


C57BL/6-Plautm1(PLAU)Bcgen Plaurtm1(PLAUR)Bcgen/Bcgen • 112324
| Product name | B-hUPA/hUPAR mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 112324 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Plautm1(PLAU)Bcgen Plaurtm1(PLAUR)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| Aliases | ATF; QPD; UPA; URK; u-PA; BDPLT5 CD87; UPAR; URKR; U-PAR;PLAUR |
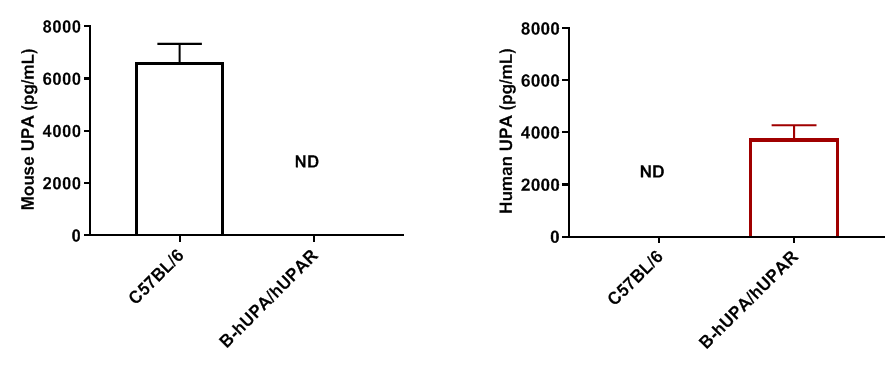
The full coding region of mouse Upa gene was replaced by human UPA coding region sequences in B-hUPA/hUPAR mice. The coding region except signal peptide of mouse Upar gene was replaced by human UPAR counterpart gene sequences in B-hUPA/hUPAR mice.
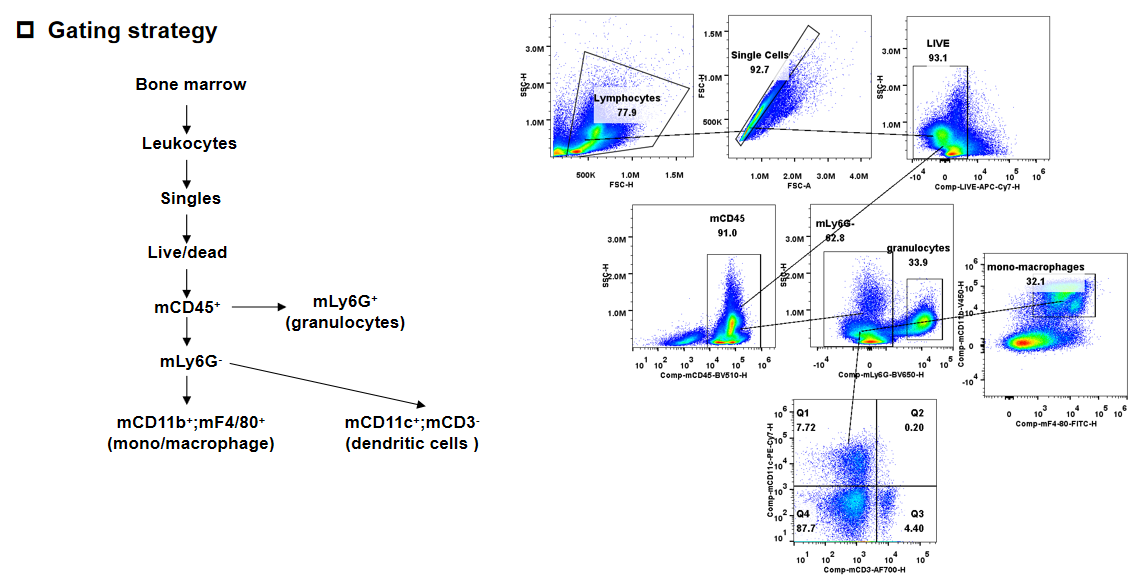
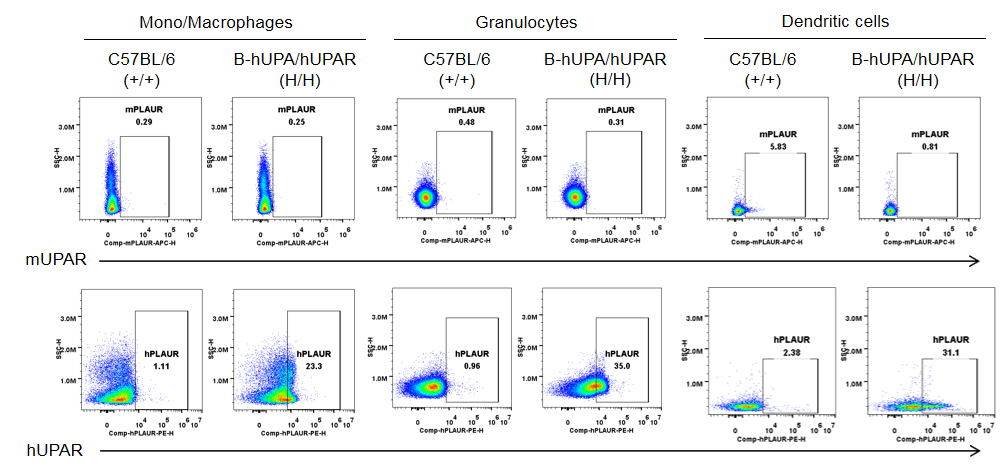
Strain specific UPAR (also named PLAUR) expression analysis in homozygous B-hUPA/hUPAR mice by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hUPA/hUPAR mice (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-UPAR antibody. Mouse UPAR was only detectable in in dendritic cells of wild-type mice. Human UPAR were exclusively detectable in mono/macrophages, granulocytes, and dendritic cells of homozygous B-hUPA/hUPAR mice but not in wild-type mice.
