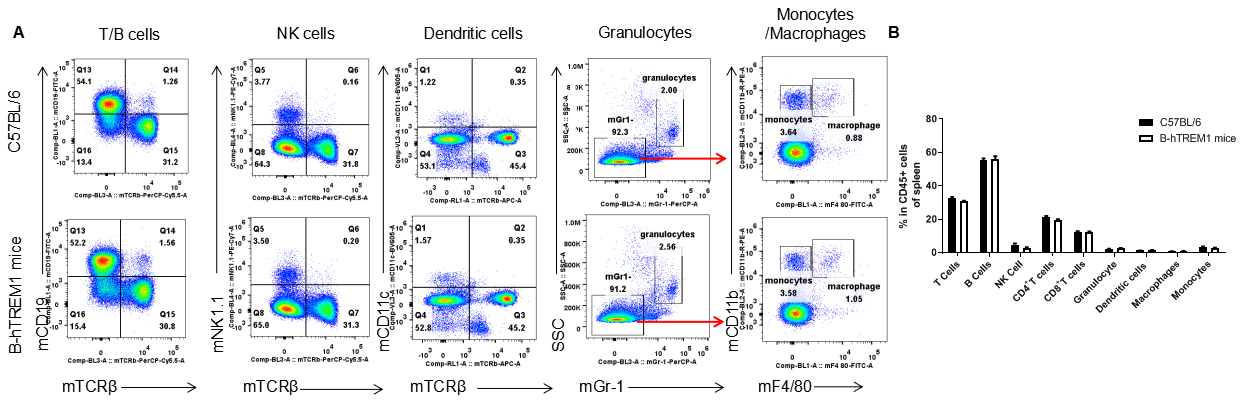
 Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in spleen
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in spleen
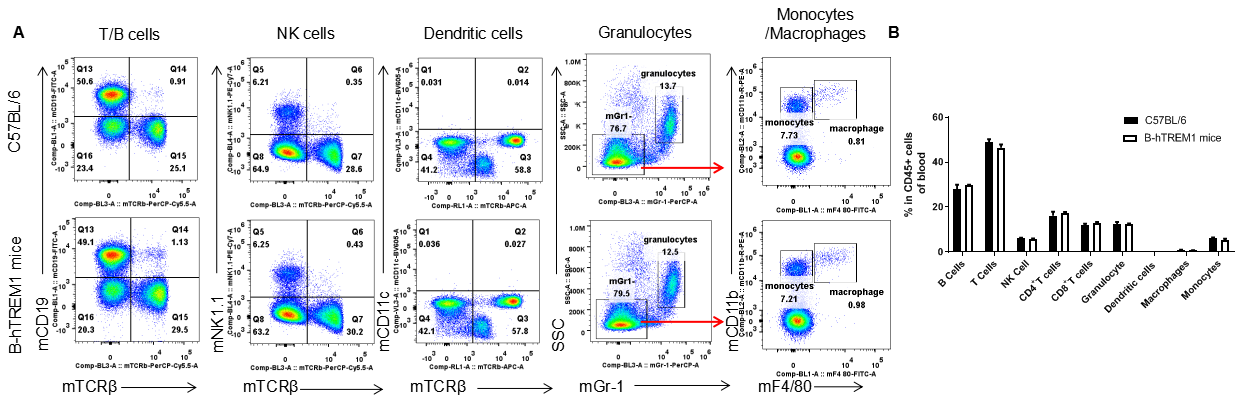
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cell, B cell, NK cell, monocyte, dendritic cell, granulocyte and macrophage in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that TREM1 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
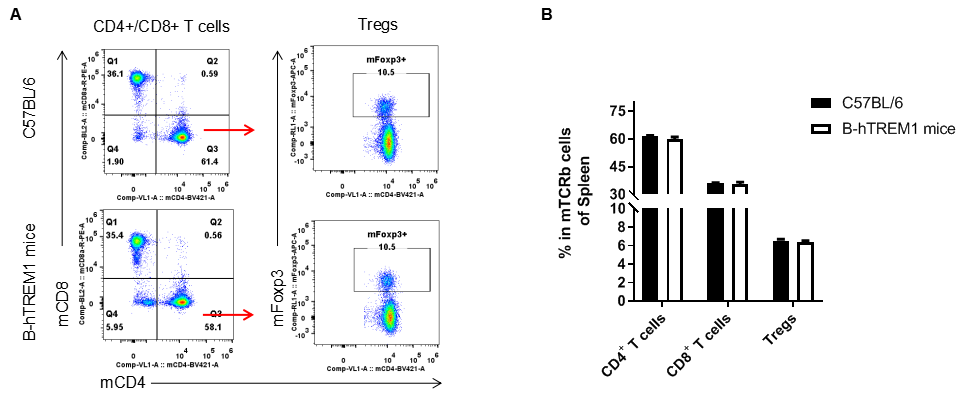
 Analysis of T cell subpopulation in spleen
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in spleen
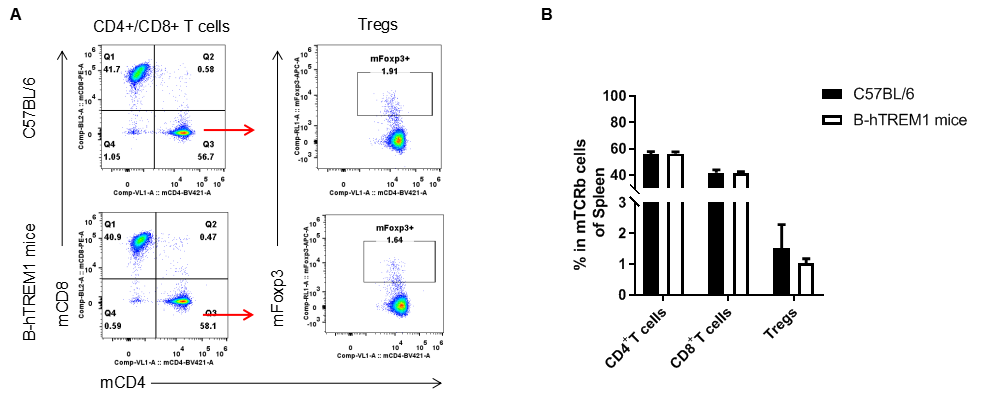
Analysis of spleen T cell subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for TCRβ+T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. There were no differences between C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice, demonstrating that humanized of TREM1 does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
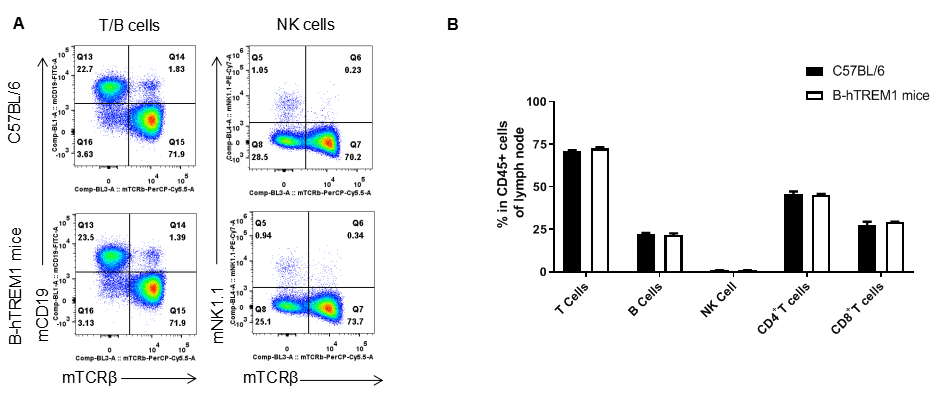
 Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in LNs
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in LNs
Analysis of LNs leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. LNs were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the LNs was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cell, B cell, NK cell in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that TREM1 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
