


C57BL/6-Tfrctm1(TFRC)Bcgen/Bcgen • 110861
| Product name | B-hTFR1 mice |
|---|---|
| Catalog number | 110861 |
| Strain name | C57BL/6-Tfrctm1(TFRC)Bcgen/Bcgen |
| Strain background | C57BL/6 |
| NCBI gene ID | 22042 |
| Aliases | CD71, IMD46, T9, TFR, TFR1, TR, TRFR, p90 |
on this page
Background:
Targeting strategy:
Validation:
Application:
Targeting strategy of B-hTFR1 mice. The exons 4-19 of mouse Tfr1 gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human TFR1 exons 4-19 in B-hTFR1 mice.
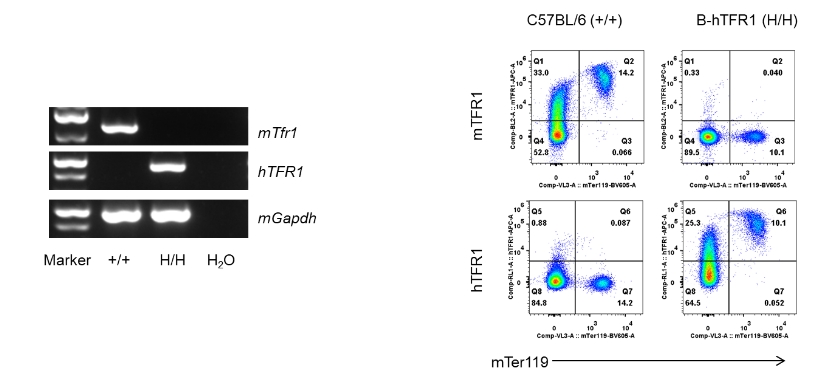
Human TFR1 mRNA and protein were only detected in homozygous B-hTFR1 mice (H/H), but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+).
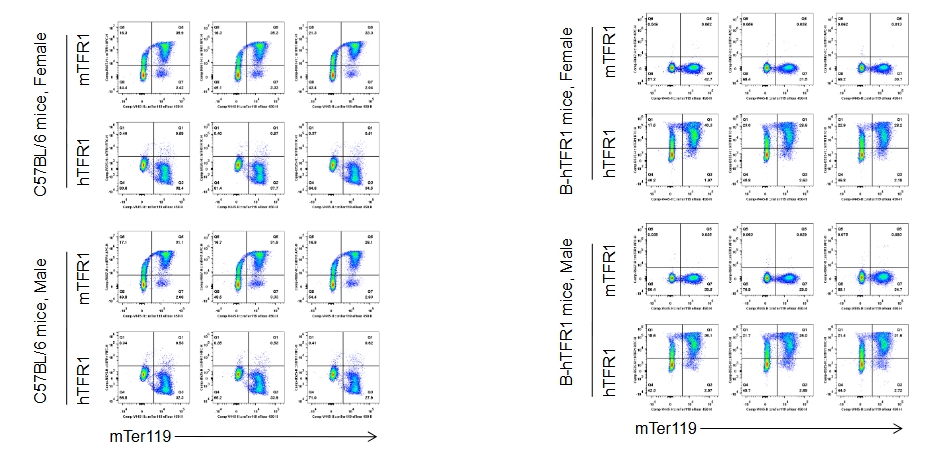
Human TFR1 was exclusively detectable in blood of homozygous B-hTFR1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice, and its expression level is independent of gender.
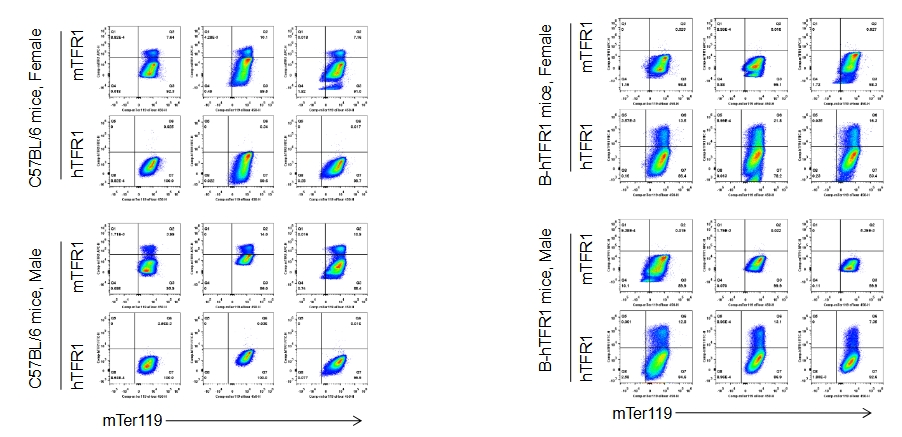
Human TFR1 was exclusively detectable in blood of homozygous B-hTFR1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice, and its expression level is independent of gender.