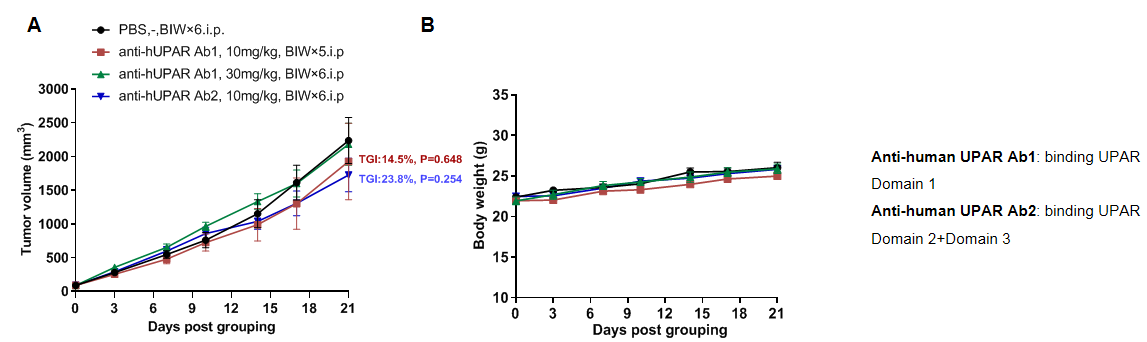
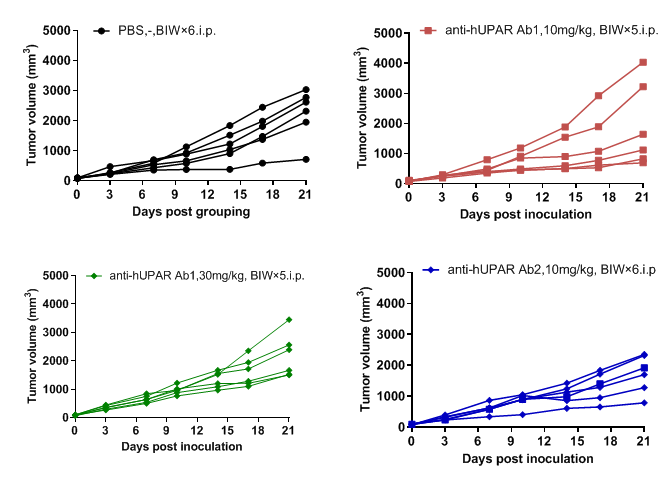
Antitumor activity of anti-UPAR antibodies in B-hUPA/hUPAR mice bearing B-hUPAR MC38 cells. Tumor growth curve in individual B-hUPA/hUPAR mice that treated with anti-UPAR antibodies (in house) indicated in the panel.
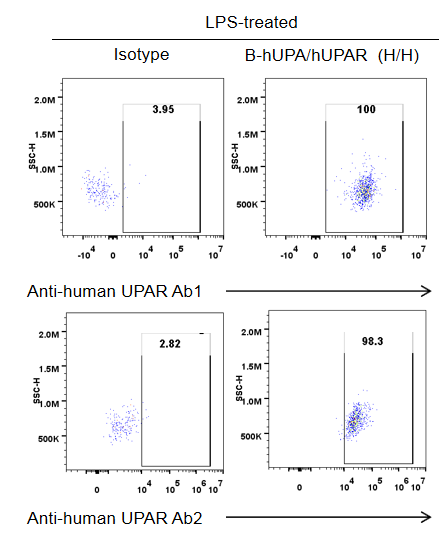
Analysis the binding of anti-human UPAR antibodies with B-hUPA/hUPAR mice by flow cytometry. Macrophages in ascites of B-hUPA/hUPAR mice were performed to assess anti-human UPAR antibodies (in house) binding. Both antibodies bind well with human UPAR in homozygous mice.
Anti-human UPAR Ab1: binding UPAR Domain 1
Anti-human UPAR Ab2: binding UPAR Domain 2+Domain 3