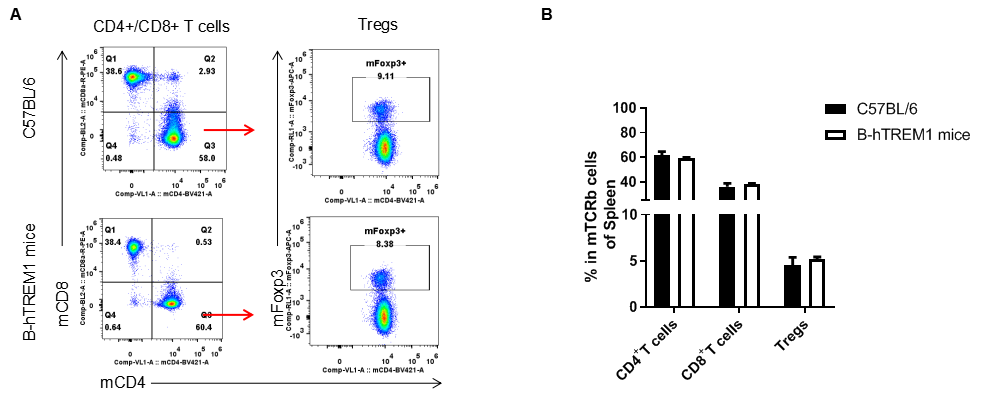
 Analysis of T cell subpopulation in LNs
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in LNs
Analysis of LNs T cell subpopulations by FACS. LNs were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the LNs was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for TCRβ+T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. . There were no differences between C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice, demonstrating that humanized of TREM1 does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
 Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in blood
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in blood
Analysis of blood leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Blood were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the blood was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cell, B cell, NK cell, monocyte, dendritic cell, granulocyte and macrophage in homozygous B-hTREM1 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that TREM1 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
 Analysis of T cell subpopulation in blood