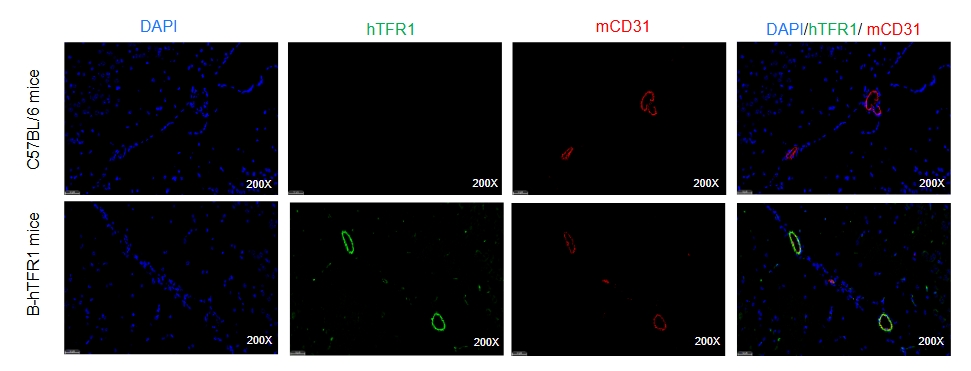
Human TFR1 was detectable on brain microvascular endothelium of homozygous B-hTFR1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
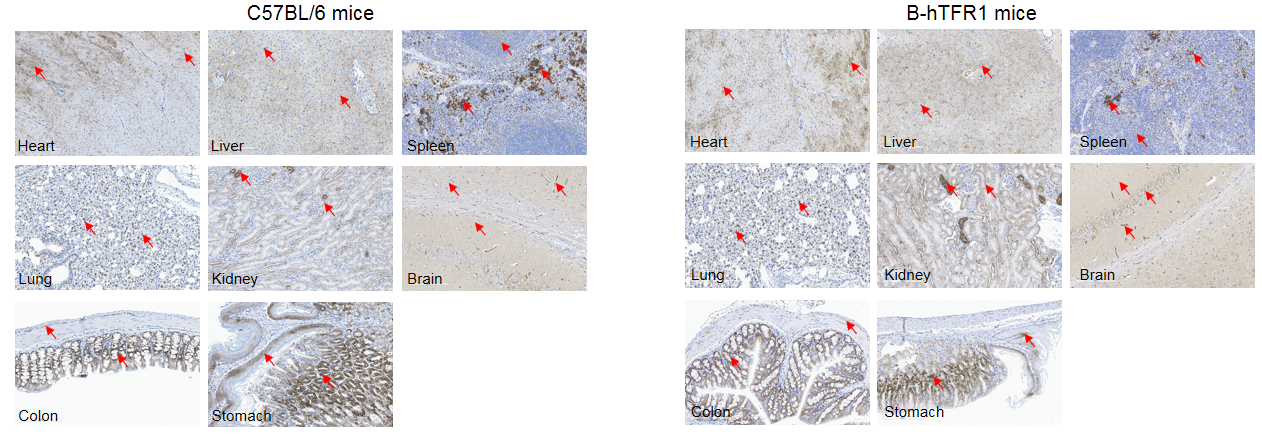
Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of TFR1 protein expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous humanized B-hTFR1 mice. Mouse tissues were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hTFR1 mice (female, 8-week-old, n=3). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-TFR1 antibody by IHC. Human TFR1 was detected in the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, brain, colon and stomach of B-hTFR1 mice, which is similar to the expression pattern of mouse TFR1 in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Red arrow: positive cells expressing TFR1.
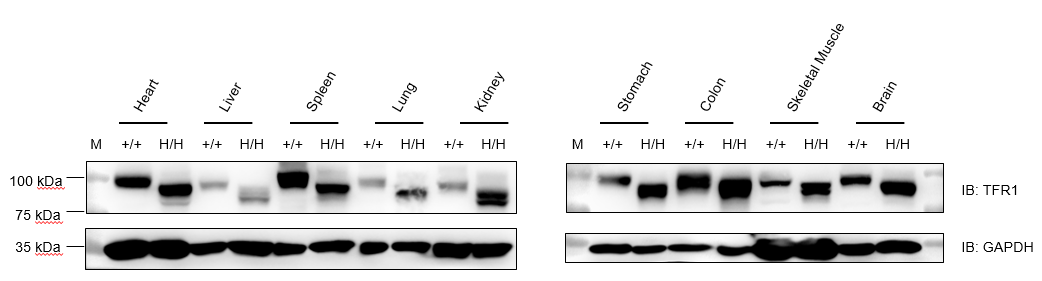
Western blot analysis of TFR1 protein expression in wild-type C57BL/6JNidc mice and homozygous B-hTFR1 mice by WB. Various tissues were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTFR1 mice (H/H), and then analyzed by western blot with anti-TFR1 antibody (abcam, ab214039). 40 μg total proteins were loaded for western blotting analysis. GAPDH were detected as internal control. TFR1 was detectable in heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, stomach, colon, muscle and brain from both C57BL/6JNifdc and homozygous B-hTFR1 mice, as the antibody was cross-reactive between human and mouse. M, marker.
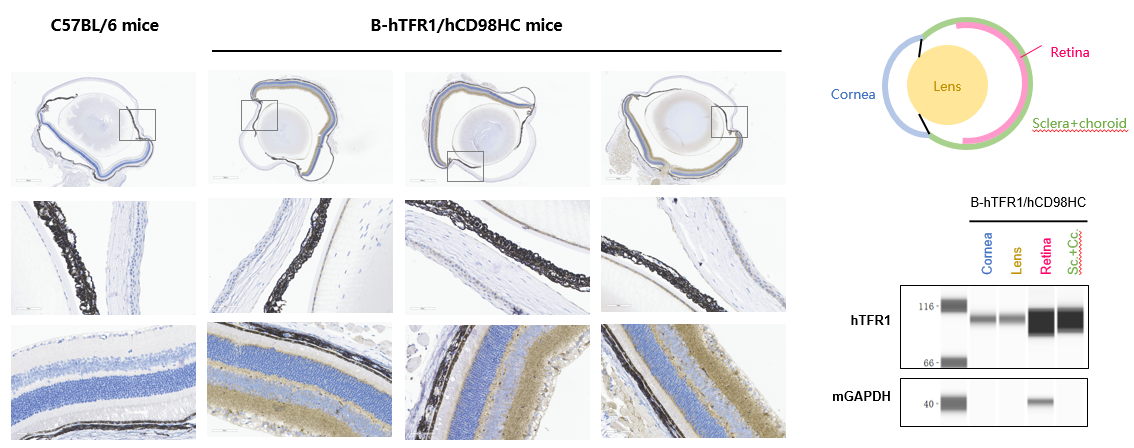
TFR1 expression analysis in eyeball. The expression of human TFR1 was observed in corneal epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and lens epithelial cells, while it was highly expressed in the retina in B-hTFR1/hCD98HC mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
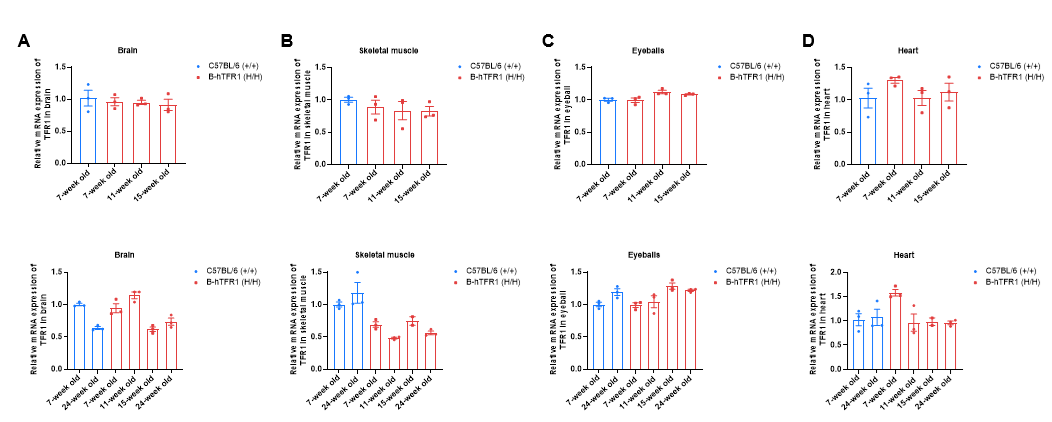
TFR1 mRNA expression analysis in homozygous B-hTFR1 mice. Brain (A), skeletal muscle (B), eyeball (C) and heart (D) RNA were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) (female, 7-week-old, n=3; male, 