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in blood
Analysis of blood T cell subpopulations by FACS. Blood were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the blood was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for TCRβ+T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. There were no differences between C57BL/6 and B-hTREM1 mice, demonstrating that humanized of TREM1 does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
 Analysis of hTREM1 function in B-hTREM1 mice
Analysis of hTREM1 function in B-hTREM1 mice
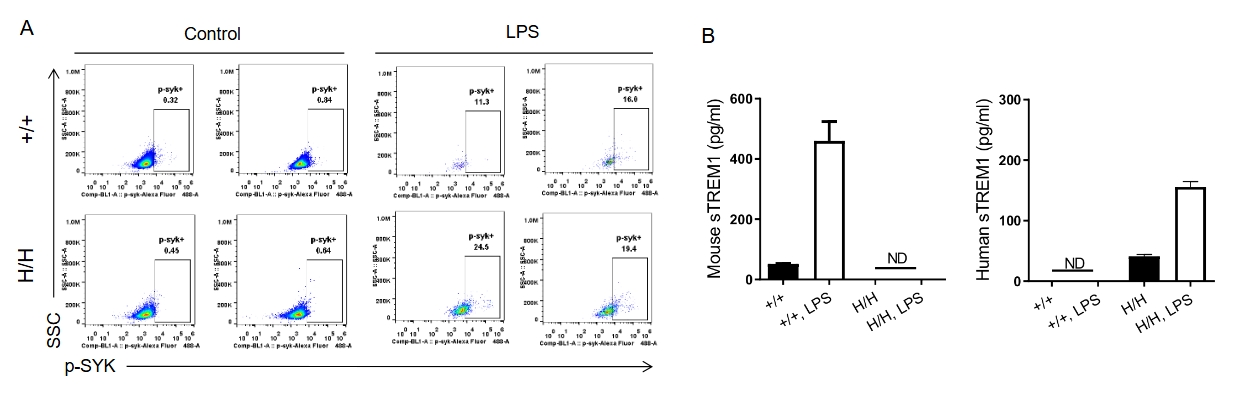
Analysis of the hTREM1 function in B-hTREM1 mice. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice(+/+) and B-hTREM1 mice(H/H) were randomly grouped and injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with LPS from E.coli(500 ug/mouse). Serum and peritoneal macrophages were collected after LPS administration. Under LPS-stimulated conditions, human TREM1 could be activated effectively and then induced rapid phosphorylation of Syk in B-hTREM1 mice(A). Additionally, soluble TREM1 were upregulated in the serum of B-hTREM1 mice (B), indicating that mouse matrix metalloproteinase(MMP) was capable of proteolytically cleaving human TREM1, and inducing the release of soluble TREM1. ND, not detected.