7-week-old and 24-week-old, n=3) and homozygous B-hTFR1 mice (H/H) (female, 7-week-old, 11-week-old, 15-week-old, n=3; male, 7-week-old, 11-week-old, 15-week-old, 24-week-old, n=3) ), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with TFR1 primers. TFR1 expression level in female homozygous B-hTFR1 mice is similar to those in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and remains consistent across different ages of mice (up). TFR1 expression level in male homozygous B-hTFR1 mice is similar to those in brain, heart and eyeball in wild-type C57BL/6 mice (down). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
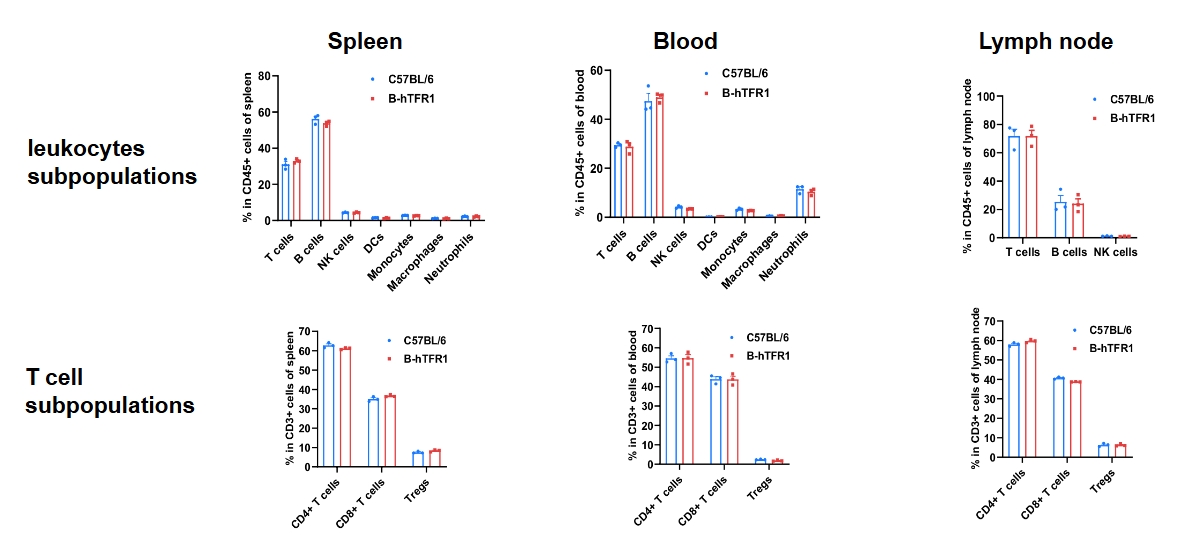
Humanization of TFR1 does not change the overall frequency or distribution of immune cell types in spleen, blood and lymph nodes. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
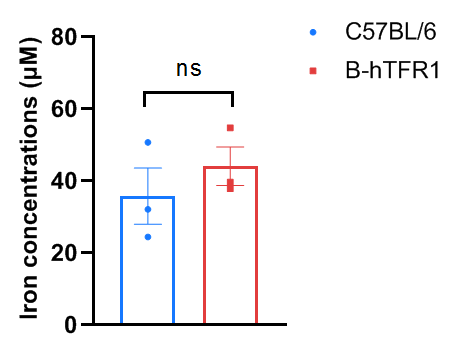
Serum iron levels in wild-type C57BL/6 and homozygous humanized B-hTFR1 mice. Serum were collected from C57BL/6 and B-hTFR1 mice (n=3, 6 week old, female), and then analyzed by Iron Assay Kit (abcam, ab83366). Serum iron levels in homozygous B-hTFR1 mice were similar to those in the wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001.