 Tumor growth curve & Body weight changes
Tumor growth curve & Body weight changes
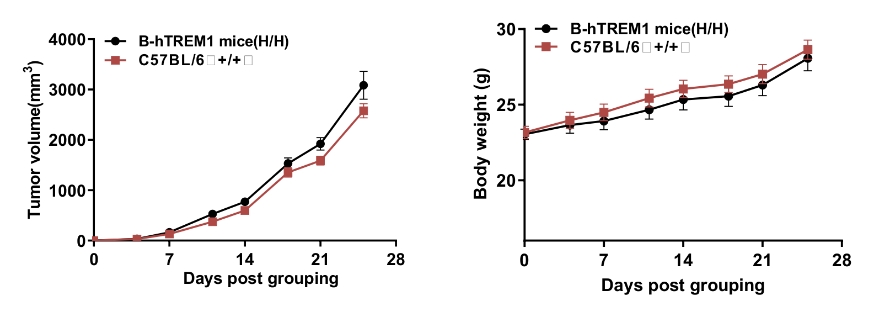
Subcutaneous homograft tumor growth of MC38 cells in B-hTREM1 mice. Wild-type MC38 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hTREM1 mice (male, 8-week-old, n=6). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume ± SEM. (B) Body weight (Mean ± SEM). Tumor volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V = 0.5 X long diameter X (short diameter)2. As shown in panel A, MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in B-hTREM1 mice and can be used for efficacy studies.
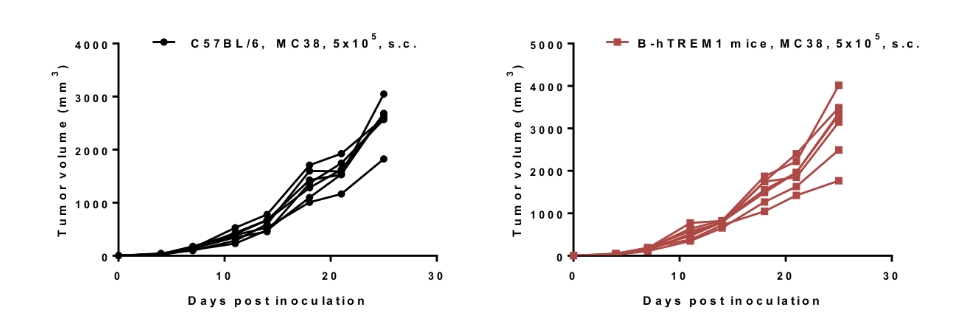
 Tumor growth curve of individual mice
Tumor growth curve of individual mice
MC38 tumor cells growth of individual mice. Wild-type MC38 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hTREM1 mice (male, 8-week-old, n=6). As shown in the panel, B-hTREM1 mice were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies.
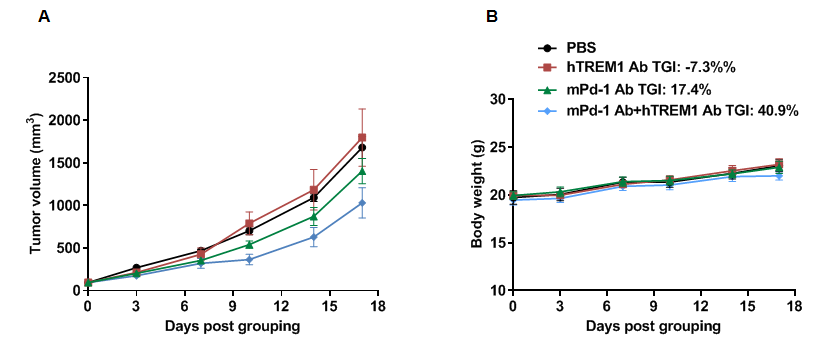
 Combination therapy of anti-mouse PD-1 antibody and anti-human TREM1 antibody
Combination therapy of anti-mouse PD-1 antibody and anti-human TREM1 antibody
Antitumor activity of anti-mouse PD-1 antibody combined with anti-human TREM1 antibody in B-hTREM1 mice. (A) Anti-mouse PD-1 antibody combined with anti-human TREM1 antibody inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hTREM1 mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hTREM1 mice (female, 9-week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 80-100 mm3, at which time they were treated with mPD-1 and hTREM1 antibodies. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, combination of anti-hTREM1 and anti-mPD-1 antibody shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups, demonstrating that the B-hTREM1 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human TREM1 antibody. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.