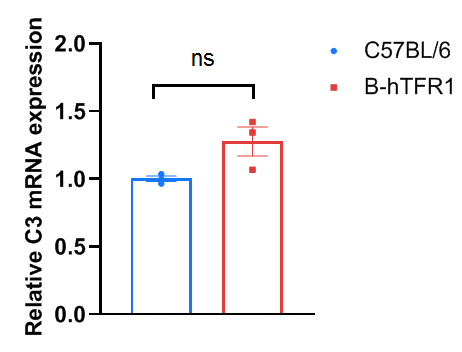
Liver complement component 3 levels in wild-type C57BL/6 and homozygous humanized B-hTFR1 mice. Liver were collected from C57BL/6 and B-hTFR1 mice (n=3, 6 week old, female), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by qPCR with mouse complement component 3 primers. The mRNA expression of mouse complement component 3 in homozygous B-hTFR1 mice was similar to those in the wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
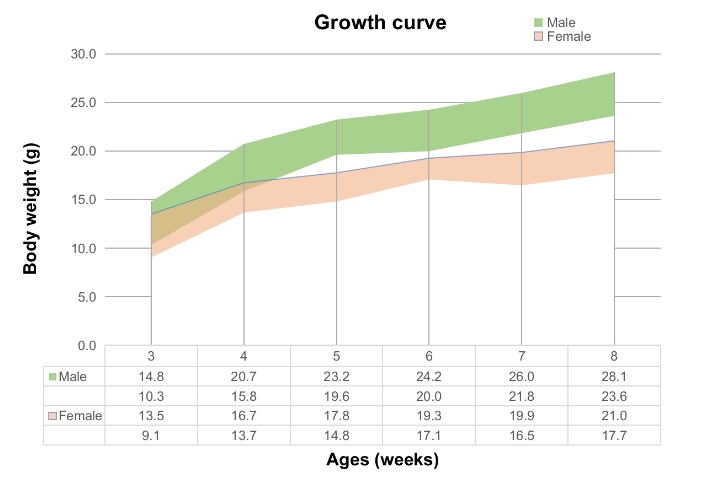
Growth curve of B-hTFR1 mice. Select mice aged 3 to 8 weeks, and randomly sample and weigh 50 males and 50 females from each age group. The minimum and maximum weights of the mice in the table are calculated as the average ± SD. The growth curve follows a normal distribution, with a 68% probability that random errors fall within the ± SD range.
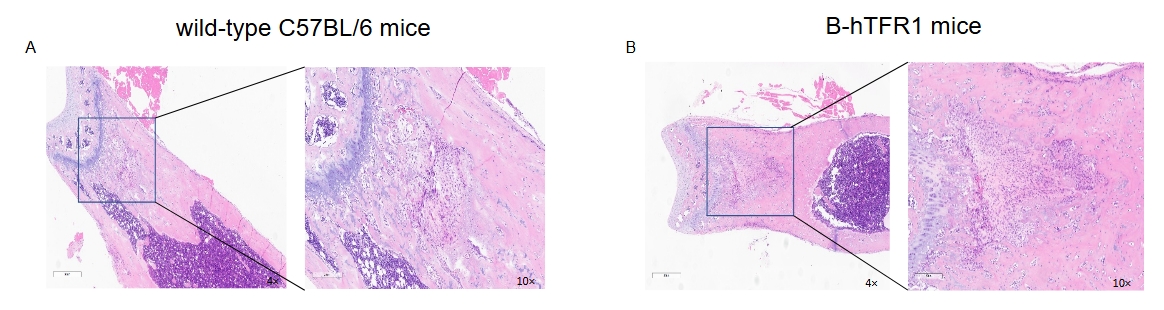
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of femur. The Femur from wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hTFR1 mice (female, 10 week-old, n=10) were collected and analyzed by H&E staining. Representative results of WT mice (A) and homozygous B-hTFR1 mice (B) are shown, and no abnormalities were found in the bone marrow of both mice. The results indicated that Humanization of TFR1 does not change the normal morphology of mouse bone marrow.
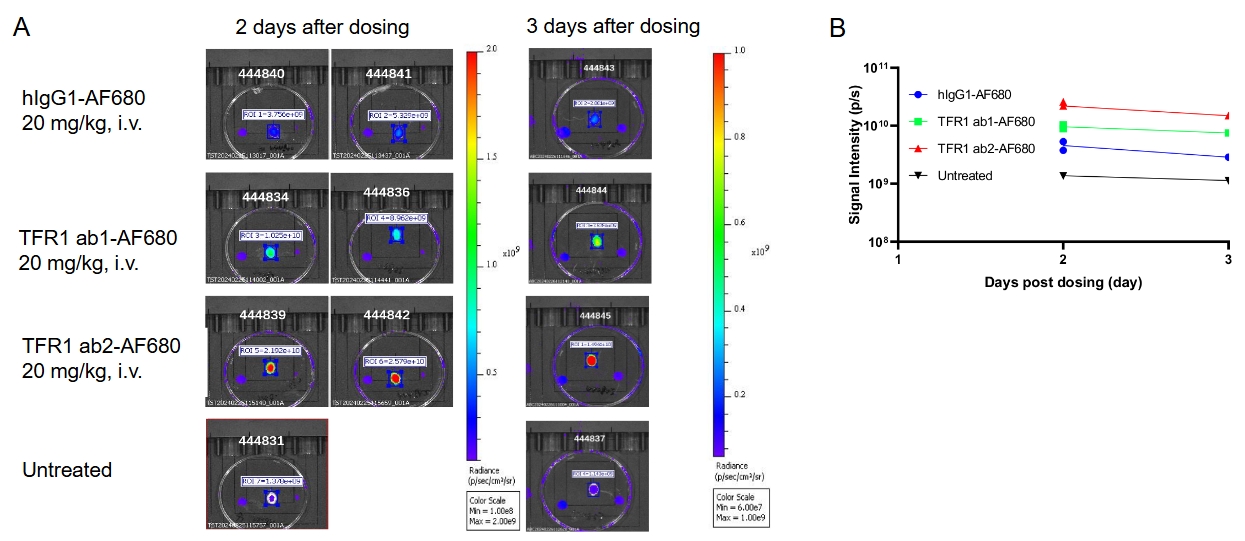
B-hTFR1 mice were intravenously injected with AF680-conjugated control hIgG1 or anti human TFR1 antibodies ab1 and ab2 (provided by a client). After 2 days or 3 days post-injection, the mice were perfused and their brains were collected for analysis. (A) Mouse brain images under imaging system. (B) Fluorescence intensity of mouse brain under imaging system. The results indicate that the uptake of anti-human TFR1 antibody ab2 in the brain of B-hTFR1 mice was higher than that of anti-human TFR1 antibody ab1.
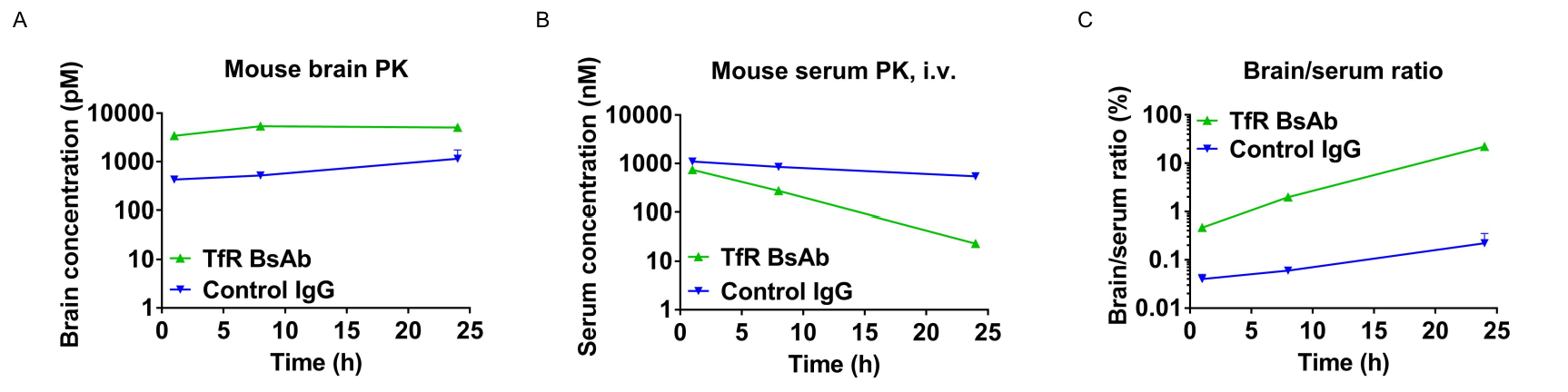
In vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) evaluation of anti-human TFR1 bispecific antibodies (BsAbs). B-hTFR1 mice were injected with control IgG (10 mpk) and anti-human TFR1 BsAbs (10.9 mpk) provided by a client via tail vein. Brain and serum were taken for in vivo PK evaluation. Brain concentrations(A), serum concentrations (B), and brain-to-serum ratio (C) of anti-human TFR1 BsAbs were quantified. As shown in panel, anti-human TFR1 BsAbs exhibited higher serum clearance and enhanced brain exposure after dose. The results confirmed that brain of B-hTFR1 mice enables uptake of an intravenously administered anti-human TFR1 BsAbs and B-hTFR1 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of effective delivery of protein therapeutics to the central nervous system (CNS). Graphs represent mean ± SEM.
Note: This experiment was performed by the client using B-hTFR1 mice. All the other materials were provided by the client.
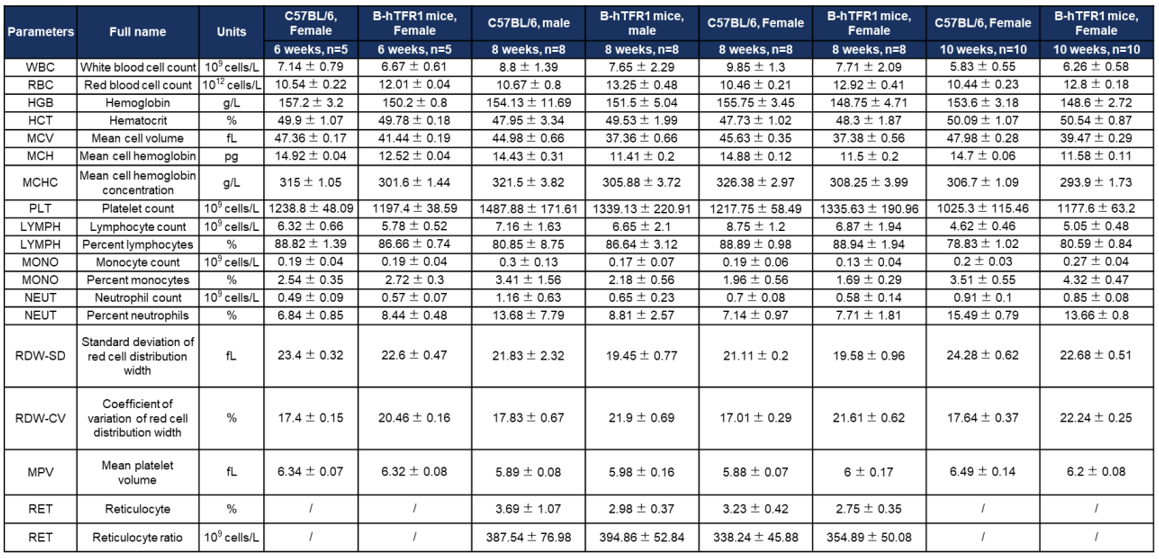
Humanization of TFR1 does not alter hematological parameters. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
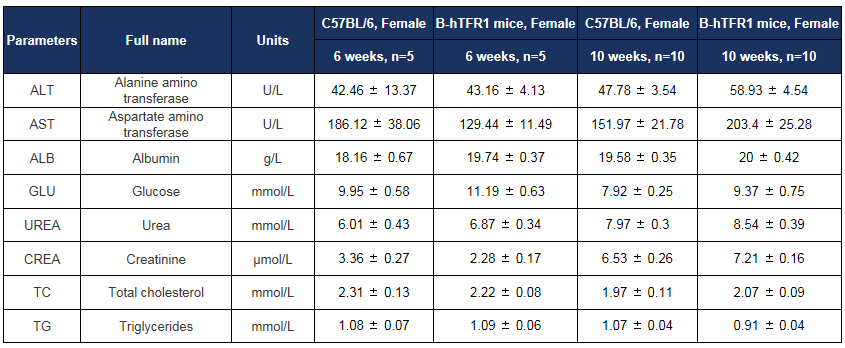
Biochemical test of B-hTFR1 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.